J Korean Acad Oral Health.
2016 Dec;40(4):277-284. 10.11149/jkaoh.2016.40.4.277.
Effects of full problem based learning of dental students on self-directed learning, communication, and problem solving abilities
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Preventive & Community Dentistry, Chonbuk National University Dental School, Jeonju, Korea. prevdent@chonbuk.ac.kr
- 2Institute of Oral-bio Science, Chonbuk National University Dental School, Jeonju, Korea.
- KMID: 2366495
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11149/jkaoh.2016.40.4.277
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
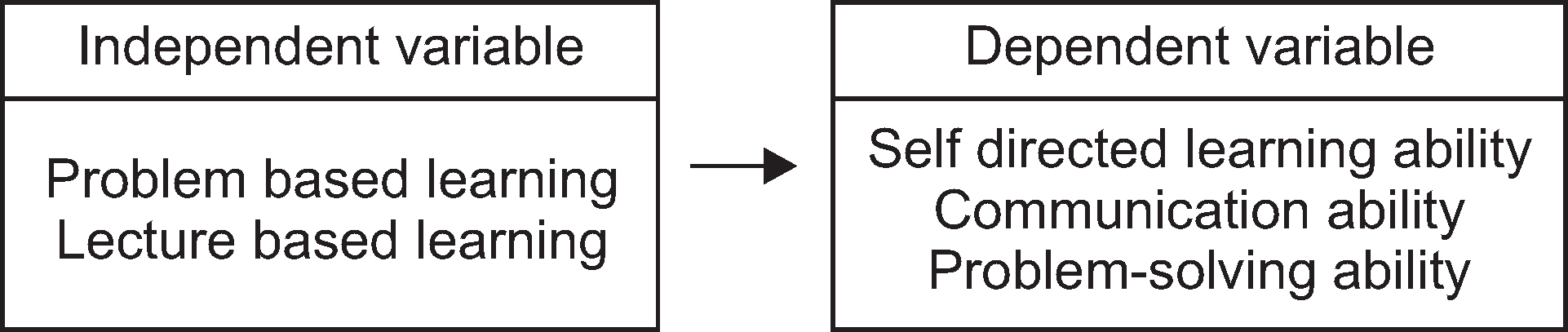
The purpose of this study was to examine the effect of problem-based learning (PBL) on dental education to dental students. The following were investigated in this study: 1. Does PBL improve the ability of self-directed learning? 2. Does PBL change communication ability? 3. Does PBL change the strategy of problem solving?
METHODS
The participants of this study were 39 students in the experimental group and 68 students in the control group. The measurement tools of this study were self-directed learning, communication, and problem solving abilities tests designed by the Korean Educational Development Institute. The data was analyzed by the two-way ANOVA and ANOVA with repeated measures.
RESULTS
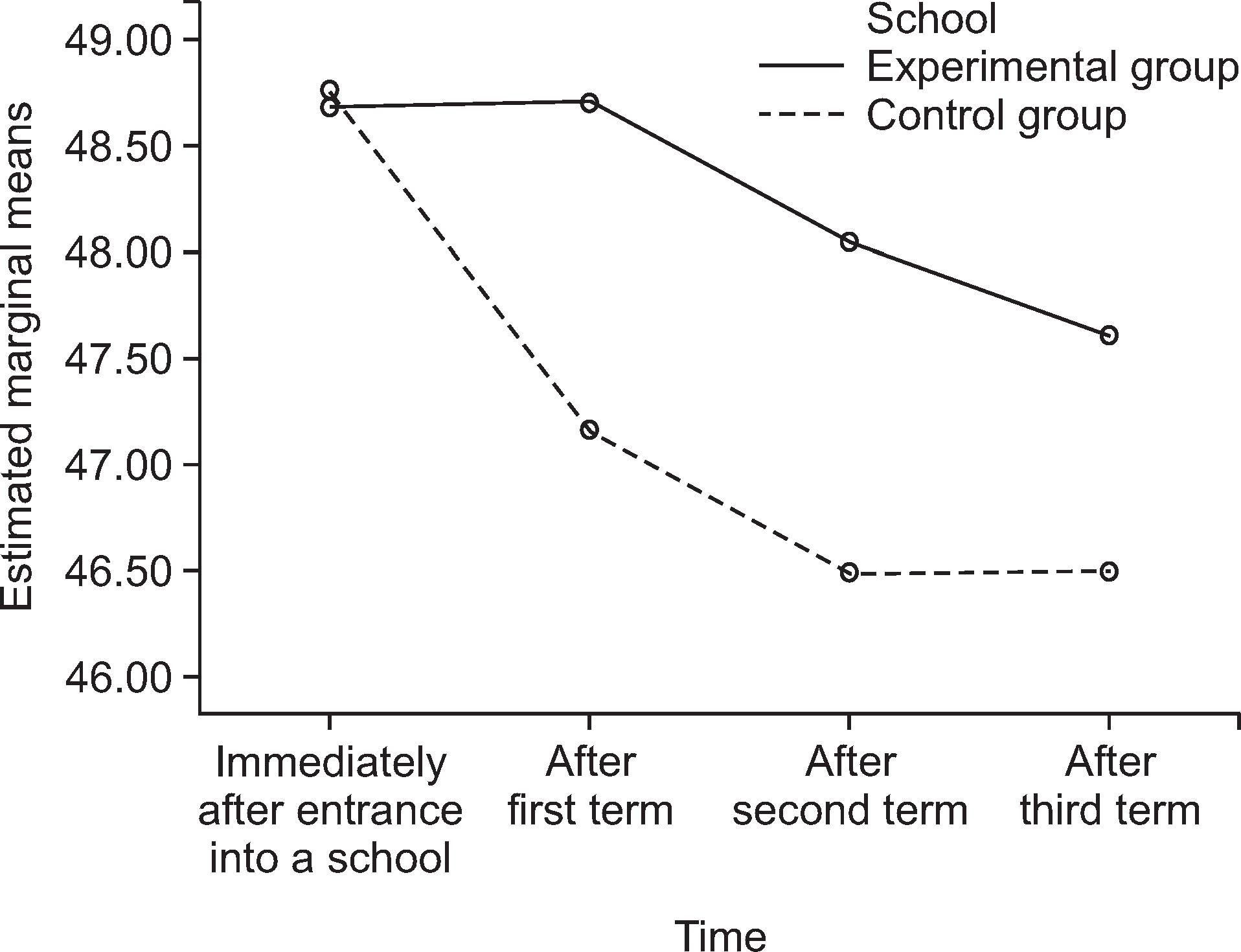
In self-directed learning ability during 3 semesters, the experimental group showed a U-shape change but the control group showed a reverse U-shape change. In the experimental group, the self-directed learning ability was decreased after one year (after the first and second semester). The level of communication ability decreased every day during the three semesters monitored in both the control and experimental groups. The level of communication ability in the experimental group continuously decreased during the three semesters, with the exception of one semester. Finally, for the problem solving ability during the three semesters, the experimental group showed a reverse U-shape change while the control group showed a U-shape change. In the experimental group, there was no change after two semesters.
CONCLUSIONS
On the basis of the findings in this study, the following conclusions can be made. First, problem-based learning has a positive educational effect compared to didactic-based learning within one year. Second, the appropriate length of PBL is two semesters, or one year. It could be recommended that dental education in Korea should be combined or hybridized with PBL; for example, PBL could be used in combination with brief lectures or block lectures by teachers.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Cho YS. Theory and reality of PBL. Seoul: Hakjisa;2006. p. 117–282.2. Hwang YY, Park CS, Chu MS. Correlations among meta cognition, critical thinking and self-efficacy of nursing students studying through problem based learning. J Korean Acad Community Health Nursing. 2007; 18:146–154.3. Choi HJ. The effects of PBL(Problem-Based Learning) on the meta-cognition, critical thinking, and problem solving process of nursing students. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2004; 34:712–721.
Article4. Bae YS, Lee SH, Kim MH, Sun KS. Effects of PBL(Problem-Based Learning) on self-directed learning and critical thinking disposition of nursing students. J Korean acad society of nursing education. 2005; 11:184–190.5. Lee SH, Kim MH, Sun GS. The clinical competence and related factors of the nursing students: focused on the subjects who studied problem-based learning. J Korean Adult Nursing. 2007; 19:753–762.6. Jeon SY, Song JK. Introduction to problem based learning. Korean J Med Educ. 1995; 6:84–87.
Article7. Kim YI, Kim JJ, Choi KY, Kim CW, Kim WH, Chnag JJ, et al. Application of the revised case matrix format to tutorial in pathology teaching: an interim approach toward problem-based learning under traditional curricular structure. J Korean Acad of Pathology. 1996; 30:653–661.8. Rho YH, Kim KS, Park HS, Kim KS, Bae KM, Ahn EH, et al. Three kinds of problem-based learning formulas experienced in Konkuk university college of medicine. Korean J Med Educ. 2000; 12:191–205.
Article9. Jung W, Cho HJ, Kim SC, Choi HS, Hong HP, Kim MC, et al. Pilot study of web-based PBL in emergency medicine clinical education. J Korean Society of Emergency Medicine. 2006; 17:203–209.10. Katoh M, Ohtsu F, Nagmatsu T, Nadai M. Development of new problem-based learning to promote problem-solving ability in therapeutics at Meijo University. Yakugaku Zasshi-J of The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan. 2010; 130:1655–1661.
Article11. Kim HA, Kim KK, Lee SW. A comparison of effect of lecture-based learning and problem-based learning on scientific reasoning in basic medicine. J Korean Acad of Oral Medicine. 2005; 30:35–44.12. Barrows HS, Pickell GC. Developing clinical problem solving skills: a guide to more effective diagnosis and treatment. New York: Norton;1991. p. 103–124.13. Eggen PD, Kauchak DP. Strategies for teacher: teaching content and thinking skills. Needham Height, MA: Allyn and Bacon;2001. Chapter7.14. Barrows HS, Tamblyn RM. Problem-based learning: an approach to medical education. New York: Springer;1980. p. 71–90.15. Park EH, Park JH, Park YN. The experience of problem-based learning in Keimyung university college of medicine. Korean J Med Educ. 2000; 12:261–270.
Article16. Lohman MC, Finkelstein M. Designing groups in problem-based learning to promote problem-solving skill and self-directedness. Instructional Science. 2000; 28:291–307.17. Ustun B. Communication skills training as part of a problem-based learning curriculum. J of Nursing Education. 2006; 45:421–424.18. Acar BS, Newman IA. Students as tutors-learning problem-solving skills by tutoring PBL. Int J Engng Ed. 2003; 19:712–716.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effects of Jigsaw Cooperation Learning on Communication Ability, Problem Solving Ability, Critical Thinking Disposition, Self-directed Learning Ability and Cooperation of Nursing Students
- Factors Influencing Problem Solving Abilities of Freshmen Nursing Students
- The Relationship between Metacognition, Learning Flow, and Problem-Solving Ability of Dental Hygiene Students
- Effects of Problem-Based Learning Combined with Simulation on the Basic Nursing Competency of Nursing Students
- The Effects of PBL (Problem-Based Learning) on the Self-Directed Learning, Critical Thinking Disposition, and Problem Solving Process of Nursing Students