Ann Lab Med.
2016 Nov;36(6):603-606. 10.3343/alm.2016.36.6.603.
Performance Evaluation of the Real-Q Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Quantification Kit Using Two Real-Time PCR Systems for Quantifying CMV DNA in Whole Blood
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. pmhhj77@gmail.com, changski@skku.edu
- 2Center for Clinical Medicine, Samsung Biomedical Research Institute, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2373601
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2016.36.6.603
Abstract
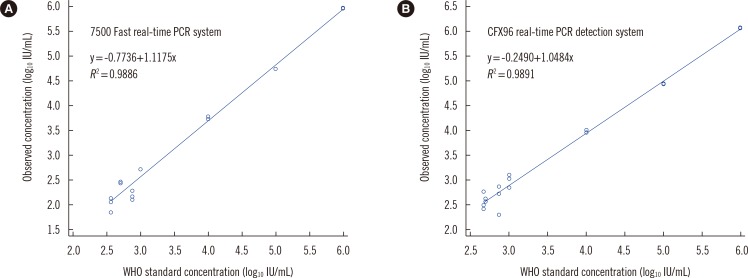
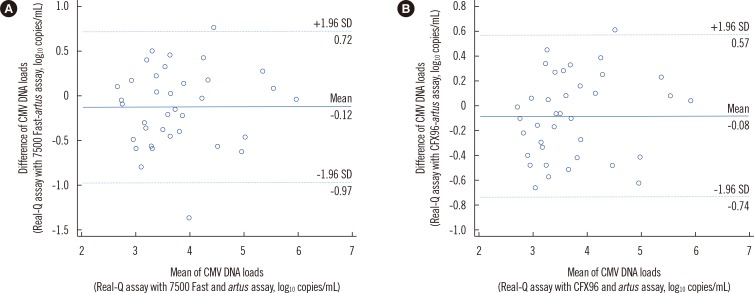
- Standardized cytomegalovirus (CMV) DNA quantification is important for managing CMV disease. We evaluated the performance of the Real-Q CMV Quantification Kit (Real-Q assay; BioSewoom, Korea) using whole blood (WB), with nucleic acid extraction using MagNA Pure 96 (Roche Diagnostics, Germany). Real-time PCR was performed on two platforms: the 7500 Fast real-time PCR (7500 Fast; Applied Biosystems, USA) and CFX96 real-time PCR detection (CFX96; Bio-Rad, USA) systems. The WHO international standard, diluted with CMV-negative WB, was used to validate the analytical performance. We used 90 WB clinical samples for comparison with the artus CMV RG PCR kit (artus assay; Qiagen, Germany). Limits of detections (LODs) in 7500 Fast and CFX96 were 367 and 479 IU/mL, respectively. The assay was linear from the LOD to 10(6) IU/mL (R2 ≥0.9886). The conversion factors from copies to IU in 7500 Fast and CFX96 were 0.95 and 1.06, respectively. Compared with the artus assay, for values <1,000 copies/mL, 100% of the samples had a variation <0.7 log10 copies/mL; >1,000 copies/mL, 73.3% and 80.6% of samples in 7500 Fast and CFX96, respectively, had <0.5 log10 copies/mL. The Real-Q assay is useful for quantifying CMV in WB with the two real-time PCR platforms.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Le Page AK, Jager MM, Iwasenko JM, Scott GM, Alain S, Rawlinson WD. Clinical aspects of cytomegalovirus antiviral resistance in solid organ transplant recipients. Clin Infect Dis. 2013; 56:1018–1029. PMID: 23243176.2. Razonable RR. Management strategies for cytomegalovirus infection and disease in solid organ transplant recipients. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2013; 27:317–342. PMID: 23714343.3. Baldanti F, Lilleri D, Gerna G. Monitoring human cytomegalovirus infection in transplant recipients. J Clin Virol. 2008; 41:237–241. PMID: 18203657.4. Gerna G, Lilleri D, Chiesa A, Zelini P, Furione M, Comolli G, et al. Virologic and immunologic monitoring of cytomegalovirus to guide preemptive therapy in solid-organ transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2011; 11:2463–2471. PMID: 21827612.5. Kraft CS, Armstrong WS, Caliendo AM. Interpreting quantitative cytomegalovirus DNA testing: understanding the laboratory perspective. Clin Infect Dis. 2012; 54:1793–1797. PMID: 22412060.6. Pang XL, Fox JD, Fenton JM, Miller GG, Caliendo AM, Preiksaitis JK. Interlaboratory comparison of cytomegalovirus viral load assays. Am J Transplant. 2009; 9:258–268. PMID: 19178413.7. Fryer JF, Heath AB, editors. Collaborative study to evaluate the proposed 1st WHO international standard for human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) for nucleic acid amplification (NAT)-based assays. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization;2010.8. CLSI. Evaluation of detection capability for clinical laboratory measurement procedures; approved guideline-Second ed. CLSI document EP17-A2. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2012.9. Miller S, Seet H, Khan Y, Wright C, Nadarajah R. Comparison of QIAGEN automated nucleic acid extraction methods for CMV quantitative PCR testing. Am J Clin Pathol. 2010; 133:558–563. PMID: 20231608.10. Lisboa LF, Asberg A, Kumar D, Pang X, Hartmann A, Preiksaitis JK, et al. The clinical utility of whole blood versus plasma cytomegalovirus viral load assays for monitoring therapeutic response. Transplantation. 2011; 91:231–236. PMID: 21048530.11. Schnepf N, Scieux C, Resche-Riggon M, Feghoul L, Xhaard A, Gallien S, et al. Fully automated quantification of cytomegalovirus (CMV) in whole blood with the new sensitive Abbott RealTime CMV assay in the era of the CMV international standard. J Clin Microbiol. 2013; 51:2096–2102. PMID: 23616450.12. Deback C, Géli J, Aït-Arkoub Z, Angleraud F, Gautheret-Dejean A, Agut H, et al. Use of the Roche LightCycler 480 system in a routine laboratory setting for molecular diagnosis of opportunistic viral infections: evaluation on whole blood specimens and proficiency panels. J Virol Methods. 2009; 159:291–294. PMID: 19490982.13. Bravo D, Clari MÁ, Costa E, Muñoz-Cobo B, Solano C, José Remigia M, et al. Comparative evaluation of three automated systems for DNA extraction in conjunction with three commercially available real-time PCR assays for quantification of plasma Cytomegalovirus DNAemia in allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients. J Clin Microbiol. 2011; 49:2899–2904. PMID: 21697323.14. Edelmann A, Eichenlaub U, Lepek S, Krüger DH, Hofmann J. Performance of the MagNA Pure 96 system for cytomegalovirus nucleic acid amplification testing in clinical samples. J Clin Microbiol. 2013; 51:1600–1601. PMID: 23467597.15. Mengelle C, Mansuy JM, Sauné K, Barthe C, Boineau J, Izopet J. A new highly automated extraction system for quantitative real-time PCRs from whole blood samples: routine monitoring of opportunistic infections in immunosuppressed patients. J Clin Virol. 2012; 53:314–319. PMID: 22296792.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Quantitation of Cytomegalovirus DNA by Real-Time PCR in Whole Blood with the Cytomegalovirus Antigenemia Assay
- Comparison Cytomegalovirus Qualitative Assay Using Real-Time PCR and Conventional PCR
- Performance Evaluation of the ELITe InGenius System for Detecting Cytomegalovirus, EpsteinBarr Virus, and BK Virus Infections
- Practical Aspects of Cytomegalovirus DNA Quantitative PCR
- Automated Nucleic Acid Extraction Systems for Detecting Cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr Virus Using Real-Time PCR: A Comparison Study Between the QIAsymphony RGQ and QIAcube Systems