J Korean Med Sci.
2016 Jun;31(6):989-996. 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.6.989.
Effects of Systemic Administration of Dexmedetomidine on Intraocular Pressure and Ocular Perfusion Pressure during Laparoscopic Surgery in a Steep Trendelenburg Position: Prospective, Randomized, Double-Blinded Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, College of Medicine, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. jmlee@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2373711
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.6.989
Abstract
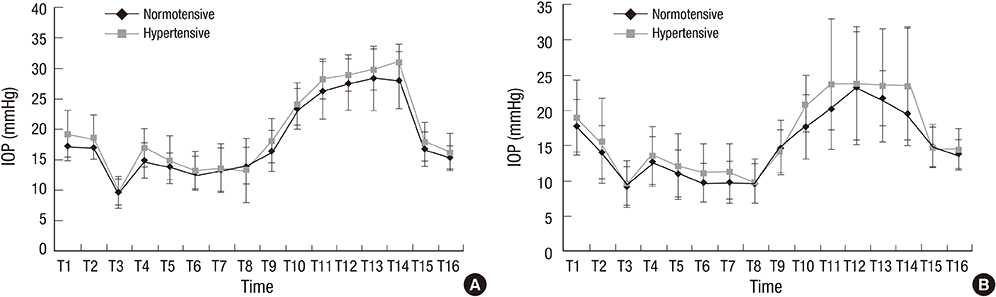
- Increased intraocular pressure (IOP) during surgery is a risk factor for postoperative ophthalmological complications. We assessed the efficacy of systemically infused dexmedetomidine in preventing the increase in IOP caused by a steep Trendelenburg position, and evaluated the influence of underlying hypertension on IOP during surgery. Sixty patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery in a steep Trendelenburg position were included. Patients in the dexmedetomidine group received a 1.0 µg/kg IV loading dose of dexmedetomidine before anesthesia, followed by an infusion of 0.5 µg/kg/hr throughout the operation. Patients in the saline group were infused with the same volume of normal saline. IOP and ocular perfusion pressure (OPP) were measured 16 times pre- and intraoperatively. In the saline group, IOP increased in the steep Trendelenburg position, and was 11.3 mmHg higher at the end of the time at the position compared with the baseline value (before anesthetic induction). This increase in IOP was attenuated in the dexmedetomidine group, for which IOP was only 4.2 mmHg higher (P < 0.001 vs. the saline group). The steep Trendelenburg position was associated with a decrease in OPP; the degree of decrease was comparable for both groups. In intragroup comparisons between patients with underlying hypertension and normotensive patients, the values of IOP at every time point were comparable. Dexmedetomidine infusion attenuated the increase in IOP during laparoscopic surgery in a steep Trendelenburg position, without further decreasing the OPP. Systemic hypertension did not seem to be associated with any additional increase in IOP during surgery. (Registration at the Clinical Research Information Service of Korea National Institute of Health ID: KCT0001482)
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Dexmedetomidine/administration & dosage/*pharmacology
Double-Blind Method
Eye Diseases/surgery
Female
Head-Down Tilt
Humans
Hypnotics and Sedatives/administration & dosage/pharmacology
Intraocular Pressure/*drug effects
Intraoperative Complications/drug therapy/prevention & control
Laparoscopy
Male
Middle Aged
Prospective Studies
Risk Factors
Tonometry, Ocular
Treatment Outcome
Dexmedetomidine
Hypnotics and Sedatives
Figure
Reference
-
1. Awad H, Santilli S, Ohr M, Roth A, Yan W, Fernandez S, Roth S, Patel V. The effects of steep trendelenburg positioning on intraocular pressure during robotic radical prostatectomy. Anesth Analg. 2009; 109:473–478.2. Molloy BL. Implications for postoperative visual loss: steep trendelenburg position and effects on intraocular pressure. AANA J. 2011; 79:115–121.3. Weber ED, Colyer MH, Lesser RL, Subramanian PS. Posterior ischemic optic neuropathy after minimally invasive prostatectomy. J Neuroophthalmol. 2007; 27:285–287.4. Vaajanen A, Mervaala E, Oksala O, Vapaatalo H. Is there a relationship between blood pressure and intraocular pressure? An experimental study in hypertensive rats. Curr Eye Res. 2008; 33:325–332.5. Farag E, Sessler DI, Kovaci B, Wang L, Mascha EJ, Bell G, Kalfas I, Rockwood E, Kurz A. Effects of crystalloid versus colloid and the alpha-2 agonist brimonidine versus placebo on intraocular pressure during prone spine surgery: a factorial randomized trial. Anesthesiology. 2012; 116:807–815.6. Kaya FN, Yavascaoglu B, Baykara M, Altun GT, Gülhan N, Ata F. Effect of oral gabapentin on the intraocular pressure and haemodynamic responses induced by tracheal intubation. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2008; 52:1076–1080.7. Pal CK, Ray M, Sen A, Hajra B, Mukherjee D, Ghanta AK. Changes in intraocular pressure following administration of suxamethonium and endotracheal intubation: influence of dexmedetomidine premedication. Indian J Anaesth. 2011; 55:573–577.8. Lam AK, Douthwaite WA. Does the change of anterior chamber depth or/and episcleral venous pressure cause intraocular pressure change in postural variation? Optom Vis Sci. 1997; 74:664–667.9. Cantor LB. The evolving pharmacotherapeutic profile of brimonidine, an alpha 2-adrenergic agonist, after four years of continuous use. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2000; 1:815–834.10. Friberg TR, Weinreb RN. Ocular manifestations of gravity inversion. JAMA. 1985; 253:1755–1757.11. Hayreh SS. Ischemic optic neuropathy. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2009; 28:34–62.12. Macri FJ, Cevario SJ. Clonidine. Arch Ophthalmol. 1978; 96:2111–2113.13. Vartiainen J, MacDonald E, Urtti A, Rouhiainen H, Virtanen R. Dexmedetomidine-induced ocular hypotension in rabbits with normal or elevated intraocular pressures. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1992; 33:2019–2023.14. Donello JE, Padillo EU, Webster ML, Wheeler LA, Gil DW. alpha(2)-adrenoceptor agonists inhibit vitreal glutamate and aspartate accumulation and preserve retinal function after transient ischemia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001; 296:216–223.15. Klein BE, Klein R, Knudtson MD. Intraocular pressure and systemic blood pressure: longitudinal perspective: the Beaver Dam Eye Study. Br J Ophthalmol. 2005; 89:284–287.16. Mitchell P, Lee AJ, Rochtchina E, Wang JJ. Open-angle glaucoma and systemic hypertension: the blue mountains eye study. J Glaucoma. 2004; 13:319–326.17. Xu L, Wang H, Wang Y, Jonas JB. Intraocular pressure correlated with arterial blood pressure: the beijing eye study. Am J Ophthalmol. 2007; 144:461–462.18. Gherghel D, Hosking SL, Orgül S. Autonomic nervous system, circadian rhythms, and primary open-angle glaucoma. Surv Ophthalmol. 2004; 49:491–508.19. Czarnik T, Gawda R, Kolodziej W, Latka D, Sznajd-Weron K, Weron R. Associations between intracranial pressure, intraocular pressure and mean arterial pressure in patients with traumatic and non-traumatic brain injuries. Injury. 2009; 40:33–39.20. Ding C, Wang P, Tian N. Effect of general anesthetics on IOP in elevated IOP mouse model. Exp Eye Res. 2011; 92:512–520.21. Benumof JL, Mazzei W, Roth S, Barach P, Lam AM, Lee LA. Multifactorial etiology of postoperative vision loss. Anesthesiology. 2002; 96:1531–1532.22. Stambough JL, Dolan D, Werner R, Godfrey E. Ophthalmologic complications associated with prone positioning in spine surgery. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2007; 15:156–165.23. Cheng MA, Todorov A, Tempelhoff R, McHugh T, Crowder CM, Lauryssen C. The effect of prone positioning on intraocular pressure in anesthetized patients. Anesthesiology. 2001; 95:1351–1355.24. Beneyto P, Barajas MA, Garcia-de-Blas F, Del Cura I, Sanz T, Vello R, Salvador C. Predictive value of tonometry with Tono-pen XL in primary care. Br J Gen Pract. 2007; 57:653–654.25. Setogawa A. Kawai. Measurement of intraocular pressure by both invasive and noninvasive techniques in rabbits exposed to head-down tilt. Jpn J Physiol. 1998; 48:25–31.26. Pinkney TD, King AJ, Walter C, Wilson TR, Maxwell-Armstrong C, Acheson AG. Raised intraocular pressure (IOP) and perioperative visual loss in laparoscopic colorectal surgery: a catastrophe waiting to happen? A systematic review of evidence from other surgical specialities. Tech Coloproctol. 2012; 16:331–335.27. Nickels TJ, Manlapaz MR, Farag E. Perioperative visual loss after spine surgery. World J Orthop. 2014; 5:100–106.28. Kim NY, Yoo YC, Park H, Choi YD, Kim CY, Bai SJ. The effect of dexmedetomidine on intraocular pressure increase in patients during robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy in the steep trendelenburg position. J Endourol. 2015; 29:310–316.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Comparison of the Effects of Propofol and Sevoflurane Anesthesias on Intraocular Pressure during Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
- The Effect of CO2 Insufflation and Trendelenburg-lithotomy Position on Intraocular Pressure during Laparoscopy
- Postural Intraocular Pressure Change at Trendelenberg Position Measured by Rebound Tonometer
- Hemodynamic parameters during robotic radical prostatectomy in elderly patients with increased cardiac risk
- Effect of Ocular Hypotensives and Honan Intraocular Pressure Reducer on Ocular Tension after Retrobulbar Anesthesia