Yonsei Med J.
2015 Jul;56(4):1128-1133. 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.4.1128.
Predicted EC50 and EC95 of Remifentanil for Smooth Removal of a Laryngeal Mask Airway Under Propofol Anesthesia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. kjyeop@ajou.ac.kr
- 2Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Gachon University, Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2366357
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2015.56.4.1128
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to determine the effect-site concentration (Ce) of remifentanil in 50% of patients (EC50) and 95% of patients (EC95) for smooth laryngeal mask airway (LMA) removal in adults under propofol and remifentanil anesthesia.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
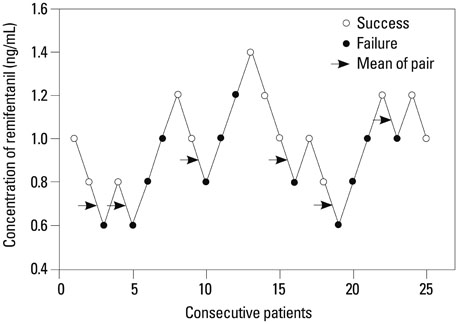
Twenty-five patients of ASA physical status I-II and ages 18-60 years who were to undergo minor gynecological or orthopedic surgery were assessed in this study. Anesthesia was induced and maintained with propofol and remifentanil target-controlled infusion (TCI). Remifentanil was maintained at a predetermined Ce during the emergence period. The modified Dixon's up-and-down method was used to determine the remifentanil concentration, starting from 1.0 ng/mL (step size of 0.2 ng/mL). Successful removal of the LMA was regarded as absence of coughing/gagging, clenched teeth, gross purposeful movements, breath holding, laryngospasm, or desaturation to SpO2<90%.
RESULTS
The mean+/-SD Ce of remifentanil for smooth LMA removal after propofol anesthesia was 0.83+/-0.16 ng/mL. Using isotonic regression with a bootstrapping approach, the estimated EC50 and EC95 of remifentanil Ce were 0.91 ng/mL [95% confidence interval (CI), 0.77-1.07 ng/mL] and 1.35 ng/mL (95% CI, 1.16-1.38 ng/mL), respectively.
CONCLUSION
Our results showed that remifentanil TCI at an established Ce is a reliable technique for achieving safe and smooth emergence without coughing, laryngospasm, or other airway reflexes.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Adult
Analgesics, Opioid/*administration & dosage
Anesthetics, Inhalation/*administration & dosage
Cough/prevention & control
Device Removal
Dose-Response Relationship, Drug
Female
Gynecologic Surgical Procedures
Humans
*Laryngeal Masks
Male
Middle Aged
Orthopedic Procedures
Piperidines/*administration & dosage
Propofol/*administration & dosage
Treatment Outcome
Young Adult
Analgesics, Opioid
Anesthetics, Inhalation
Piperidines
Propofol
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gataure PS, Latto IP, Rust S. Complications associated with removal of the laryngeal mask airway: a comparison of removal in deeply anaesthetised versus awake patients. Can J Anaesth. 1995; 42:1113–1116.
Article2. Pappas AL, Sukhani R, Lurie J, Pawlowski J, Sawicki K, Corsino A. Severity of airway hyperreactivity associated with laryngeal mask airway removal: correlation with volatile anesthetic choice and depth of anesthesia. J Clin Anesth. 2001; 13:498–503.
Article3. Cameron AJ, Sellers WF. Early vs late LMA removal; risks to patients and damage to equipment. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2001; 29:80–81.4. Nunez J, Hughes J, Wareham K, Asai T. Timing of removal of the laryngeal mask airway. Anaesthesia. 1998; 53:126–130.
Article5. Baird MB, Mayor AH, Goodwin AP. Removal of the laryngeal mask airway: factors affecting the incidence of post-operative adverse respiratory events in 300 patients. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 1999; 16:251–256.
Article6. Aouad MT, Al-Alami AA, Nasr VG, Souki FG, Zbeidy RA, Siddik-Sayyid SM. The effect of low-dose remifentanil on responses to the endotracheal tube during emergence from general anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 2009; 108:1157–1160.
Article7. Chen J, Li W, Wang D, Hu X. The effect of remifentanil on cough suppression after endoscopic sinus surgery: a randomized study. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2010; 54:1197–1203.
Article8. Nho JS, Lee SY, Kang JM, Kim MC, Choi YK, Shin OY, et al. Effects of maintaining a remifentanil infusion on the recovery profiles during emergence from anaesthesia and tracheal extubation. Br J Anaesth. 2009; 103:817–821.
Article9. Ozkan D, Ergil J, Alptekin A, Aktürk N, Gümüs H. Target controlled remifentanil infusion for smooth laryngeal mask airway removal during emergence from desflurane-remifentanil anesthesia. J Anesth. 2012; 26:369–374.
Article10. Marsh B, White M, Morton N, Kenny GN. Pharmacokinetic model driven infusion of propofol in children. Br J Anaesth. 1991; 67:41–48.
Article11. Minto CF, Schnider TW, Egan TD, Youngs E, Lemmens HJ, Gambus PL, et al. Influence of age and gender on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of remifentanil. I. Model development. Anesthesiology. 1997; 86:10–23.
Article12. Dixon WJ. Staircase bioassay: the up-and-down method. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1991; 15:47–50.
Article13. Stylianou M, Flournoy N. Dose finding using the biased coin up-and-down design and isotonic regression. Biometrics. 2002; 58:171–177.
Article14. Pace NL, Stylianou MP. Advances in and limitations of up-and-down methodology: a précis of clinical use, study design, and dose estimation in anesthesia research. Anesthesiology. 2007; 107:144–152.15. Arain SR, Shankar H, Ebert TJ. Desflurane enhances reactivity during the use of the laryngeal mask airway. Anesthesiology. 2005; 103:495–499.
Article16. White PF, Tang J, Wender RH, Yumul R, Stokes OJ, Sloninsky A, et al. Desflurane versus sevoflurane for maintenance of outpatient anesthesia: the effect on early versus late recovery and perioperative coughing. Anesth Analg. 2009; 109:387–393.
Article17. Batra YK, Ivanova M, Ali SS, Shamsah M, Al Qattan AR, Belani KG. The efficacy of a subhypnotic dose of propofol in preventing laryngospasm following tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy in children. Paediatr Anaesth. 2005; 15:1094–1097.
Article18. Hohlrieder M, Tiefenthaler W, Klaus H, Gabl M, Kavakebi P, Keller C, et al. Effect of total intravenous anaesthesia and balanced anaesthesia on the frequency of coughing during emergence from the anaesthesia. Br J Anaesth. 2007; 99:587–591.
Article19. Abdi W, Amathieu R, Adhoum A, Poncelet C, Slavov V, Kamoun W, et al. Sparing the larynx during gynecological laparoscopy: a randomized trial comparing the LMA Supreme and the ETT. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2010; 54:141–146.
Article20. Cho HB, Kim JY, Kim DH, Kim DW, Chae YJ. Comparison of the optimal effect-site concentrations of remifentanil for preventing cough during emergence from desflurane or sevoflurane anaesthesia. J Int Med Res. 2012; 40:174–183.
Article21. Lee B, Lee JR, Na S. Targeting smooth emergence: the effect site concentration of remifentanil for preventing cough during emergence during propofol-remifentanil anaesthesia for thyroid surgery. Br J Anaesth. 2009; 102:775–778.
Article22. Chang CH, Lee JW, Choi JR, Shim YH. Effect-site concentration of remifentanil to prevent cough after laryngomicrosurgery. Laryngoscope. 2013; 123:3105–3109.
Article23. Hoymork SC, Raeder J. Why do women wake up faster than men from propofol anaesthesia? Br J Anaesth. 2005; 95:627–633.
Article24. Hans P, Marechal H, Bonhomme V. Effect of propofol and sevoflurane on coughing in smokers and non-smokers awakening from general anaesthesia at the end of a cervical spine surgery. Br J Anaesth. 2008; 101:731–737.
Article25. Bouillon TW, Bruhn J, Radulescu L, Andresen C, Shafer TJ, Cohane C, et al. Pharmacodynamic interaction between propofol and remifentanil regarding hypnosis, tolerance of laryngoscopy, bispectral index, and electroencephalographic approximate entropy. Anesthesiology. 2004; 100:1353–1372.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Predicted Effect-site Concentration of Remifentanil for Facilitating Laryngeal Mask Airway Insertion with Propofol Target-Controlled Infusion
- EC50 of remifentanil to prevent pain during injection of microemulsion propofol
- Remifentanil dose for laryngeal mask airway insertion with a single standard dose of propofol during emergency airway management in elderly patients
- Comparative Effects of Laryngeal Mask Airway Removal and Tracheal Extubation on Intraocular Pressure during Emergence from Propofol Anesthesia
- Median Effective Concentration (EC(50)) of Propofol for Insertion of Laryngeal Mask Airway and Laryngeal Tube in Children