Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2016 Jul;20(4):367-378. 10.4196/kjpp.2016.20.4.367.
Minimal systems analysis of mitochondria-dependent apoptosis induced by cisplatin
- Affiliations
-
- 1BioLead Inc., 609 Korea Mediventure Center, Daegu 41061 Korea.
- 2Iwata Chemical CO., LTD, Shizuoka 438-0078, Japan.
- 3Department of Mechanical and Biomedical Engineering, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon 24341, Korea. ebshim@kangwon.ac.kr
- 4Department of Biochemistry, Suzuka University of Medical Science, Suzuka, mie 513-8670, Japan.
- 5Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Daejeon 34141, Korea.
- KMID: 2371054
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2016.20.4.367
Abstract
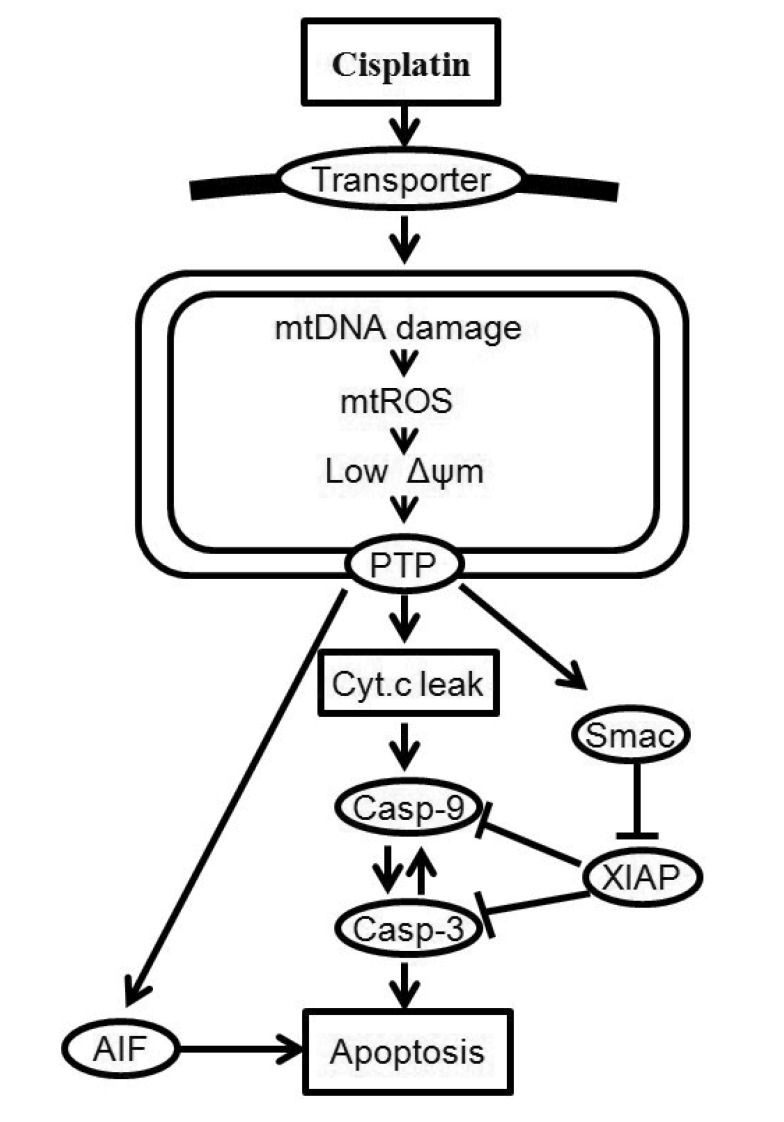
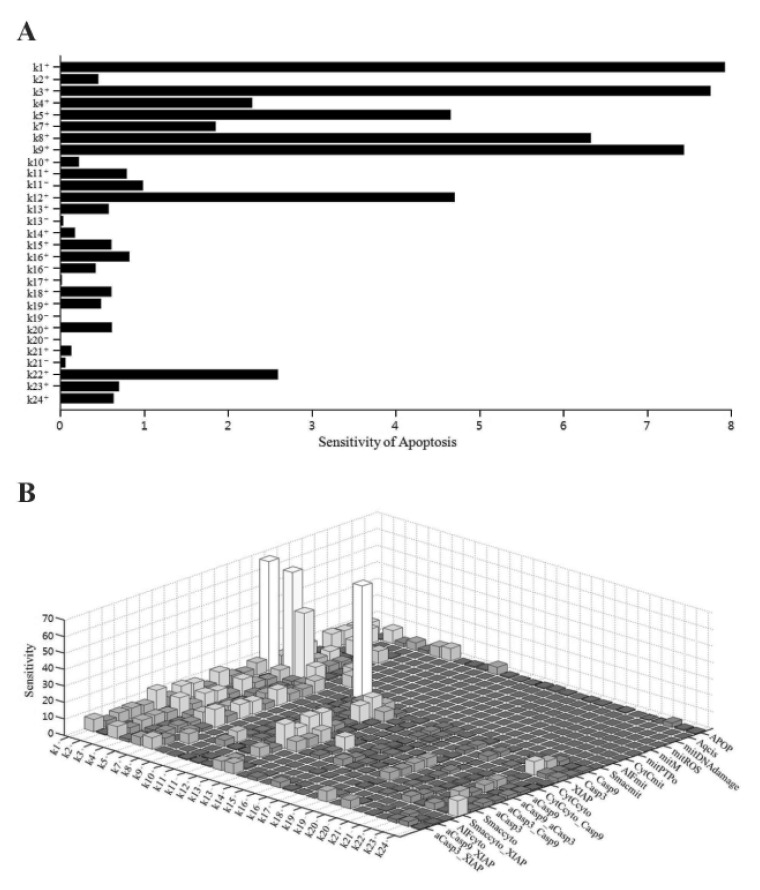
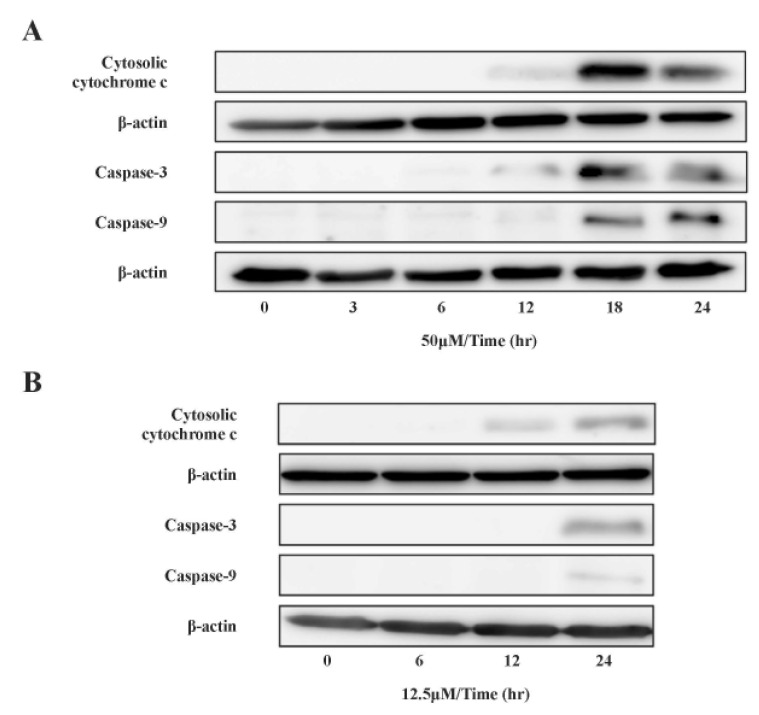
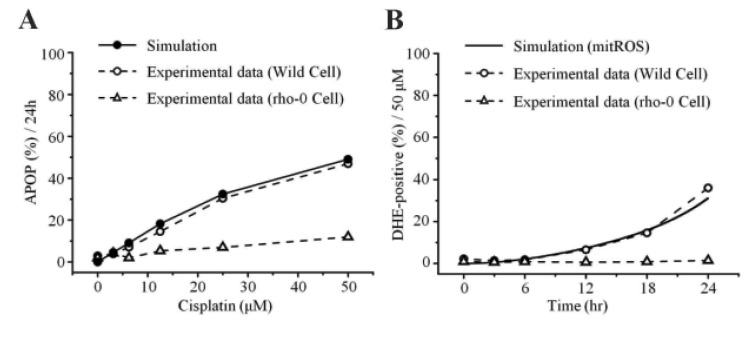
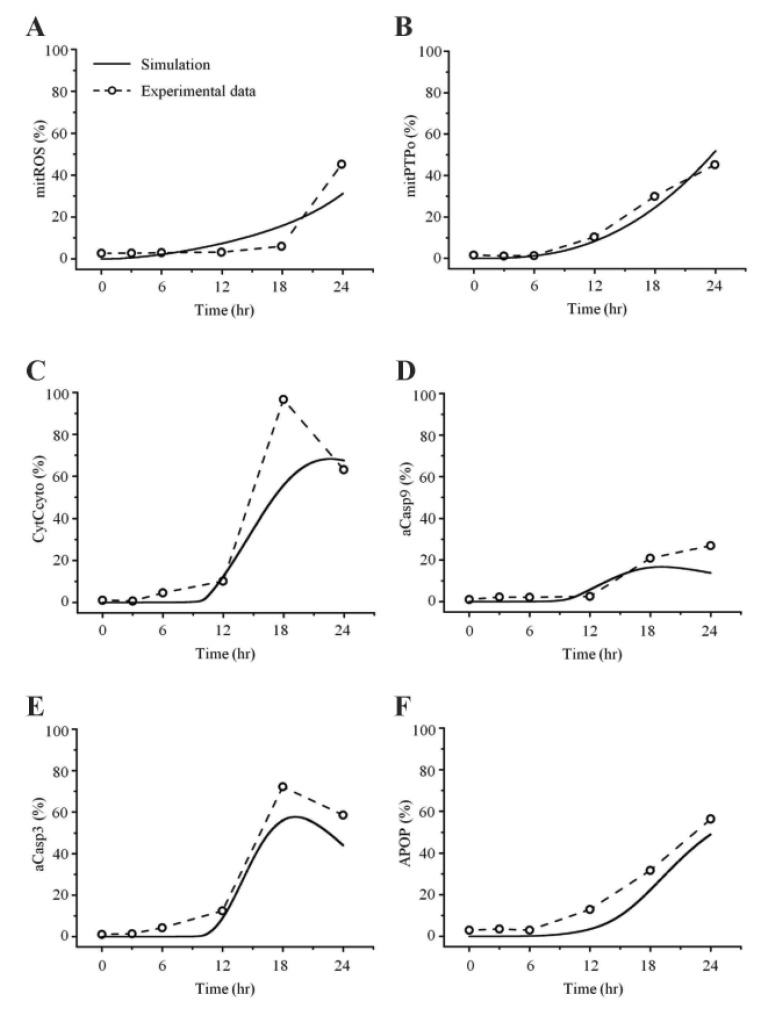
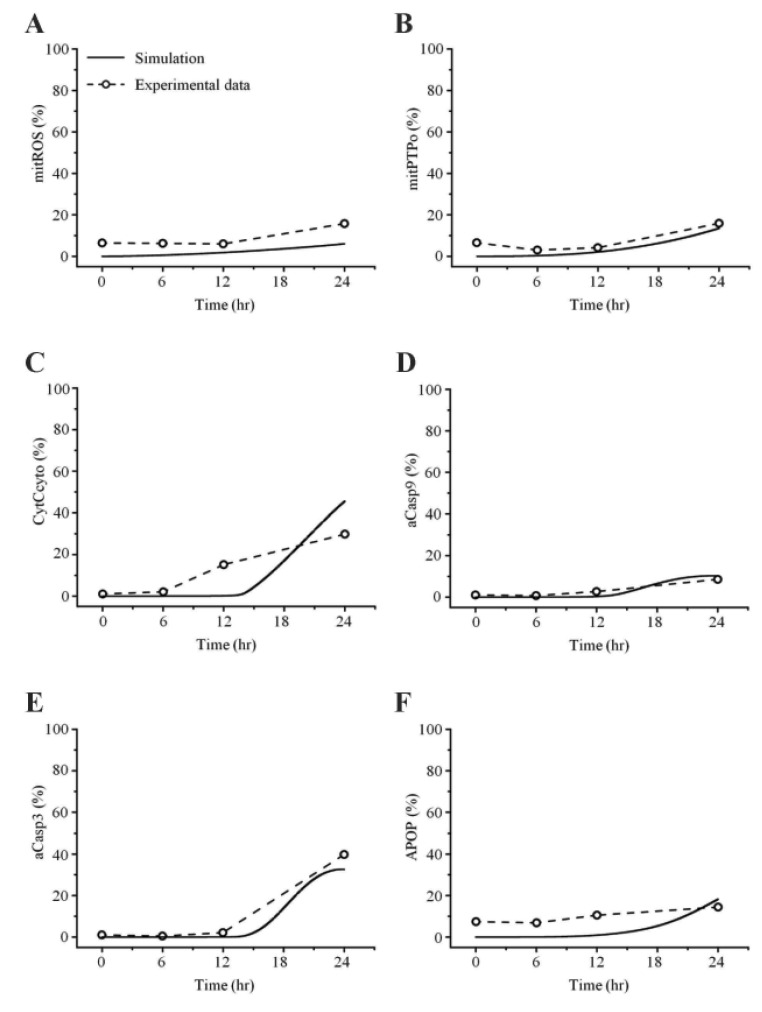
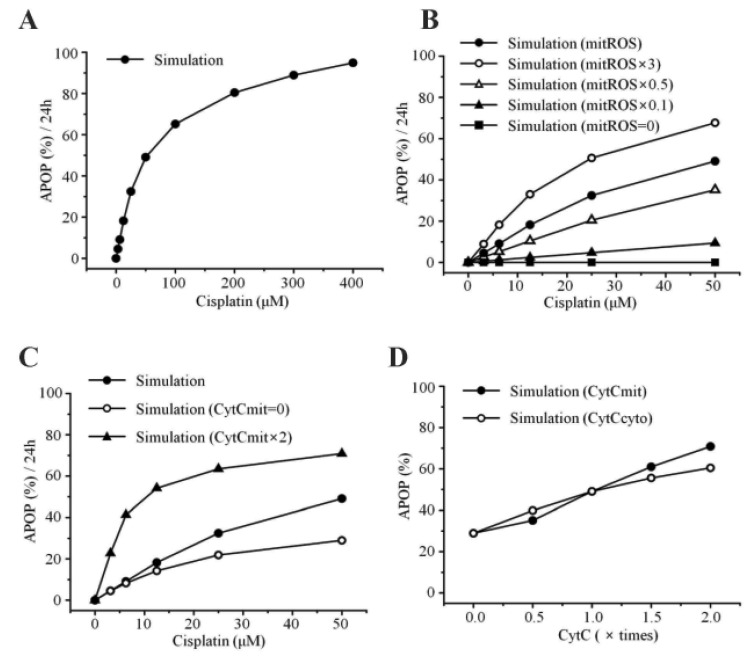
- Recently, it was reported that the role of mitochondria-reactive oxygen species (ROS) generating pathway in cisplatin-induced apoptosis is remarkable. Since a variety of molecules are involved in the pathway, a comprehensive approach to delineate the biological interactions of the molecules is required. However, quantitative modeling of the mitochondria-ROS generating pathway based on experiment and systemic analysis using the model have not been attempted so far. Thus, we conducted experiments to measure the concentration changes of critical molecules associated with mitochondrial apoptosis in both human mesothelioma H2052 and their Ï0 cells lacking mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). Based on the experiments, a novel mathematical model that can represent the essential dynamics of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway induced by cisplatin was developed. The kinetic parameter values of the mathematical model were estimated from the experimental data. Then, we have investigated the dynamical properties of this model and predicted the apoptosis levels for various concentrations of cisplatin beyond the range of experiments. From parametric perturbation analysis, we further found that apoptosis will reach its saturation level beyond a certain critical cisplatin concentration.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Basu A, Krishnamurthy S. Cellular responses to Cisplatin-induced DNA damage. J Nucleic Acids. 2010; DOI: 10.4061/2010/201367.
Article2. Miller RP, Tadagavadi RK, Ramesh G, Reeves WB. Mechanisms of Cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Toxins (Basel). 2010; 2:2490–2518. PMID: 22069563.
Article3. Kohno K, Wang KY, Takahashi M, Kurita T, Yoshida Y, Hirakawa M, Harada Y, Kuma A, Izumi H, Matsumoto S. Mitochondrial transcription factor A and mitochondrial genome as molecular targets for Cisplatin-based cancer chemotherapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2015; 16:19836–19850. PMID: 26307971.4. Budihardjo I, Oliver H, Lutter M, Luo X, Wang X. Biochemical pathways of caspase activation during apoptosis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1999; 15:269–290. PMID: 10611963.
Article5. Chen M, Wang J. Initiator caspases in apoptosis signaling pathways. Apoptosis. 2002; 7:313–319. PMID: 12101390.6. Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I, Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Alnemri ES, Wang X. Cytochrome c and dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an apoptotic protease cascade. Cell. 1997; 91:479–489. PMID: 9390557.
Article7. Mayer B, Oberbauer R. Mitochondrial regulation of apoptosis. News Physiol Sci. 2003; 18:89–94. PMID: 12750442.
Article8. Marchi S, Giorgi C, Suski JM, Agnoletto C, Bononi A, Bonora M, De Marchi E, Missiroli S, Patergnani S, Poletti F, Rimessi A, Duszynski J, Wieckowski MR, Pinton P. Mitochondria-ROS crosstalk in the control of cell death and aging. J Signal Transduct. 2012; 2012:329635. DOI: 10.1155/2012/329635. PMID: 22175013.
Article9. Hong JY, Kim GH, Kim JW, Kwon SS, Sato EF, Cho KH, Shim EB. Computational modeling of apoptotic signaling pathways induced by cisplatin. BMC Syst Biol. 2012; 6:122. DOI: 10.1186/1752-0509-6-122. PMID: 22967854.
Article10. Waterhouse NJ, Goldstein JC, von Ahsen O, Schuler M, Newmeyer DD, Green DR. Cytochrome c maintains mitochondrial transmembrane potential and ATP generation after outer mitochondrial membrane permeabilization during the apoptotic process. J Cell Biol. 2001; 153:319–328. PMID: 11309413.
Article11. Green DR, Kroemer G. The pathophysiology of mitochondrial cell death. Science. 2004; 305:626–629. PMID: 15286356.
Article12. Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Brenner C. Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization in cell death. Physiol Rev. 2007; 87:99–163. PMID: 17237344.
Article13. Crompton M, Virji S, Doyle V, Johnson N, Ward JM. The mitochondrial permeability transition pore. Biochem Soc Symp. 1999; 66:167–179. PMID: 10989666.
Article14. Hua F, Cornejo MG, Cardone MH, Stokes CL, Lauffenburger DA. Effects of Bcl-2 levels on Fas signaling-induced caspase-3 activation: molecular genetic tests of computational model predictions. J Immunol. 2005; 175:985–995. PMID: 16002698.
Article15. Sun XM, Bratton SB, Butterworth M, MacFarlane M, Cohen GM. Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL inhibit CD95-mediated apoptosis by preventing mitochondrial release of Smac/DIABLO and subsequent inactivation of X-linked inhibitor-of-apoptosis protein. J Biol Chem. 2002; 277:11345–11351. PMID: 11801595.
Article16. Nakatsui M, Horimoto K, Okamoto M, Tokumoto Y, Miyake J. Parameter optimization by using differential elimination: a general approach for introducing constraints into objective functions. BMC Syst Biol. 2010; 4(Suppl 2):S9. PMID: 20840736.
Article17. Kane DJ, Sarafian TA, Anton R, Hahn H, Gralla EB, Valentine JS, Ord T, Bredesen DE. Bcl-2 inhibition of neural death: decreased generation of reactive oxygen species. Science. 1993; 262:1274–1277. PMID: 8235659.
Article18. Hara K, Kasahara E, Takahashi N, Konishi M, Inoue J, Jikumaru M, Kubo S, Okamura H, Sato E, Inoue M. Mitochondria determine the efficacy of anticancer agents that interact with DNA but not the cytoskeleton. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011; 337:838–845. PMID: 21421738.
Article19. Qian W, Nishikawa M, Haque AM, Hirose M, Mashimo M, Sato E, Inoue M. Mitochondrial density determines the cellular sensitivity to cisplatin-induced cell death. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2005; 289:C1466–C1475. PMID: 16107504.
Article20. Cao LC, Honeyman TW, Cooney R, Kennington L, Scheid CR, Jonassen JA. Mitochondrial dysfunction is a primary event in renal cell oxalate toxicity. Kidney Int. 2004; 66:1890–1900. PMID: 15496160.
Article21. de Arriba G, Calvino M, Benito S, Parra T. Cyclosporine A-induced apoptosis in renal tubular cells is related to oxidative damage and mitochondrial fission. Toxicol Lett. 2013; 218:30–38. PMID: 23347876.
Article22. Morales AI, Detaille D, Prieto M, Puente A, Briones E, Arévalo M, Leverve X, López-Novoa JM, El-Mir MY. Metformin prevents experimental gentamicin-induced nephropathy by a mitochondria-dependent pathway. Kidney Int. 2010; 77:861–869. PMID: 20164825.
Article23. Wallace KB. Doxorubicin-induced cardiac mitochondrionopathy. Pharmacol Toxicol. 2003; 93:105–115. PMID: 12969434.
Article24. Biroccio A, Benassi B, Amodei S, Gabellini C, Del Bufalo D, Zupi G. c-Myc down-regulation increases susceptibility to cisplatin through reactive oxygen species-mediated apoptosis in M14 human melanoma cells. Mol Pharmacol. 2010; 60:174–182. PMID: 11408612.
Article25. Miyajima A, Nakashima J, Yoshioka K, Tachibana M, Tazaki H, Murai M. Role of reactive oxygen species in cis-dichlorodiammineplatinum-induced cytotoxicity on bladder cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 1997; 76:206–210. PMID: 9231920.
Article26. Kruidering M, Van de Water B, de Heer E, Mulder GJ, Nagelkerke JF. Cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in porcine proximal tubular cells: mitochondrial dysfunction by inhibition of complexes I to IV of the respiratory chain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997; 280:638–649. PMID: 9023274.27. Masuda H, Tanaka T, Takahama U. Cisplatin generates superoxide anion by interaction with DNA in a cell-free system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994; 203:1175–1180. PMID: 8093036.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cisplatin-Induced Apoptosis by Cisplatin in Human Glioblastoma Cell Line
- Role of Annexin A5 on Mitochondria-Dependent Apoptosis Induced by Tetramethoxystilbene in Human Breast Cancer Cells
- Activation of NF-kappa B in the cisplatin-induced apoptosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma
- Schisandrin C Protects YD-38 Cells from Cisplatin-induced Cell Death by Inhibiting Cytochrome c Release from Mitochondria
- Underlying Mechanism of Cisplatin-induced Apoptosis in PC-12 Cells