Yonsei Med J.
2016 Mar;57(2):321-327. 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.2.321.
Darapladib, a Lipoprotein-Associated Phospholipase A2 Inhibitor, Reduces Rho Kinase Activity in Atherosclerosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Cardiology, The Second Hospital of Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong Province, China. awwa6940@sina.com
- 2Shandong Blood Center, Jinan, Shandong Province, China.
- 3The Key Laboratory of Cardiovascular Remodeling and Function Research of the Chinese Ministry of Education and Public Health, Shandong University Qilu Hospital, Jinan, Shandong Province, China.
- KMID: 2374035
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2016.57.2.321
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Increased lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) activity and Rho kinase activity may be associated with atherosclerosis. The principal aim of this study was to examine whether darapladib (a selective Lp-PLA2 inhibitor) could reduce the elevated Lp-PLA2 and Rho kinase activity in atherosclerosis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Studies were performed in male Sprague-Dawley rats. The atherosclerosis rats were prepared by feeding them with a high-cholesterol diet for 10 weeks. Low-dose darapladib (25 mg.kg-1.d-1) and high-dose darapladib (50 mg.kg-1.d-1) interventions were then administered over the course of 2 weeks.
RESULTS
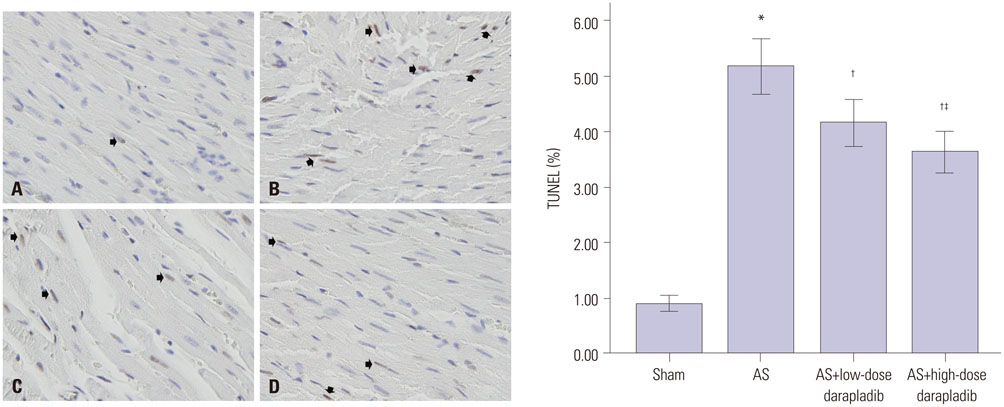
The serum levels of triglycerides, total cholesterol (TC), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), and Lp-PLA2, significantly increased in atherosclerosis model groups, as did Rho kinase activity and cardiomyocyte apoptosis (p<0.05 vs. sham group), whereas nitric oxide (NO) production was reduced. Levels of TC, LDL-C, CRP, Lp-PLA2, and Rho kinase activity were respectively reduced in darapladib groups, whereas NO production was enhanced. When compared to the low-dose darapladib group, the reduction of the levels of TC, LDL-C, CRP, and Lp-PLA2 was more prominent in the high-dose darapladib group (p<0.05), and the increase of NO production was more prominent (p<0.05). Cardiomyocyte apoptosis of the high-dose darapladib group was also significantly reduced compared to the low-dose darapladib group (p<0.05). However, there was no significant difference in Rho kinase activity between the low-dose darapladib group and the high-dose darapladib group (p>0.05).
CONCLUSION
Darapladib, a Lp-PLA2 inhibitor, leads to cardiovascular protection that might be mediated by its inhibition of both Rho kinase and Lp-PLA2 in atherosclerosis.
MeSH Terms
-
1-Alkyl-2-acetylglycerophosphocholine Esterase/*antagonists & inhibitors/blood/drug effects
Animals
Atherosclerosis/blood/*drug therapy/*enzymology
*Benzaldehydes
C-Reactive Protein/metabolism
Cholesterol/blood
Cholesterol, HDL/blood
Cholesterol, LDL/blood
Dose-Response Relationship, Drug
Male
*Oximes
Phospholipase A2 Inhibitors/*administration & dosage/adverse effects
Rats
Rats, Sprague-Dawley
Triglycerides/blood
rho-Associated Kinases/*metabolism
1-Alkyl-2-acetylglycerophosphocholine Esterase
Benzaldehydes
C-Reactive Protein
Cholesterol
Cholesterol, HDL
Cholesterol, LDL
Oximes
Phospholipase A2 Inhibitors
Triglycerides
rho-Associated Kinases
Figure
Reference
-
1. Murray CJ, Lopez AD. Alternative projections of mortality and disability by cause 1990-2020: Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet. 1997; 349:1498–1504.
Article2. Ocaranza MP, Rivera P, Novoa U, Pinto M, González L, Chiong M, et al. Rho kinase inhibition activates the homologous angiotensinconverting enzyme-angiotensin-(1-9) axis in experimental hypertension. J Hypertens. 2011; 29:706–715.
Article3. Soga J, Noma K, Hata T, Hidaka T, Fujii Y, Idei N, et al. Rho-associated kinase activity, endothelial function, and cardiovascular risk factors. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011; 31:2353–2359.
Article4. Ocaranza MP, Gabrielli L, Mora I, Garcia L, McNab P, Godoy I, et al. Markedly increased Rho-kinase activity in circulating leukocytes in patients with chronic heart failure. Am Heart J. 2011; 161:931–937.
Article5. Zhang J, Bian HJ, Li XX, Liu XB, Sun JP, Li N, et al. ERK-MAPK signaling opposes rho-kinase to reduce cardiomyocyte apoptosis in heart ischemic preconditioning. Mol Med. 2010; 16:307–315.
Article6. Bao W, Hu E, Tao L, Boyce R, Mirabile R, Thudium DT, et al. Inhibition of Rho-kinase protects the heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res. 2004; 61:548–558.
Article7. Nohria A, Grunert ME, Rikitake Y, Noma K, Prsic A, Ganz P, et al. Rho kinase inhibition improves endothelial function in human subjects with coronary artery disease. Circ Res. 2006; 99:1426–1432.
Article8. Matsui T, Amano M, Yamamoto T, Chihara K, Nakafuku M, Ito M, et al. Rho-associated kinase, a novel serine/threonine kinase, as a putative target for small GTP binding protein Rho. EMBO J. 1996; 15:2208–2216.
Article9. Coleman ML, Sahai EA, Yeo M, Bosch M, Dewar A, Olson MF. Membrane blebbing during apoptosis results from caspase-mediated activation of ROCK I. Nat Cell Biol. 2001; 3:339–345.
Article10. Feng J, Ito M, Kureishi Y, Ichikawa K, Amano M, Isaka N, et al. Rhoassociated kinase of chicken gizzard smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1999; 274:3744–3752.
Article11. Wirth A. Rho kinase and hypertension. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010; 1802:1276–1284.
Article12. Ait-Oufella H, Mallat Z, Tedgui A. [Lp-PLA2 and sPLA2: cardiovascular biomarkers]. Med Sci (Paris). 2014; 30:526–531.13. Rosenson RS, Hurt-Camejo E. Phospholipase A2 enzymes and the risk of atherosclerosis. Eur Heart J. 2012; 33:2899–2909.
Article14. Cai GJ, Miao CY, Xie HH, Lu LH, Su DF. Arterial baroreflex dysfunction promotes atherosclerosis in rats. Atherosclerosis. 2005; 183:41–47.
Article15. Leng X, Zhan R, Wang Y, Liu X, Gong J, Gao X, et al. Anti-heat shock protein 70 autoantibody epitope changes and BD091 promotes atherosclerosis in rats. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2010; 15:947–958.
Article16. Zhang J, Li XX, Bian HJ, Liu XB, Ji XP, Zhang Y. Inhibition of the activity of Rho-kinase reduces cardiomyocyte apoptosis in heart ischemia/reperfusion via suppressing JNK-mediated AIF translocation. Clin Chim Acta. 2009; 401:76–80.
Article17. Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951; 193:265–275.
Article18. Libby P, Ridker PM, Maseri A. Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2002; 105:1135–1143.
Article19. Ridker PM, Rifai N, Rose L, Buring JE, Cook NR. Comparison of Creactive protein and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels in the prediction of first cardiovascular events. N Engl J Med. 2002; 347:1557–1565.
Article20. Otake H, Shite J, Shinke T, Watanabe S, Tanino Y, Ogasawara D, et al. Relation between plasma adiponectin, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, and coronary plaque components in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 2008; 101:1–7.
Article21. Ridker PM. C-reactive protein: eighty years from discovery to emergence as a major risk marker for cardiovascular disease. Clin Chem. 2009; 55:209–215.
Article22. Koenig W, Khuseyinova N, LÖwel H, Trischler G, Meisinger C. Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 adds to risk prediction of incident coronary events by C-reactive protein in apparently healthy middle-aged men from the general population: results from the 14-year follow-up of a large cohort from southern Germany. Circulation. 2004; 110:1903–1908.
Article23. Ballantyne CM, Hoogeveen RC, Bang H, Coresh J, Folsom AR, Heiss G, et al. Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, and risk for incident coronary heart disease in middle-aged men and women in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. Circulation. 2004; 109:837–842.
Article24. May HT, Horne BD, Anderson JL, Wolfert RL, Muhlestein JB, Renlund DG, et al. Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 independently predicts the angiographic diagnosis of coronary artery disease and coronary death. Am Heart J. 2006; 152:997–1003.
Article25. Brilakis ES, McConnell JP, Lennon RJ, Elesber AA, Meyer JG, Berger PB. Association of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 levels with coronary artery disease risk factors, angiographic coronary artery disease, and major adverse events at follow-up. Eur Heart J. 2005; 26:137–144.
Article26. Nunes KP, Rigsby CS, Webb RC. RhoA/Rho-kinase and vascular diseases: what is the link? Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010; 67:3823–3836.
Article27. Dong M, Yan BP, Yu CM. Current status of rho-associated kinases (ROCKs) in coronary atherosclerosis and vasospasm. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2009; 7:322–330.
Article28. Zhou Q, Gensch C, Liao JK. Rho-associated coiled-coil-forming kinases (ROCKs): potential targets for the treatment of atherosclerosis and vascular disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2011; 32:167–173.
Article29. Sauzeau V, Le Jeune H, Cario-Toumaniantz C, Smolenski A, Lohmann SM, Bertoglio J, et al. Cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase signaling pathway inhibits RhoA-induced Ca2+ sensitization of contraction in vascular smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 2000; 275:21722–21729.
Article30. Chitaley K, Webb RC. Nitric oxide induces dilation of rat aorta via inhibition of rho-kinase signaling. Hypertension. 2002; 39(2 Pt 2):438–442.
Article31. Carter RW, Begaye M, Kanagy NL. Acute and chronic NOS inhibition enhances alpha(2)-adrenoreceptor-stimulated RhoA and Rho kinase in rat aorta. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2002; 283:H1361–H1369.32. Tektaş AK, Uslu S, Yalçin AU, Sahin G, Temiz G, Kara M, et al. Effects of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 on arginase/nitric oxide pathway in hemodialysis patients. Ren Fail. 2012; 34:738–743.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Production of Phospholipase A2 in Different Types of Cultured Human Intervertebral Disc Cells
- D60-sensitive tyrosine phosphorylation is involved in Fas-mediated phospholipase D activation
- The Inhibitory Mechanism of Gentamicin on Electrical Field Stimulation Response in Rat Bladder Smooth Muscle
- Cromakalim blocks membrane phosphoinositide activated signals in the guinea pig lung mast cells stimulated with antigen-antibody reactions
- Prevention of Vasculogenic Erectile Dysfunction in Rat Model by the Chronic Administration of Oral Rho Kinase Inhibitor