J Dent Anesth Pain Med.
2016 Dec;16(4):245-252. 10.17245/jdapm.2016.16.4.245.
Regional anesthesia for maxillofacial surgery in developing countries
- Affiliations
-
- 1Oral and Maxillofacial Microvascular Reconstruction LAB, Brong Ahafo Regional Hospital, Sunyani, Ghana.
- 2Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Dental Research Institute, School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. leejongh@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2366152
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2016.16.4.245
Abstract
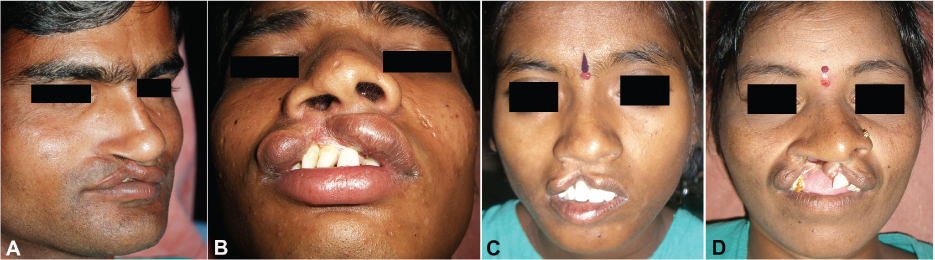
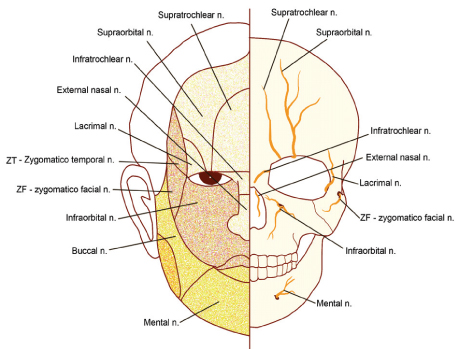
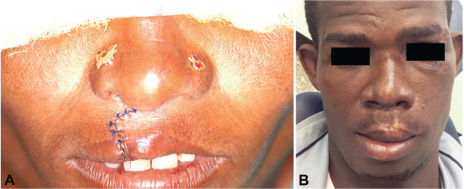
- Regional anesthesia in the maxillofacial region is safer and more efficient than general anesthesia when its indications are carefully considered. In addition, the majority of medical institutions in developing countries are not well equipped for proper anesthesia and elective surgery. In this review, we describe regional anesthesia and cutaneous nerve divisions in the maxillofacial region. In addition, we summarize detailed regional anesthetic techniques adapted for representative cleft lip cases in developing countries.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Moskovitz JB, Sabatino F. Regional nerve blocks of the face. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2013; 31:517–527.
Article2. Mosby Inc. Mosby's Medical Dictionary. 8th ed. Mosby/Elsevier;2009.
Article3. Bedforth NM, Chambers WA, Checketts MR, Colvin LA, Connolly C, Croner GA, et al. McLeod GA, McCartney CJL, Wildsmith JAW, editors. Principles and practice of regional anaesthesia. 4th ed. Oxford: Oxford University Press;2012.
Article4. Nussbaum RL, McInnes RR, Willard HF. Thompson & Thompson Genetics in Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders;2007.
Article5. Rajamani A, Kamat V, Rajavel VP, Murthy J, Hussain SA. A comparison of bilateral infraorbital nerve block with intravenous fentanyl for analgesia following cleft lip repair in children. Paediatr Anaesth. 2007; 17:133–139.
Article6. Weinand FS, Pavlovic S, Dick B. Endophthalmitis after inraoral block of the infraorbital nerve. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 1997; 210:402–404.
Article7. Gray H. Lewis WH, editor. Anatomy of the Human Body. 20th ed. Lea & Febiger;2007.8. Kretzschmar JL, Peters JE. Nerve blocks for regional anesthesia of the face. Am Fam Physician. 1997; 55:1701–1704.9. Smith DW, Peterson MR, DeBerard SC. Regional anesthesia. Nerve blocks of the extremities and face. Postgrad Med. 1999; 106:69–73. 77–78.
Article10. Hodges SC, Hodges AM. A protocol for safe anesthesia for cleft lip and palate surgery in developing countries. Anaesthesia. 2000; 55:436–441.
Article11. Prabhu KP, Wig J, Grewal S. Bilateral infraorbital nerve block is superior to peri-incisional infiltration for analgesia after repair of cleft lip. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg. 1997; 33:83–87.12. Ahuja S, Datta A, Krishna A, Bhattacharya A. Infra-orbital nerve blocks for relief of postoperative pain following cleft lip surgery in infants. Anaesthesia. 1994; 49:441–444.13. Mayer MN, Bennaceur S, Barrier G, Couly G. Infraorbital block in early primary cheiloplasty. Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac. 1997; 98:246–247.
Article14. Simion C, Corcoran J, Iyer A, Suresh S. Postoperative pain control for primary cleft lip repair in infants: is there and advantage in performing peripheral nerve blocks? Paediatr Anaesth. 2008; 18:1060–1065.
Article15. Aggarwal A, Kaur H, Gupta T, Tubbs RS, Sahni D, Batra YK, et al. Anatomical study of the infraorbital foramen: a basis for successful infraorbital nerve block. Clin Anat. 2015; 28:753–760.
Article16. Eipe N, Choudhrie A, Pillai AD, Choudhrie R. Regional anesthesia for cleft lip repair: a preliminary study. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2006; 43:138–141.
Article17. Chiono J, Raux O, Bringuier S, Sola C, Biqorre M, Capdevila X, et al. Bilateral suprazygomatic maxillary nerve block for cleft palate repair in children: a prospective, randomized, double-blind study versus placebo. Anesthesiology. 2014; 120:1362–1369.
Article18. Sola C, Raux O, Savath L, Macq C, Capdevila X, Daeure C. Ultrasound guidance characteristics and efficiency of suprazygomatic maxillary nerve blocks in infants: a descriptive prospective study. Paediatr Anaesth. 2012; 22:841–846.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A working paradigm for managing mandibular fractures under regional anesthesia
- Dracunculiasis in oral and maxillofacial surgery
- Comparison of the Frequency of Postoperative Delirium in Elderly between General Anesthesia and Regional Anesthesia
- Caring Behaviors and Anxiety during Surgery among Patients Undergoing Surgery with Regional Anesthesia
- A Clinical Study about Comparison of Inhalation Anesthesia and Intravenous Anesthesia in Oral and Maxillofacial Patients