J Dent Rehabil Appl Sci.
2016 Dec;32(4):345-350. 10.14368/jdras.2016.32.4.345.
Application of ARCUS digma I, II systems for full mouth reconstruction: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, School of Dentistry, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Republic of Korea. upgradepc@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2369076
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14368/jdras.2016.32.4.345
Abstract
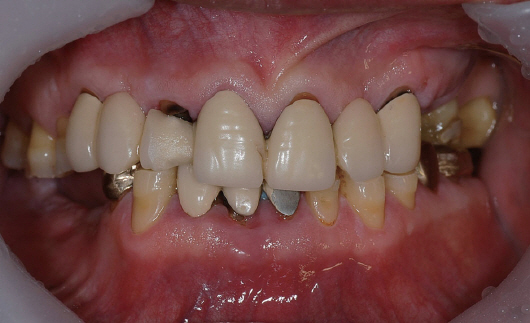
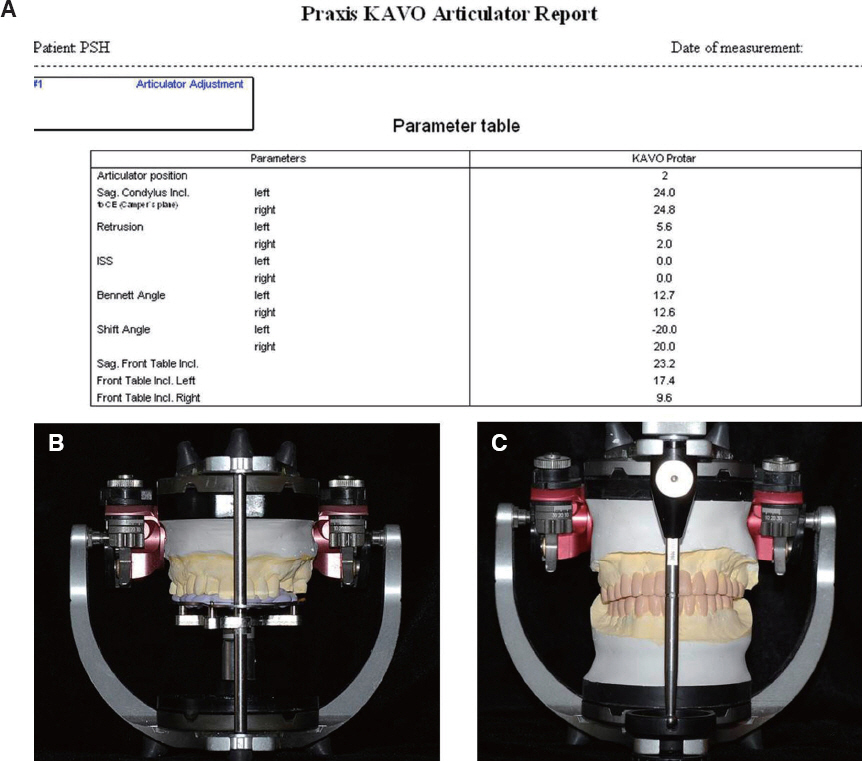
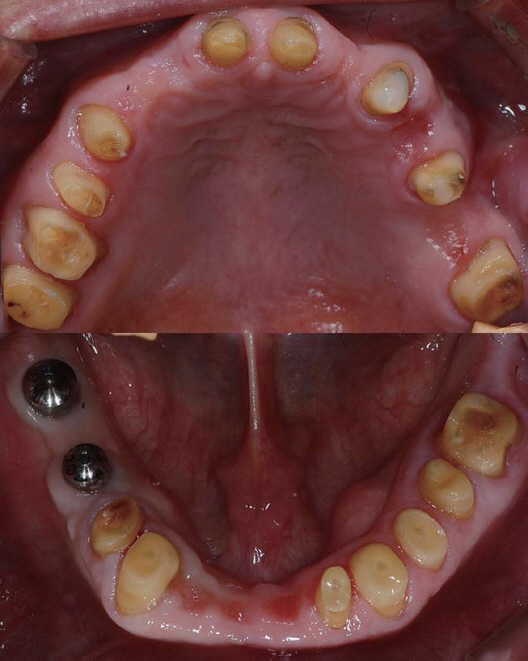
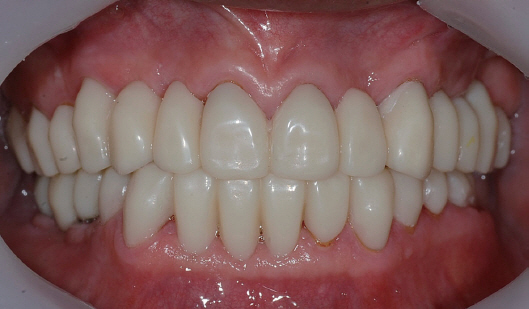
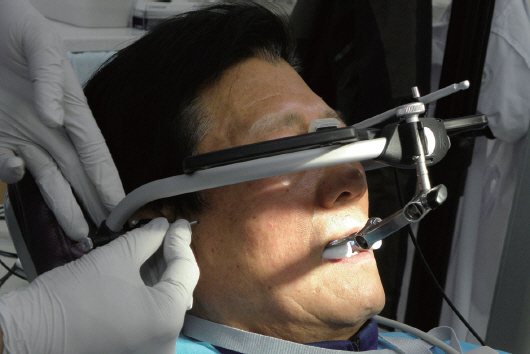
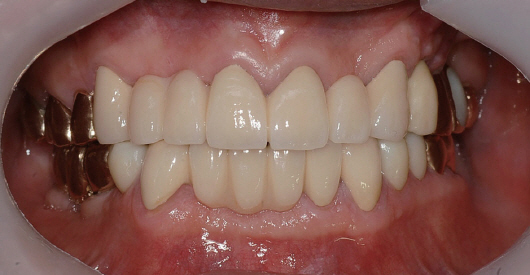
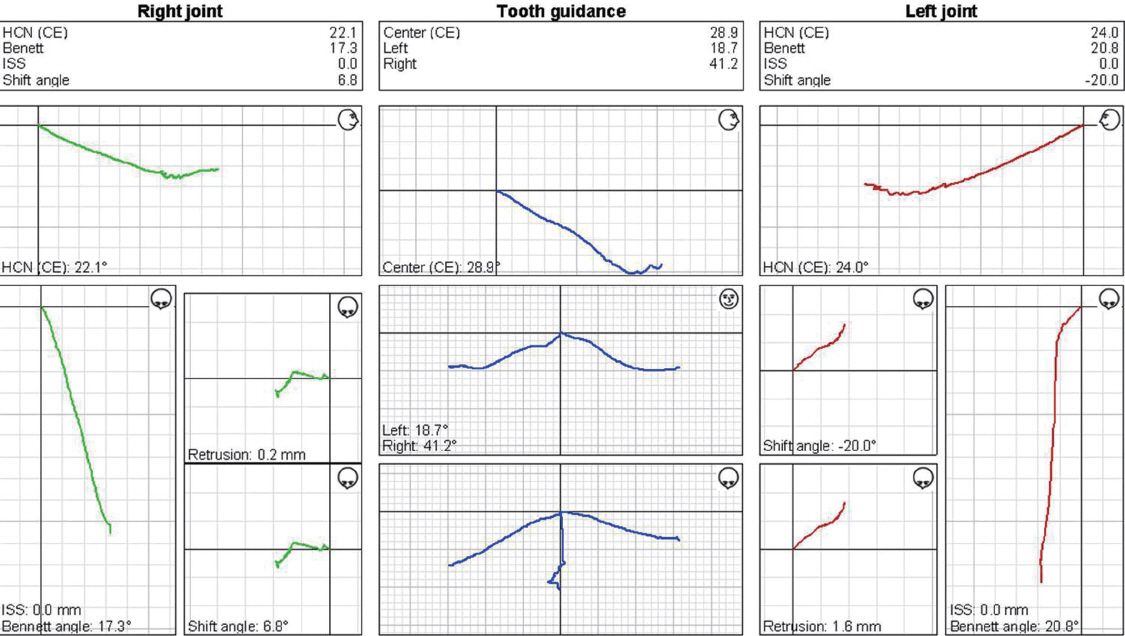
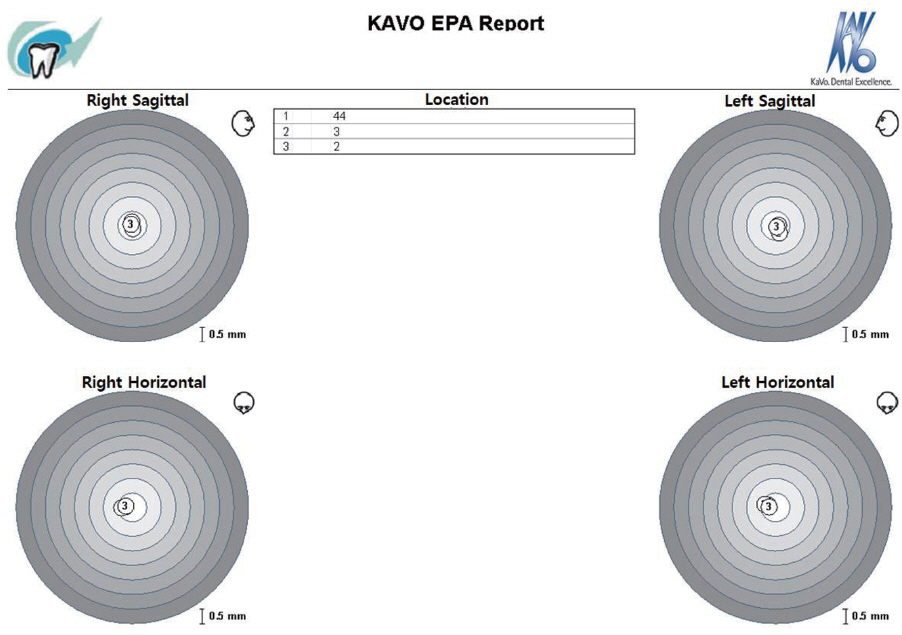
- Transferring condylar and anterior guidance on an articulator is essential to the diagnosis of a patient for full mouth reconstruction. In this clinical report, ARCUS digma I system was used to measure inherent condylar guidance of a patient requiring full mouth reconstruction in preoperate treatment, and the patients was given provisional restoration based on a functional anterior guidance. Then, ARCUS digma II system was used to mount the final casting model on an articulator, and the definitive prosthesis was placed in the patient. An esthetic and functionally proper clinical result regarding inherent condylar path of the patient was observed, and results from comparison of the two systems are given in this case.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Mullick SC, Stackhouse JA Jr, Vincent GR. A study of interocclusal record materials. J Prosthet Dent. 1981; 46:304–7. DOI: 10.1016/0022-3913(81)90219-5.2. Adrien P, Schouver J. Methods for minimizing the errors in madibular model mounting on an articulator. J Oral Rehabil. 1997; 24:929–35. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2842.1997.00564.x. PMID: 9467996.3. Craddock FW. The accuracy and practical value records of condyle path inclination. J Am Dent Assoc. 1949; 38:697–710. DOI: 10.14219/jada.archive.1949.0066. PMID: 18150040.4. Olsson A, Posselt U. Relationship of various skull reference lines. J Prosthet Dent. 1961; 11:1045–9. DOI: 10.1016/0022-3913(61)90041-5.5. El-Gheriani AS, Winstanley RB. Graphic tracings of condylar paths and measurements of condylar angles. J Prosthet Dent. 1989; 61:77–87. DOI: 10.1016/0022-3913(89)90113-3.6. dos Santos J Jr, Nelson S, Nowlin T. Comparison of condylar guidance setting obtained from a wax record versus an extraoral tracing: a pilot study. J Prosthet Dent. 2003; 89:54–9. DOI: 10.1067/mpr.2003.11. PMID: 12589287.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Implant treatment on anterior cross-bite of a patient who had orthognathic surgery 20 years ago
- Reconstruction of the corners of the mouth in burn-induced microstomia: A case report
- A full-mouth rehabilitation using zirconia all-ceramic crowns: a case report
- Full mouth rehabilitation in a patient with peri-implantitis: A case report
- Full mounth rehabilitation using OP finder ® system for patient with inadequate occlusal plane and multiple occlusal wear tooth state: a case report