J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2017 Mar;58(3):367-371. 10.3341/jkos.2017.58.3.367.
A Case Report of Occipital Lobe Epilepsy and Related Optical Coherence Tomography Findings
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Myongji Hospita, Seonam University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea. skdh17@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Neurology, Myongji Hospital, Seonam University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- KMID: 2371922
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2017.58.3.367
Abstract
- PURPOSE
In the present case report, visual pathway damage confirmed by retinal ganglion cell layer (GCL) damage on optical coherence tomography (OCT) in occipital lobe epilepsy was described.
CASE SUMMARY
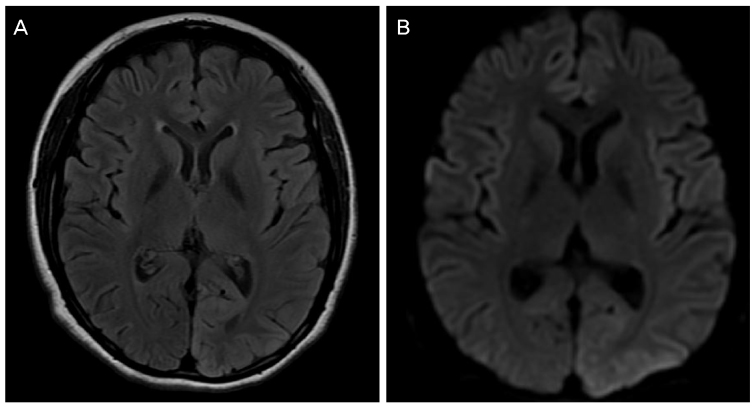
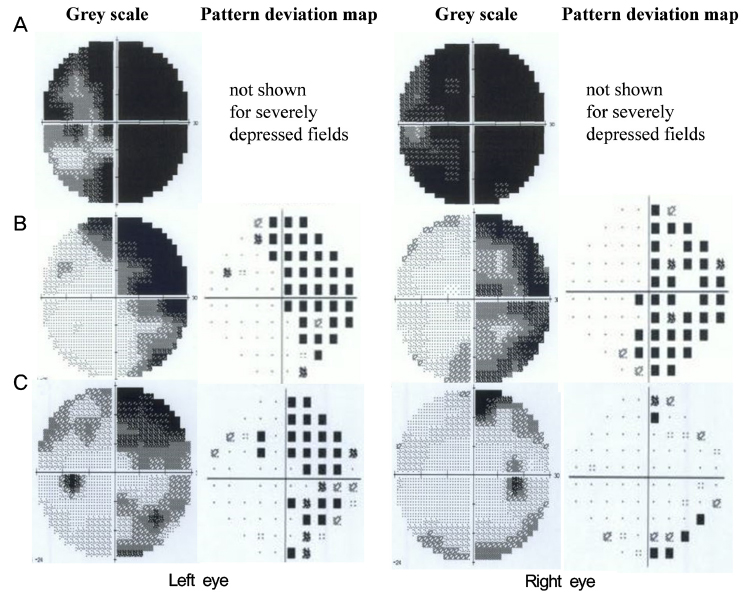
A 25-year-old female with idiopathic generalized epilepsy developed visual blurring followed by a generalized seizure. On brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), very subtle changes of the cortex in the left parietooccipital lobe were observed. Two days after the attack, even after the disappearance of epileptiform wave on electroencephalogram (EEG), visual acuity in both eyes was 0.5 and a perimetry revealed nearly complete visual defect in both eyes. OCT showed severe thinning of GCL and mild thinning of retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL). No additional seizure attack occurred thereafter. One month after the attack, her visual acuity was recovered to 1.0 in both eyes and her left visual hemifield defect was recovered. However, even 6 months after the attack, her right visual hemifield defect and GCL damage persisted in both eyes.
CONCLUSIONS
We reported a case in which the visual pathway damage caused by occipital lobe epilepsy was identified using OCT, despite very subtle changes in brain imaging. This case indicated GCL thinning is an objective and prognostic index for the irreversible visual field defect in occipital lobe epilepsy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lawthom C, Smith PE, Wild JM. Nasal retinal nerve fiber layer attenuation: a biomarker for vigabatrin toxicity. Ophthalmology. 2009; 116:565–571.2. Akçakaya AA, Gökçeer S, Erbil HH, et al. Detecting retinal vigabatrin toxicity in patients with partial symptomatic or cryptogenic epilepsy. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2010; 20:763–769.3. Clayton LM, Dévilé M, Punte T, et al. Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in vigabatrin-exposed patients. Ann Neurol. 2011; 69:845–854.4. Moseng L, Sæter M, Mørch-Johnsen GH, et al. Retinal nerve fibre layer attenuation: clinical indicator for vigabatrin toxicity. Acta Ophthalmol. 2011; 89:452–458.5. Clayton LM, Devile M, Punte T, et al. Patterns of peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer thinning in vigabatrin-exposed individuals. Ophthalmology. 2012; 119:2152–2160.6. Gomceli YB, Dogan B, Genc F, et al. Optical coherence tomography parameters in patients with photosensitive juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. Seizure. 2016; 35:36–40.7. Balestrini S, Clayton LM, Bartmann AP, et al. Retinal nerve fibre layer thinning is associated with drug resistance in epilepsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2016; 87:396–401.8. Ropper A, Samuels MA. Epilepsy and Other Seizure Disorders. Ropper A, Samuels MA. Adams and Victor's Principles of Neurology. 9th ed. New York: McGraw Hill;2009. p. chap. 16.9. Joseph JM, Louis S. Transient ictal cortical blindness during middle age. A case report and review of the literature. J Neuroophthalmol. 1995; 15:39–42.10. Lee SK, Lee SY, Kim DW, et al. Occipital lobe epilepsy: clinical characteristics, surgical outcome, and role of diagnostic modalities. Epilepsia. 2005; 46:688–695.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Concomitant Absence and Occipital Lobe Epilepsy in an Adolescent
- Surgical Strategy of Epilepsy Arising from Parietal and Occipital Lobes
- Availability of Optical Coherence Tomography in Diagnosis and Classification of Choroidal Neovascularization
- Occipital Lobe Epilepsy with Hemicrania Epileptica
- Surgical treatment of occipital lobe epilepsies