Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2017 Jul;9(4):360-367. 10.4168/aair.2017.9.4.360.
CCR3 Monoclonal Antibody Inhibits Eosinophilic Inflammation and Mucosal Injury in a Mouse Model of Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. djsong506@korea.ac.kr
- 2Environmental Health Center for Childhood Asthma, Korea University Anam Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2378199
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2017.9.4.360
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Although the role of eosinophils in eosinophilic gastroenteritis (EGE) is not fully understood, they are believed to be a principal effector cell. Previous studies have demonstrated that eotaxin and its specific receptor, cysteine-cysteine chemokine receptor-3 (CCR3), play a central role in eosinophil trafficking into the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Thus, we examined the targeting of CCR3 as a potential therapeutic intervention for EGE in a mouse model.
METHODS
Eight- to 10-week-old BALB/c mice were intraperitoneally sensitized and intragastrically challenged with ovalbumin (OVA). Different groups of mice were administered either an anti-CCR3 antibody or a control IgG by intraperitoneal injection 1 hour before each OVA challenge. Eosinophilic inflammation in the intestinal mucosa, mucosal injury, and severity of diarrhea were compared between different groups at 1 hour after final OVA challenge.
RESULTS
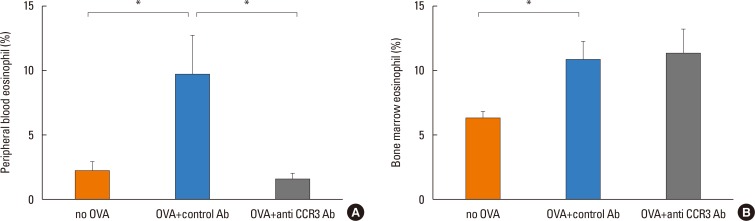
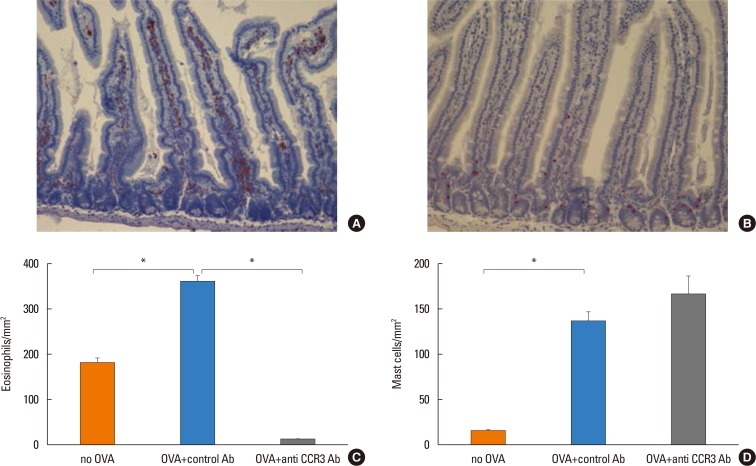
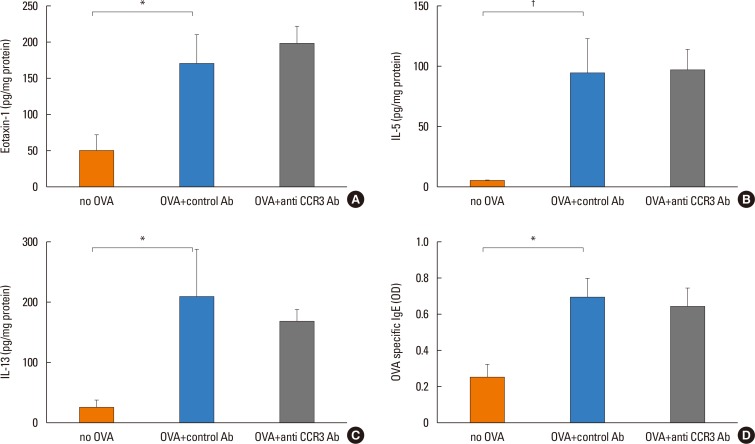
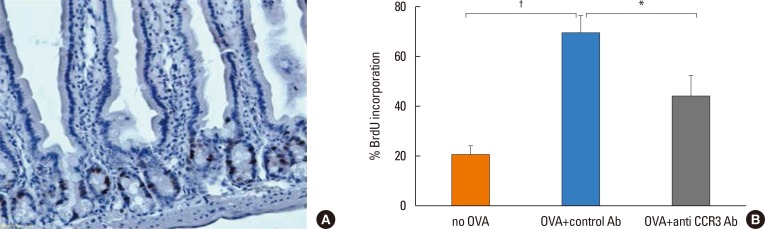
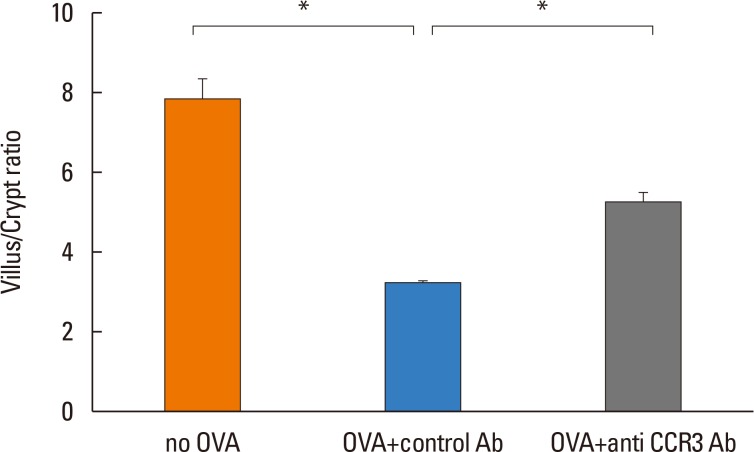
Anti-CCR3 antibody reduced the number of eosinophils in peripheral blood and intestinal mucosa, but not in bone marrow. This reduction was associated with restoration of reduced villous crypt ratio, increased intestinal epithelial cell proliferation, and weight loss induced by OVA challenge. However, Anti-CCR3 antibody had no effect on the level of OVA specific immunoglobulin E (IgE) and the expression of critical chemokines or cytokines in eosinophil trafficking into the GI tract, such as eotaxin-1, interleukin (IL)-5, and IL-13.
CONCLUSIONS
Anti-CCR3 antibody significantly reduced the severity of eosinophilic inflammation, mucosal injury, and diarrhea in a mouse model of food allergen-induced GI eosinophilic inflammation. CCR3 may be a novel therapeutic target for treatment of EGE and other GI eosinophil-mediated diseases.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Bone Marrow
Chemokine CCL11
Chemokines
Cytokines
Diarrhea
Eosinophils*
Epithelial Cells
Gastroenteritis*
Gastrointestinal Tract
Immunoglobulin E
Immunoglobulin G
Immunoglobulins
Inflammation*
Injections, Intraperitoneal
Interleukin-13
Interleukins
Intestinal Mucosa
Mice*
Ovalbumin
Ovum
Weight Loss
Chemokine CCL11
Chemokines
Cytokines
Immunoglobulin E
Immunoglobulin G
Immunoglobulins
Interleukin-13
Interleukins
Ovalbumin
Figure
Reference
-
1. Guajardo JR, Plotnick LM, Fende JM, Collins MH, Putnam PE, Rothenberg ME. Eosinophil-associated gastrointestinal disorders: a world-wide-web based registry. J Pediatr. 2002; 141:576–581. PMID: 12378201.
Article2. Spergel JM, Book WM, Mays E, Song L, Shah SS, Talley NJ, et al. Variation in prevalence, diagnostic criteria, and initial management options for eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases in the United States. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2011; 52:300–306. PMID: 21057327.
Article3. Rothenberg ME. Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders (EGID). J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 113:11–28. PMID: 14713902.
Article4. Chehade M, Aceves SS. Food allergy and eosinophilic esophagitis. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 10:231–237. PMID: 20410819.
Article5. Song DJ, Cho JY, Miller M, Strangman W, Zhang M, Varki A, et al. Anti-Siglec-F antibody inhibits oral egg allergen induced intestinal eosinophilic inflammation in a mouse model. Clin Immunol. 2009; 131:157–169. PMID: 19135419.
Article6. Jose PJ, Griffiths-Johnson DA, Collins PD, Walsh DT, Moqbel R, Totty NF, et al. Eotaxin: a potent eosinophil chemoattractant cytokine detected in a guinea pig model of allergic airways inflammation. J Exp Med. 1994; 179:881–887. PMID: 7509365.
Article7. Matthews AN, Friend DS, Zimmermann N, Sarafi MN, Luster AD, Pearlman E, et al. Eotaxin is required for the baseline level of tissue eosinophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998; 95:6273–6278. PMID: 9600955.
Article8. Broide D, Sriramarao P. Eosinophil trafficking to sites of allergic inflammation. Immunol Rev. 2001; 179:163–172. PMID: 11292020.
Article9. Blanchard C, Rothenberg ME. Biology of the eosinophil. Adv Immunol. 2009; 101:81–121. PMID: 19231593.10. Brandt EB, Strait RT, Hershko D, Wang Q, Muntel EE, Scribner TA, et al. Mast cells are required for experimental oral allergen-induced diarrhea. J Clin Invest. 2003; 112:1666–1677. PMID: 14660743.
Article11. Ben S, Li X, Xu F, Xu W, Li W, Wu Z, et al. Treatment with anti-CC chemokine receptor 3 monoclonal antibody or dexamethasone inhibits the migration and differentiation of bone marrow CD34 progenitor cells in an allergic mouse model. Allergy. 2008; 63:1164–1176. PMID: 18699933.12. Zhang M, Angata T, Cho JY, Miller M, Broide DH, Varki A. Defining the in vivo function of Siglec-F, a CD33-related Siglec expressed on mouse eosinophils. Blood. 2007; 109:4280–4287. PMID: 17272508.
Article13. Cho JY, Miller M, Baek KJ, Han JW, Nayar J, Lee SY, et al. Inhibition of airway remodeling in IL-5-deficient mice. J Clin Invest. 2004; 113:551–560. PMID: 14966564.
Article14. Friend DS, Ghildyal N, Austen KF, Gurish MF, Matsumoto R, Stevens RL. Mast cells that reside at different locations in the jejunum of mice infected with Trichinella spiralis exhibit sequential changes in their granule ultrastructure and chymase phenotype. J Cell Biol. 1996; 135:279–290. PMID: 8858180.
Article15. Mishra A, Hogan SP, Brandt EB, Rothenberg ME. An etiological role for aeroallergens and eosinophils in experimental esophagitis. J Clin Invest. 2001; 107:83–90. PMID: 11134183.
Article16. Chehade M, Magid MS, Mofidi S, Nowak-Wegrzyn A, Sampson HA, Sicherer SH. Allergic eosinophilic gastroenteritis with protein-losing enteropathy: intestinal pathology, clinical course, and long-term follow-up. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2006; 42:516–521. PMID: 16707973.17. Tan AC, Kruimel JW, Naber TH. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis treated with non-enteric-coated budesonide tablets. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001; 13:425–427. PMID: 11338074.
Article18. Siewert E, Lammert F, Koppitz P, Schmidt T, Matern S. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis with severe protein-losing enteropathy: successful treatment with budesonide. Dig Liver Dis. 2006; 38:55–59. PMID: 16326154.
Article19. Hogan SP, Mishra A, Brandt EB, Royalty MP, Pope SM, Zimmermann N, et al. A pathological function for eotaxin and eosinophils in eosinophilic gastrointestinal inflammation. Nat Immunol. 2001; 2:353–360. PMID: 11276207.
Article20. Pease JE, Horuk R. Recent progress in the development of antagonists to the chemokine receptors CCR3 and CCR4. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2014; 9:467–483. PMID: 24641500.
Article21. Neighbour H, Boulet LP, Lemiere C, Sehmi R, Leigh R, Sousa AR, et al. Safety and efficacy of an oral CCR3 antagonist in patients with asthma and eosinophilic bronchitis: a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Clin Exp Allergy. 2014; 44:508–516. PMID: 24286456.
Article22. Grimaldi JC, Yu NX, Grunig G, Seymour BW, Cottrez F, Robinson DS, et al. Depletion of eosinophils in mice through the use of antibodies specific for C-C chemokine receptor 3 (CCR3). J Leukoc Biol. 1999; 65:846–853. PMID: 10380909.
Article23. de Paulis A, Annunziato F, Di Gioia L, Romagnani S, Carfora M, Beltrame C, et al. Expression of the chemokine receptor CCR3 on human mast cells. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2001; 124:146–150. PMID: 11306952.
Article24. Collington SJ, Westwick J, Williams TJ, Weller CL. The function of CCR3 on mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells in vitro. Immunology. 2010; 129:115–124. PMID: 20050333.25. Gurish MF, Humbles A, Tao H, Finkelstein S, Boyce JA, Gerard C, et al. CCR3 is required for tissue eosinophilia and larval cytotoxicity after infection with Trichinella spiralis. J Immunol. 2002; 168:5730–5736. PMID: 12023373.
Article