J Dent Anesth Pain Med.
2016 Dec;16(4):313-316. 10.17245/jdapm.2016.16.4.313.
Perioperative airway management of a patient with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dental Anesthesiology, Kyushu University Hospital, Fukuoka, Japan. tsukamoto@dent.kyushu-u.ac.jp
- 2Department of Dental Anesthesiology, Faculty of Dental Science, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan.
- KMID: 2366161
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2016.16.4.313
Abstract
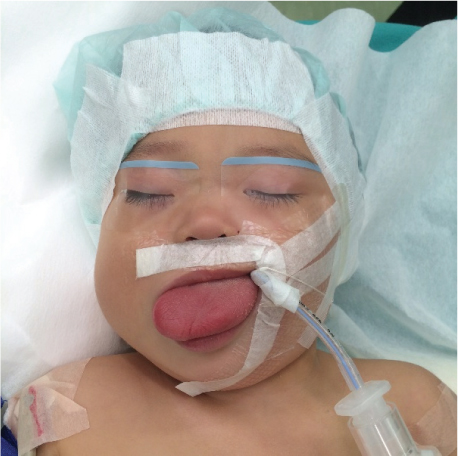
- Airway obstruction in pediatric patients always poses a challenge for anesthesiologists. Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome causes various abnormalities such as macroglossia and omphalocele. Patients with these abnormalities often need corrective surgeries. Management of difficult airway caused by conditions such as macroglossia in patients with this syndrome could be challenging. We encountered a case of difficult airway in an infant with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. It was predicted that macroglossia might cause difficult ventilation, intubation, and extubation. Preoperative assessment and preparations for difficult airway should be considered.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim Y, Shibutani T, Hirota Y, Mahbub SF, Matsuura H. Anesthetic considerations of two sisters with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. Anesth Prog. 1996; 43:24–28.2. Tobias JD, Lowe S, Holcomb GW 3rd. Anesthetic considerations of an infant with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. J Clin Anesth. 1992; 4:484–486.
Article3. Batra M, Valecha UK. Anesthetic management of tongue reduction in a case of Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2014; 30:562–564.
Article4. Suan C, Ojeda R, García-Perla JL, Pérez-Torres MC. Anaesthesia and the Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. Paediatr Anaesth. 1996; 6:231–233.
Article5. Celiker V, Basgul E, Karagoz AH. Anesthesia in Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. Paediatr Anaesth. 2004; 14:778–780.
Article6. Channabasapa SM, Pradeep SH, Dharmapa S, Sarji D. Anesthetic management of a neonate with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome posted for repair of exomphalos. Saudi J Anaesth. 2016; 10:249–250.
Article7. Kimura Y, Kamada Y, Kimura S. Anesthetic management of two cases of Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. J Anesth. 2008; 22:93–95.
Article8. Gurkowski MA, Rasch DK. Anesthetic considerations for Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. Anesthesiology. 1989; 70:711–712.
Article9. Greenspun JC, Hannallah RS, Welborn LG, Norden JM. Comparison of sevoflurane and halothane anesthesia in children undergoing outpatient ear, nose, and throat surgery. J Clin Anesth. 1995; 7:398–402.
Article10. Okutani R, Arima Y, Oda Y. Anesthetic management in a child with Rolland-Desbuquois type dyssegmental dysplasia. J Clin Anesth. 2014; 26:676–678.
Article11. Priebe HJ. Should anesthesiologists have to confirm effective facemask ventilation before administering the muscle relaxant? J Anesth. 2016; 30:132–137.
Article12. Kadouch DJ, Maas SM, Dubois L, van der Horst CM. Surgical treatment of macroglossia in patients with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome: a 20-year experience and review of the literature. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012; 41:300–308.
Article13. Kittur MA, Padgett J, Drake D. Management of macroglossia in Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013; 51:6–8.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Anesthetic management of children with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome : Two cases report
- A Case of Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome
- Beckwith-Wiedemann Sydrome with Left Adrenal Cortical Neoplasm
- Testicular Yolk Sac Tumor in Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome
- Mesenchymal Hamartoma of the Liver in Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome: A Case Report