Chonnam Med J.
2017 May;53(2):127-132. 10.4068/cmj.2017.53.2.127.
The Effect of Perineural Administration of Dexmedetomidine on Narcotic Consumption and Pain Intensity in Patients Undergoing Femoral Shaft Fracture Surgery; A Randomized Single-Blind Clinical Trial
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology, Imam Hossein Hospital, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
- 2Department of Anesthesiology, Modaress Hospital, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
- 3Department of Pathology, School of Veterinary Medicine, Shahrekord University, Shahrekord, Iran. s-shirian@razi.tums.ac.ir
- 4Shiraz Molecular Pathology Research Center, Dr Daneshbod Lab, Shiraz, Iran.
- KMID: 2379285
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4068/cmj.2017.53.2.127
Abstract
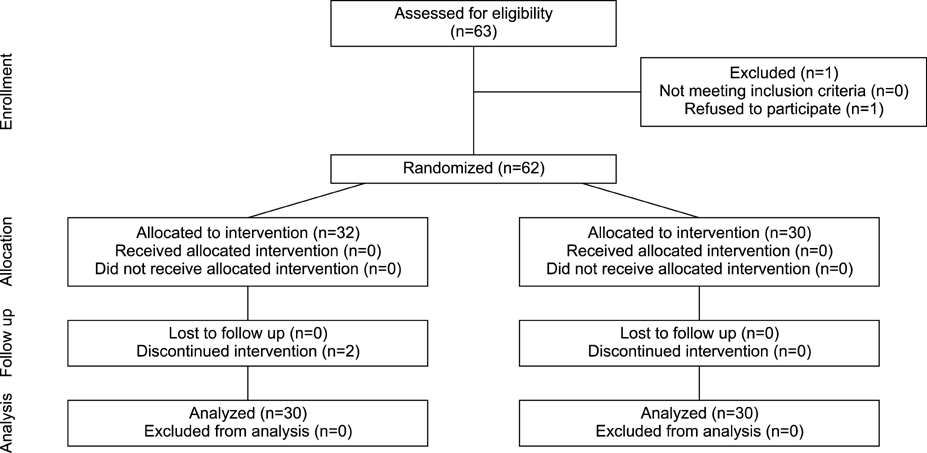
- Dexmedetomidine is a selective α-2 adrenoceptor agonist with anxiolytic, sedative, and analgesic properties that prolongs analgesia and decreases opioid-related side effects when used in neuraxial and perineural areas as a local anesthetics adjuvant. The current study was designed to evaluate the effects of a single perineural administration of dexmedetomidine without local anesthetics on narcotic consumption and pain intensity in patients with femoral shaft fractures undergoing surgery. This prospective randomized single-blind clinical trial was conducted in patients undergoing femoral fracture shaft surgery. Based on block permuted randomization, the patients were randomly divided into intervention and control groups. The intervention group received 100µg dexmedetomidine, for a femoral nerve block without any local anesthetics. Total intraoperative opioid consumption, postoperative opioid consumption, visual analogue score (VAS) for pain, and hemodynamic parameters were recorded and compared. Finally the data from 60 patients with a mean age of 30.4±12.3 were analyzed (90% male). There were no significant differences between the baseline characteristics of the two groups (p>0.05). The mean total consumption of narcotics was reduced during induction and maintenance of anesthesia in the intervention group (p<0.05). The amount of postoperative narcotics required showed a significant difference in the intervention group compared with the control group (p<0.05). It is likely that perineural administration of dexmedetomidine significantly not only reduced intra and postoperative narcotic requirement but also decreased postoperative pain intensity in patients undergoing femoral shaft surgery. Femoral blockade by dexmedetomidine can provide excellent analgesia while minimizing the side-effects of opioids.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mulroy MF, Larkin KL, Batra MS, Hodgson PS, Owens BD. Femoral nerve block with 0.25% or 0.5% bupivacaine improves postoperative analgesia following outpatient arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament repair. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2001; 26:24–29.
Article2. Fletcher AK, Rigby AS, Heyes FL. Three-in-one femoral nerve block as analgesia for fractured neck of femur in the emergency department: a randomized, controlled trial. Ann Emerg Med. 2003; 41:227–233.
Article3. Williams BA, Kentor ML, Vogt MT, Williams JP, Chelly JE, Valalik S, et al. Femoral-sciatic nerve blocks for complex outpatient knee surgery are associated with less postoperative pain before same-day discharge: a review of 1,200 consecutive cases from the period 1996-1999. Anesthesiology. 2003; 98:1206–1213.
Article4. Joshi GP. Multimodal analgesia techniques and postoperative rehabilitation. Anesthesiol Clin North America. 2005; 23:185–202.
Article5. Lin TF, Yeh YC, Lin FS, Wang YP, Lin CJ, Sun WZ, et al. Effect of combining dexmedetomidine and morphine for intravenous patient-controlled analgesia. Br J Anaesth. 2009; 102:117–122.
Article6. Le Guen M, Liu N, Tounou F, Augé M, Tuil O, Chazot T, et al. Dexmedetomidine reduces propofol and remifentanil requirements during bispectral index-guided closed-loop anesthesia: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Anesth Analg. 2014; 118:946–955.
Article7. Rancourt MP, Albert NT, Côté M, Létourneau DR, Bernard PM. Posterior tibial nerve sensory blockade duration prolonged by adding dexmedetomidine to ropivacaine. Anesth Analg. 2012; 115:958–962.
Article8. Gertler R, Brown HC, Mitchell DH, Silvius EN. Dexmedetomidine: a novel sedative-analgesic agent. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2001; 14:13–21.
Article9. Mason KP, Lerman J. Review article: Dexmedetomidine in children: current knowledge and future applications. Anesth Analg. 2011; 113:1129–1142.10. Burow BK, Johnson ME, Packer DL. Metabolic acidosis associated with propofol in the absence of other causative factors. Anesthesiology. 2004; 101:239–241.
Article11. Ohtani N, Kida K, Shoji K, Yasui Y, Masaki E. Recovery profiles from dexmedetomidine as a general anesthetic adjuvant in patients undergoing lower abdominal surgery. Anesth Analg. 2008; 107:1871–1874.
Article12. Segal IS, Vickery RG, Walton JK, Doze VA, Maze M. Dexmedetomidine diminishes halothane anesthetic requirements in rats through a postsynaptic alpha 2 adrenergic receptor. Anesthesiology. 1988; 69:818–823.
Article13. Sen S, Chakraborty J, Santra S, Mukherjee P, Das B. The effect of dexmedetomidine infusion on propofol requirement for maintenance of optimum depth of anaesthesia during elective spine surgery. Indian J Anaesth. 2013; 57:358–363.
Article14. Wang PH, Tsai CL, Lee JS, Wu KC, Cheng KI, Jou IM. Effects of topical corticosteroids on the sciatic nerve: an experimental study to adduce the safety in treating carpal tunnel syndrome. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2011; 36:236–243.
Article15. Ali Erdogan M, Polat A, Yucel A, Aydogan MS, Parlakpinar H, Tekin S, et al. Effects of perineural administration of dexmedetomidine in combination with levobupivacaine in a rat sciatic nerve block. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2013; 74:74–78.
Article16. Pöpping DM, Elia N, Marret E, Wenk M, Tramèr MR. Clonidine as an adjuvant to local anesthetics for peripheral nerve and plexus blocks: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Anesthesiology. 2009; 111:406–415.
Article17. Brummett CM, Hong EK, Janda AM, Amodeo FS, Lydic R. Perineural dexmedetomidine added to ropivacaine for sciatic nerve block in rats prolongs the duration of analgesia by blocking the hyperpolarization-activated cation current. Anesthesiology. 2011; 115:836–843.
Article18. Mirkheshti A, Saadatniaki A, Salimi A, Manafi Rasi A, Memary E, Yahyaei H. Effects of dexmedetomidine versus ketorolac as local anesthetic adjuvants on the onset and duration of infraclavicular brachial plexus block. Anesth Pain Med. 2014; 4:e17620.
Article19. Blaudszun G, Lysakowski C, Elia N, Tramèr MR. Effect of perioperative systemic α2 agonists on postoperative morphine consumption and pain intensity: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Anesthesiology. 2012; 116:1312–1322.
Article20. Wu HH, Wang HT, Jin JJ, Cui GB, Zhou KC, Chen Y, et al. Does dexmedetomidine as a neuraxial adjuvant facilitate better anesthesia and analgesia? A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e93114.
Article21. Brummett CM, Amodeo FS, Janda AM, Padda AK, Lydic R. Perineural dexmedetomidine provides an increased duration of analgesia to a thermal stimulus when compared with a systemic control in a rat sciatic nerve block. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2010; 35:427–431.
Article22. Esmaoglu A, Yegenoglu F, Akin A, Turk CY. Dexmedetomidine added to levobupivacaine prolongs axillary brachial plexus block. Anesth Analg. 2010; 111:1548–1551.
Article23. Abdel-Aleem M, Osman A, Morsy K. Effect of coadministration of dexamethasone with intrathecal morphine on postoperative outcomes after cesarean delivery. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2012; 116:158–161.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Role of dexmedetomidine as adjuvant in postoperative sciatic popliteal and adductor canal analgesia in trauma patients: a randomized controlled trial
- Comparison of intrathecal versus intra-articular dexmedetomidine as an adjuvant to bupivacaine on postoperative pain following knee arthroscopy: a randomized clinical trial
- Effect of preoperative administration of systemic alpha-2 agonists on postoperative pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- The effect of pre-anesthetic administration of dexmedetomidine on the consumption of opioids in postoperative gynecologic patients
- Stress Fracture of the Femoral shaft