Korean J Gastroenterol.
2015 Aug;66(2):70-74. 10.4166/kjg.2015.66.2.70.
Underlying Mechanisms and Management of Refractory Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. kjleemd@hotmail.com
- KMID: 2373317
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2015.66.2.70
Abstract
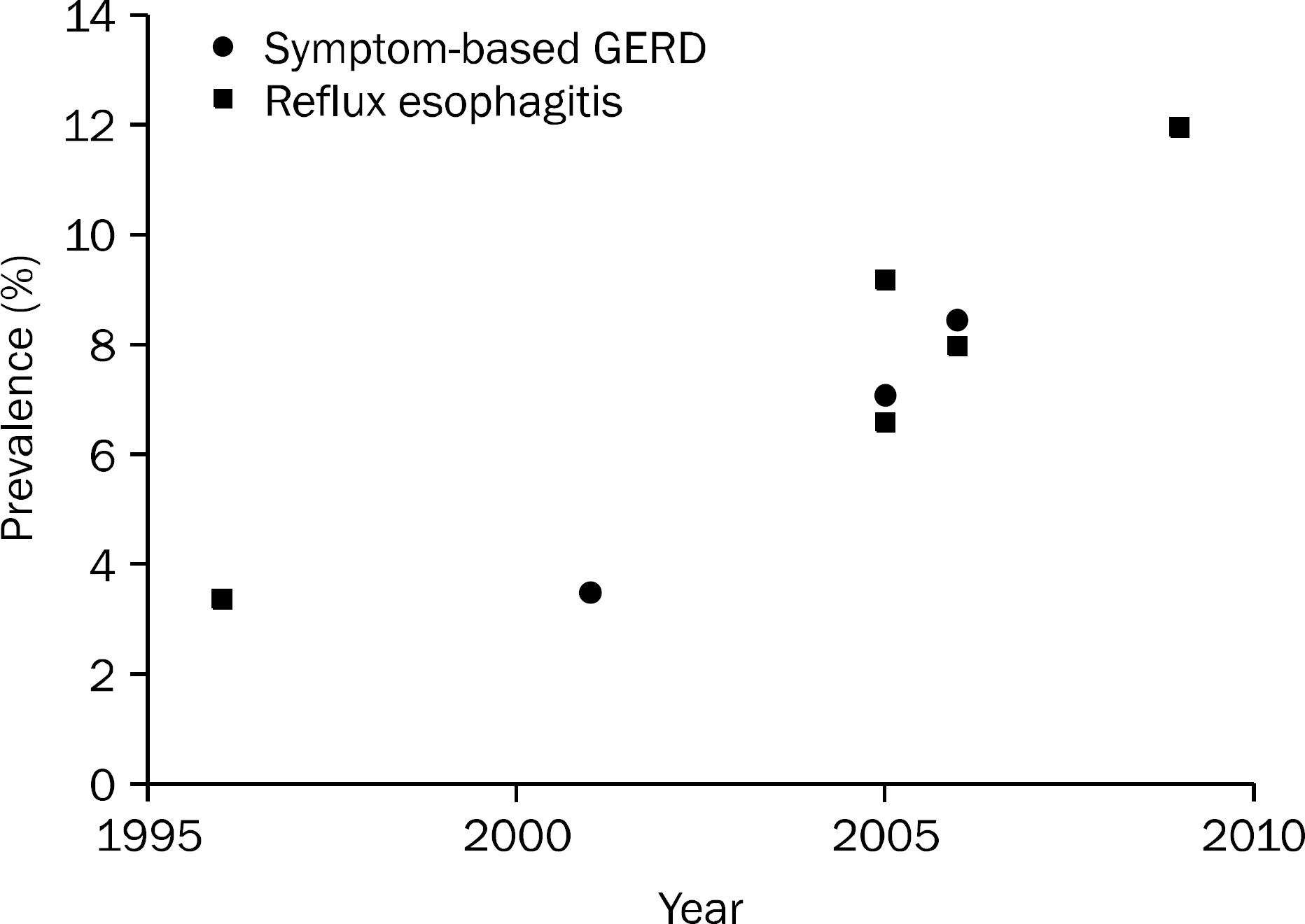
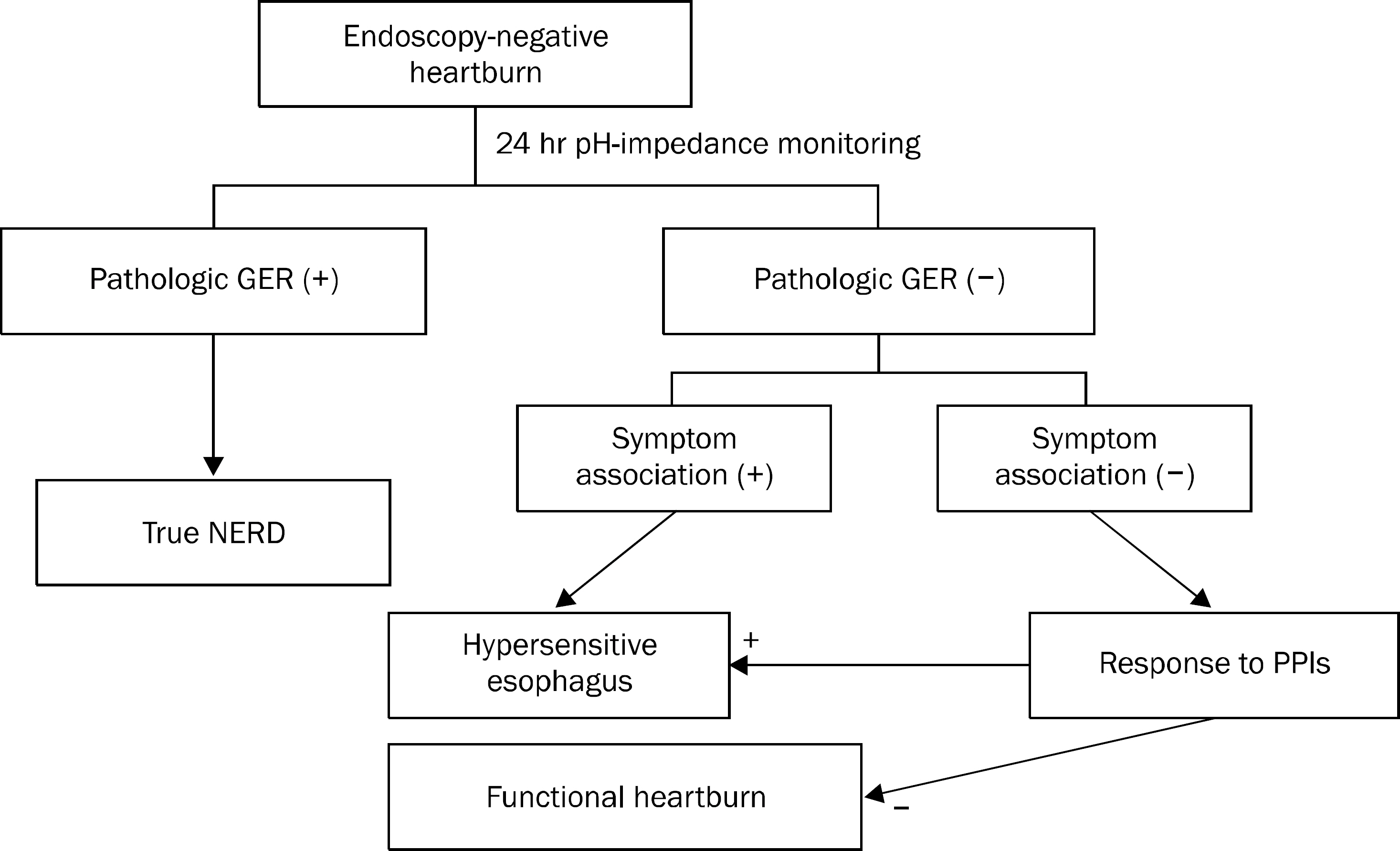
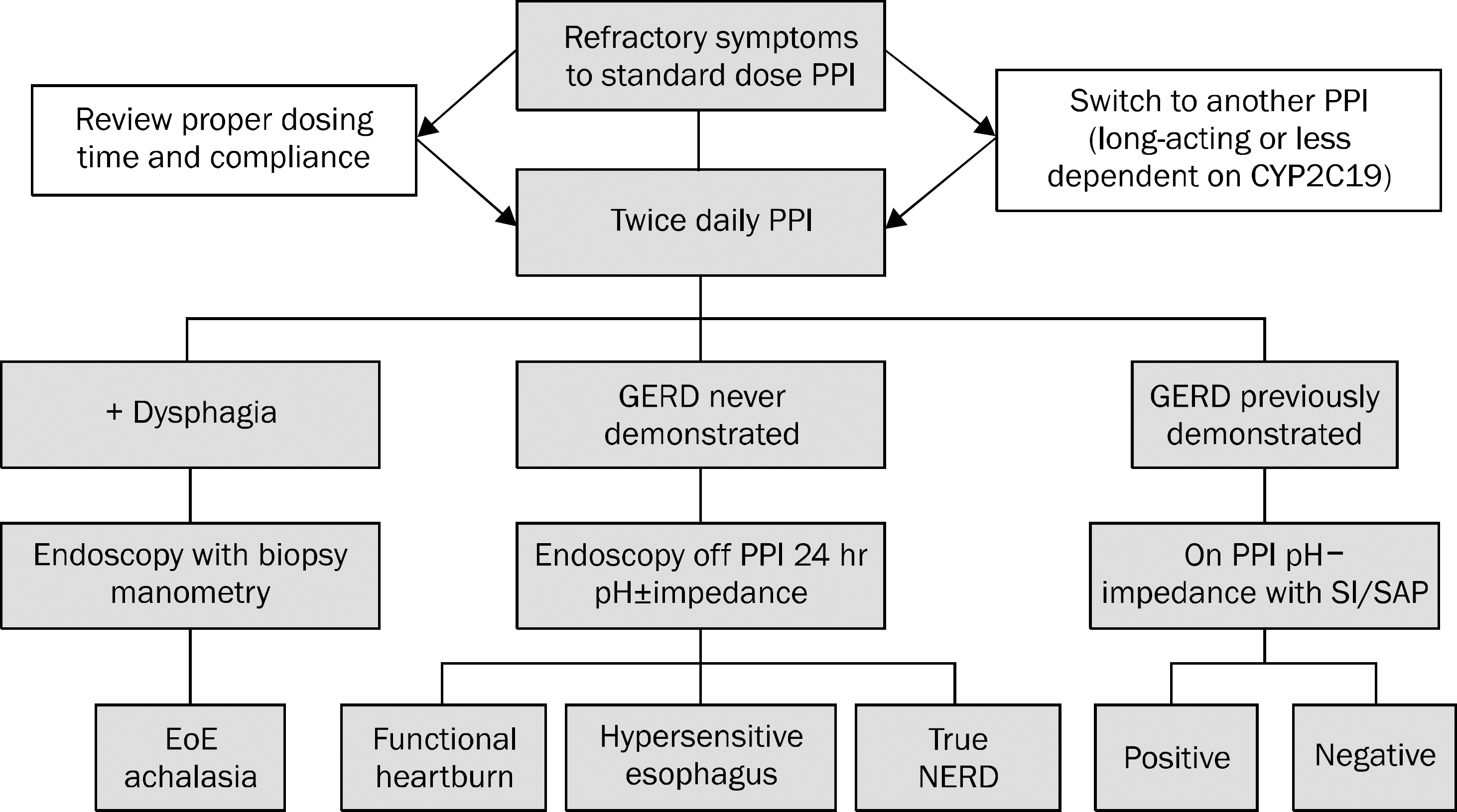
- The prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) in South Korea has increased over the past 10 years. Patients with erosive reflux disease (ERD) shows better response to proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) than those with non-erosive reflux disease (NERD). NERD is a heterogeneous condition, showing pathological gastroesophageal reflux or esophageal hypersensitivity to reflux contents. NERD patients with pathological gastroesophageal reflux or hypersensitivity to acid may respond to PPIs. However, many patients with esophageal hypersensitivity to nonacid or functional heartburn do not respond to PPIs. Therefore, careful history and investigations are required when managing patients with refractory GERD who show poor response to conventional dose PPIs. Combined pH-impedance studies and a PPI diagnostic trial are recommended to reveal underlying mechanisms of refractory symptoms. For those with ongoing reflux-related symptoms, split dose administration, change to long-acting PPIs or PPIs less influenced by CYP2C19 genotypes, increasing dose of PPIs, and the addition of alginate preparations, prokinetics, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, or tricyclic antidepressants can be considered. Pain modulators, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, or tricyclic antidepressants are more likely to be effective for those with reflux-unrelated symptoms. Surgery or endoscopic per oral fundoplication may be effective in selected patients.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Cho YS, Choi MG, Jeong JJ, et al. Prevalence and clinical spectrum of gastroesophageal reflux: a population-based study in Asan-si, Korea. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005; 100:747–753.
Article2. Lee SY, Lee KJ, Kim SJ, Cho SW. Prevalence and risk factors for overlaps between gastroesophageal reflux disease, dyspepsia, and irritable bowel syndrome: a population-based study. Digestion. 2009; 79:196–201.
Article3. Lee D, Lee KJ, Kim KM, Lim SK. Prevalence of asymptomatic erosive esophagitis and factors associated with symptom presentation of erosive esophagitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2013; 48:906–912.
Article4. Kim SE, Kim N, Oh S, et al. Predictive factors of response to proton pump inhibitors in korean patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2015; 21:69–77.
Article5. Hatlebakk JG, Katz PO, Camacho-Lobato L, Castell DO. Proton pump inhibitors: better acid suppression when taken before a meal than without a meal. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2000; 14:1267–1272.
Article6. Kim JH, Rhee PL. Recent advances in noncardiac chest pain in Korea. Gut Liver. 2012; 6:1–9.
Article7. Yamada S, Onda M, Kato S, et al. Genetic differences in CYP2C19 single nucleotide polymorphisms among four Asian populations. J Gastroenterol. 2001; 36:669–672.
Article8. Sugimoto M, Shirai N, Nishino M, et al. Comparison of acid inhibition with standard dosages of proton pump inhibitors in relation to CYP2C19 genotype in Japanese. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2014; 70:1073–1078.
Article9. Hammer J, Schmidt B. Effect of splitting the dose of esomeprazole on gastric acidity and nocturnal acid breakthrough. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004; 19:1105–1110.
Article10. Kahrilas PJ, McColl K, Fox M, et al. The acid pocket: a target for treatment in reflux disease? Am J Gastroenterol. 2013; 108:1058–1064.
Article11. Savarino V, Savarino E, Parodi A, Dulbecco P. Functional heartburn and nonerosive reflux disease. Dig Dis. 2007; 25:172–174.
Article12. Lee KJ, Kwon HC, Cheong JY, Cho SW. Demographic, clinical, and psychological characteristics of the heartburn groups classified using the Rome III criteria and factors associated with the responsiveness to proton pump inhibitors in the gastroesophageal reflux disease group. Digestion. 2009; 79:131–136.13. Scarpignato C. Poor effectiveness of proton pump inhibitors in nonerosive reflux disease: the truth in the end! Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2012; 24:697–704.
Article14. Jung HK, Hong SJ, Jo YJ, et al. Korean Society of Neurogastroenterology and Motility. Updated guidelines 2012 for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2012; 60:195–218.
Article15. Kim E, Lee H, Jung HK, Lee KJ. Achalasia in Korea: an epidemiologic study using a national healthcare database. J Korean Med Sci. 2014; 29:576–580.
Article16. Park H. An overview of eosinophilic esophagitis. Gut Liver. 2014; 8:590–597.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Refractory Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Diagnosis and Management
- Proton Pump Inhibitor for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Intelligent Prescription
- Upper Gastrointestinal Cancer and Reflux Disease
- A case of chronic recurrent obstructive bronchitis associated with gastro-esophageal reflux
- Radiologic studies on gastroesophageal reflux