Tuberc Respir Dis.
2017 Apr;80(2):201-209. 10.4046/trd.2017.80.2.201.
Predictive Factors of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infection in Elderly Patients with Community-Onset Pneumonia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Jeju National University Hospital, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea. lovlet@paran.com
- KMID: 2375990
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2017.80.2.201
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection is a severe and life-threatening disease in patients with community-onset (CO) pneumonia. However, the current guidelines lack specificity for a screening test for MRSA infection.
METHODS
This study was retrospectively conducted in elderly patients aged ≥65 years, who had contracted CO-pneumonia during hospitalization at the Jeju National University Hospital, between January 2012 and December 2014. We analyzed the risk factors of MRSA in these patients and developed a scoring system to predict MRSA infection.
RESULTS
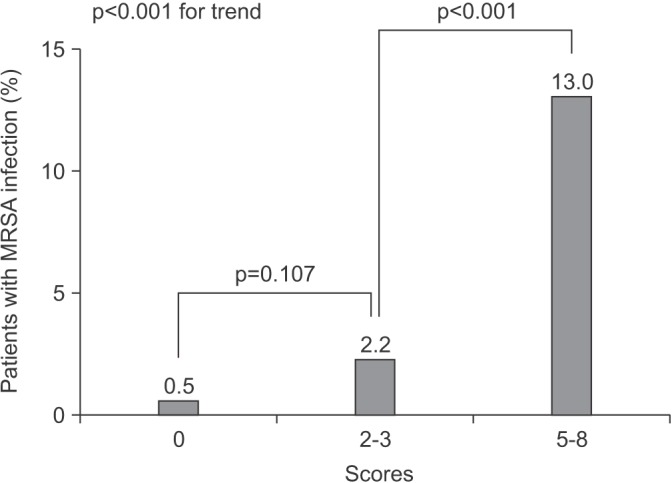
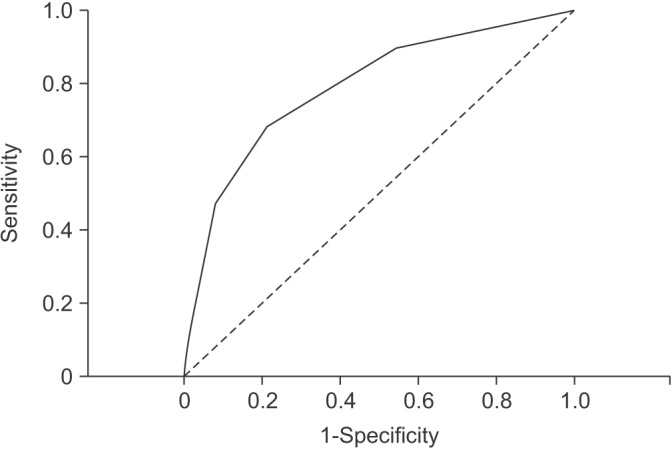
A total of 762 patients were enrolled in this study, including 19 (2.4%) with MRSA infection. Healthcare-associated pneumonia (HCAP) showed more frequent MRSA infection compared to community-acquired pneumonia (4.4% vs. 1.5%, respectively; p=0.016). In a multivariate logistic regression analysis, admissions during the influenza season (odds ratio [OR], 2.896; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.022-8.202; p=0.045), chronic kidney disease (OR, 3.555; 95% CI, 1.157-10.926; p=0.027), and intensive care unit admission (OR, 3.385; 95% CI, 1.035-11.075; p=0.044) were identified as predictive factors for MRSA infection. However, the presence of HCAP was not significantly associated with MRSA infection (OR, 1.991; 95% CI, 0.720-5.505; p=0.185). The scoring system consisted of three variables based on the multivariate analysis, and showed moderately accurate diagnostic prediction (area under curve, 0.790; 95% CI, 0.680-0.899; p<0.001).
CONCLUSION
MRSA infection would be considered in elderly CO-pneumonia patients, with three risk factors identified herein. When managing elderly patients with pneumonia, clinicians might keep in mind that these risk factors are associated with MRSA infection, which may help in selecting appropriate antibiotics.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Aged*
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Community-Acquired Infections
Hospitalization
Humans
Influenza, Human
Intensive Care Units
Logistic Models
Mass Screening
Methicillin Resistance*
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus*
Mortality
Multivariate Analysis
Pneumonia*
Renal Insufficiency, Chronic
Retrospective Studies
Risk Factors
Seasons
Sensitivity and Specificity
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kwong JC, Chua K, Charles PG. Managing severe community-acquired pneumonia due to community methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2012; 14:330–338. PMID: 22430229.2. Rubinstein E, Kollef MH, Nathwani D. Pneumonia caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Clin Infect Dis. 2008; 46(Suppl 5):S378–S385. PMID: 18462093.3. Lobo LJ, Reed KD, Wunderink RG. Expanded clinical presentation of community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia. Chest. 2010; 138:130–136. PMID: 20173050.4. Jung WJ, Kang YA, Park MS, Park SC, Leem AY, Kim EY, et al. Prediction of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in patients with non-nosocomial pneumonia. BMC Infect Dis. 2013; 13:370. PMID: 23937553.
Article5. Kalil AC, Metersky ML, Klompas M, Muscedere J, Sweeney DA, Palmer LB, et al. Management of adults with hospital-acquired and ventilator-associated pneumonia: 2016 clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the American Thoracic Society. Clin Infect Dis. 2016; 63:e61–e111. PMID: 27418577.6. Mandell LA, Wunderink RG, Anzueto A, Bartlett JG, Campbell GD, Dean NC, et al. Infectious Diseases Society of America/American Thoracic Society consensus guidelines on the management of community-acquired pneumonia in adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2007; 44(Suppl 2):S27–S72. PMID: 17278083.
Article7. Shorr AF, Myers DE, Huang DB, Nathanson BH, Emons MF, Kollef MH. A risk score for identifying methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in patients presenting to the hospital with pneumonia. BMC Infect Dis. 2013; 13:268. PMID: 23742753.
Article8. Fein AM, Niederman MS. Severe pneumonia in the elderly. Clin Geriatr Med. 1994; 10:121–143. PMID: 8168019.
Article9. Li W, Ding C, Yin S. Severe pneumonia in the elderly: a multivariate analysis of risk factors. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015; 8:12463–12475. PMID: 26550157.10. American Thoracic Society. Infectious Diseases Society of America. Guidelines for the management of adults with hospital-acquired, ventilator-associated, and healthcare-associated pneumonia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005; 171:388–416. PMID: 15699079.11. Teshome BF, Lee GC, Reveles KR, Attridge RT, Koeller J, Wang CP, et al. Application of a methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus risk score for community-onset pneumonia patients and outcomes with initial treatment. BMC Infect Dis. 2015; 15:380. PMID: 26385225.
Article12. Geckler RW, Gremillion DH, McAllister CK, Ellenbogen C. Microscopic and bacteriological comparison of paired sputa and transtracheal aspirates. J Clin Microbiol. 1977; 6:396–399. PMID: 334796.
Article13. Trouillet JL, Chastre J, Vuagnat A, Joly-Guillou ML, Combaux D, Dombret MC, et al. Ventilator-associated pneumonia caused by potentially drug-resistant bacteria. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998; 157:531–539. PMID: 9476869.
Article14. Cosgrove SE, Sakoulas G, Perencevich EN, Schwaber MJ, Karchmer AW, Carmeli Y. Comparison of mortality associated with methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: a meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis. 2003; 36:53–59. PMID: 12491202.15. Bartlett JG, Mundy LM. Community-acquired pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 1995; 333:1618–1624. PMID: 7477199.
Article16. Fridkin SK, Hageman JC, Morrison M, Sanza LT, Como-Sabetti K, Jernigan JA, et al. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus disease in three communities. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:1436–1444. PMID: 15814879.17. Hageman JC, Uyeki TM, Francis JS, Jernigan DB, Wheeler JG, Bridges CB, et al. Severe community-acquired pneumonia due to Staphylococcus aureus, 2003-04 influenza season. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006; 12:894–899. PMID: 16707043.18. Kallen AJ, Brunkard J, Moore Z, Budge P, Arnold KE, Fosheim G, et al. Staphylococcus aureus community-acquired pneumonia during the 2006 to 2007 influenza season. Ann Emerg Med. 2009; 53:358–365. PMID: 18534715.19. Moran GJ, Krishnadasan A, Gorwitz RJ, Fosheim GE, Albrecht V, Limbago B, et al. Prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus as an etiology of community-acquired pneumonia. Clin Infect Dis. 2012; 54:1126–1133. PMID: 22438343.20. Francis JS, Doherty MC, Lopatin U, Johnston CP, Sinha G, Ross T, et al. Severe community-onset pneumonia in healthy adults caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carrying the Panton-Valentine leukocidin genes. Clin Infect Dis. 2005; 40:100–107. PMID: 15614698.21. Gillet Y, Issartel B, Vanhems P, Fournet JC, Lina G, Bes M, et al. Association between Staphylococcus aureus strains carrying gene for Panton-Valentine leukocidin and highly lethal necrotising pneumonia in young immunocompetent patients. Lancet. 2002; 359:753–759. PMID: 11888586.22. Labandeira-Rey M, Couzon F, Boisset S, Brown EL, Bes M, Benito Y, et al. Staphylococcus aureus Panton-Valentine leukocidin causes necrotizing pneumonia. Science. 2007; 315:1130–1133. PMID: 17234914.23. Olsen RJ, Kobayashi SD, Ayeras AA, Ashraf M, Graves SF, Ragasa W, et al. Lack of a major role of Staphylococcus aureus Panton-Valentine leukocidin in lower respiratory tract infection in nonhuman primates. Am J Pathol. 2010; 176:1346–1354. PMID: 20093487.24. Peyrani P, Allen M, Wiemken TL, Haque NZ, Zervos MJ, Ford KD, et al. Severity of disease and clinical outcomes in patients with hospital-acquired pneumonia due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains not influenced by the presence of the Panton-Valentine leukocidin gene. Clin Infect Dis. 2011; 53:766–771. PMID: 21880581.25. Shindo Y, Ito R, Kobayashi D, Ando M, Ichikawa M, Shiraki A, et al. Risk factors for drug-resistant pathogens in community-acquired and healthcare-associated pneumonia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013; 188:985–995. PMID: 23855620.
Article26. Chalmers JD, Rother C, Salih W, Ewig S. Healthcare-associated pneumonia does not accurately identify potentially resistant pathogens: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis. 2014; 58:330–339. PMID: 24270053.
Article27. Matsuda S, Ogasawara T, Sugimoto S, Kato S, Umezawa H, Yano T, et al. Prospective open-label randomized comparative, non-inferiority study of two initial antibiotic strategies for patients with nursing- and healthcare-associated pneumonia: guideline-concordant therapy versus empiric therapy. J Infect Chemother. 2016; 22:400–406. PMID: 27062334.
Article28. Metersky ML, Frei CR, Mortensen EM. Predictors of Pseudomonas and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in hospitalized patients with healthcare-associated pneumonia. Respirology. 2016; 21:157–163. PMID: 26682638.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Nosocomial Infections
- Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA)
- A Case of Community-Acquired Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Pneumonia
- Detection of Multidrug Resistant Patterns and Associated - genes of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus ( MRSA ) Isolated from Clinical Specimens
- Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Infection in Neonates