Ann Rehabil Med.
2016 Dec;40(6):1135-1139. 10.5535/arm.2016.40.6.1135.
Effects of Radiation Therapy on Established Neurogenic Heterotopic Ossification
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Eulji Hospital, Eulji University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. md52516@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology, Eulji Hospital, Eulji University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2371348
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2016.40.6.1135
Abstract
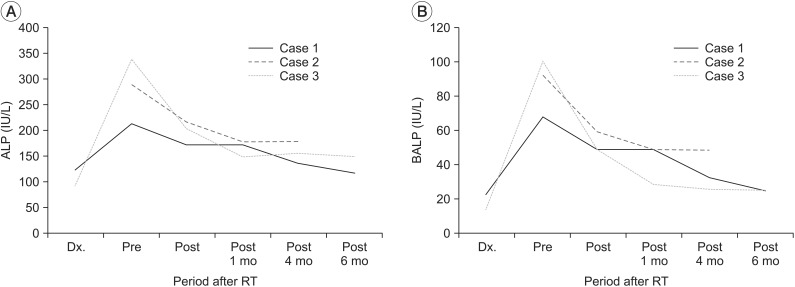
- Heterotopic ossification (HO) is frequently seen on rehabilitation units after spinal cord injuries, fractures, brain injuries, and limb amputations. Currently, there is no effective treatment for HO other than prophylaxis with anti-inflammatory medications, irradiation, and bisphosphonate administration. These prophylactic treatments are not effective for managing ectopic bone once it has formed. Here we describe three cases of established neurogenic HO treated with radiation therapy (RT). All patients had decreased serum alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and bone-specific ALP levels with decreased pain but increased range of motion immediately after RT. Post-treatment X-rays revealed no further growth of the HO. All patients maintained clinical and laboratory improvements 4 or 6 months after the RT. Our results suggest that RT is safe and effective in decreasing pain and activity of neurogenic HO.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kaplan FS, Glaser DL, Hebela N, Shore EM. Heterotopic ossification. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2004; 12:116–125. PMID: 15089085.
Article2. Orzel JA, Rudd TG. Heterotopic bone formation: clinical, laboratory, and imaging correlation. J Nucl Med. 1985; 26:125–132. PMID: 3918147.3. Broyles DL, Nielsen RG, Bussett EM, Lu WD, Mizrahi IA, Nunnelly PA, et al. Analytical and clinical performance characteristics of Tandem-MP Ostase, a new immunoassay for serum bone alkaline phosphatase. Clin Chem. 1998; 44:2139–2147. PMID: 9761247.
Article4. Cipriano C, Pill SG, Rosenstock J, Keenan MA. Radiation therapy for preventing recurrence of neurogenic heterotopic ossification. Orthopedics. 2009; 32:687–689.
Article5. Schaeffer MA, Sosner J. Heterotopic ossification: treatment of established bone with radiation therapy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1995; 76:284–286. PMID: 7717824.
Article6. Jang SH, Shin SW, Ahn SH, Cho IH, Kim SH. Radiation therapy for heterotopic ossification in a patient with traumatic brain injury. Yonsei Med J. 2000; 41:536–539. PMID: 10992819.
Article7. Garland DE. Clinical observations on fractures and heterotopic ossification in the spinal cord and traumatic brain injured populations. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988; (233):86–101.
Article8. Sullivan MP, Torres SJ, Mehta S, Ahn J. Heterotopic ossification after central nervous system trauma: a current review. Bone Joint Res. 2013; 2:51–57. PMID: 23610702.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Heterotopic Ossification Mimics Neurogenic Tumor: A Case Report
- Radiation therapy for heterotopic ossification in a patient with traumatic brain injury
- Osteomyelitis in Heterotopic Ossification after Trochanteric Pressure Sore Reconstruction: A Case Report
- Prevention of heterotopic bone formation after total hip arthroplasty using 600 rad in single dose in high risk patient
- Heterotopic Ossification of a Partially Ruptured Achilles Tendon (A Case Report)