J Clin Neurol.
2016 Jan;12(1):79-84. 10.3988/jcn.2016.12.1.79.
Safety and Efficacy of Cerebrolysin in Infants with Communication Defects due to Severe Perinatal Brain Insult: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
- Affiliations
-
- 1Pediatric Department, Children's Hospital, Faculty of Medicine, Ain Shams University, Abassia square, Cairo, Egypt. saharhassanein@med.asu.edu.eg
- 2Community Medicine Department, Faculty of Medicine, Ain Shams University, Abassia square, Cairo, Egypt.
- 3Clinical Pharmacology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University, Dakahlia, Egypt.
- KMID: 2364923
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2016.12.1.79
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
The neuroregenerative drug Cerebrolysin has demonstrated efficacy in improving cognition in adults with stroke and Alzheimer's disease. The aim of this study was to determine the efficacy and safety of Cerebrolysin in the treatment of communication defects in infants with severe perinatal brain insult.
METHODS
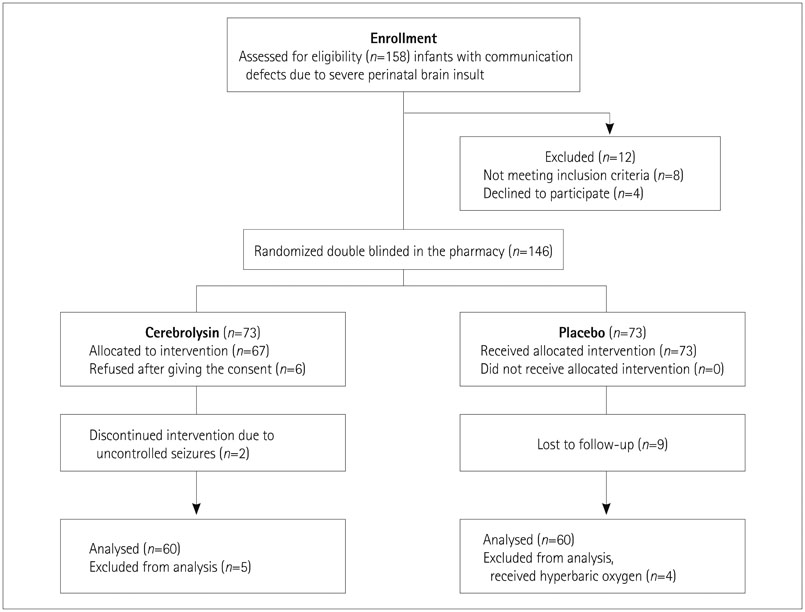
A randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial was conducted in which 158 infants (age 6-21 months) with communication defects due to severe perinatal brain insult were enrolled; 120 infants completed the study. The Cerebrolysin group (n=60) received twice-weekly Cerebrolysin injections of 0.1 mL/kg body weight for 5 weeks (total of ten injections). The placebo group (n=60) received the same amount and number of normal saline injections.
RESULTS
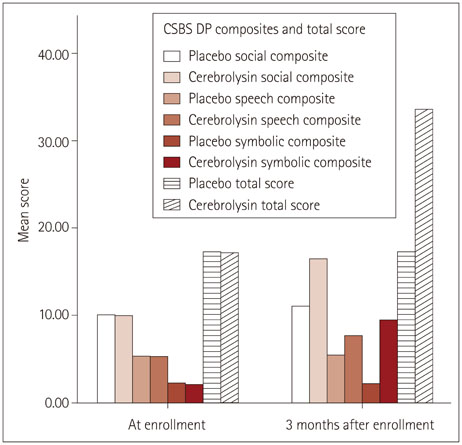
The baseline Communication and Symbolic-Behavior-Scale-Developmental Profile scores were comparable between the two groups. After 3 months, the placebo group exhibited improvements in the social (p<0.01) and speech composite (p=0.02) scores, with 10% and 1.5% increases from baseline, respectively. The scores of the Cerebrolysin group changed from concern to no concern, with increases of 65.44%, 45.54%, 358.06%, and 96.00% from baseline in the social (p<0.001), speech (p<0.001), symbolic (p<0.001), and total (p<0.001) scores.
CONCLUSIONS
Cerebrolysin dramatically improved infants' communication especially symbolic behavior which positively affected social interaction. These findings suggest that cerebrolysin may be an effective and feasible way equivalent to stem cell therapy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Human Umbilical Cord Blood CD34-Positive Cells as Predictors of the Incidence and Short-Term Outcome of Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy: A Pilot Study
Sahar M. A. Hassanein, Mohamed Hassan Nasr Eldin, Hanaa A. Amer, Adel E. Abdelhamid, Moustafa El Houssinie, Abir Ibrahim
J Clin Neurol. 2017;13(1):84-90. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2017.13.1.84.
Reference
-
1. Vannucci RC, Perlman JM. Interventions for perinatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatrics. 1997; 100:1004–1014.
Article2. Adamson SJ, Alessandri LM, Badawi N, Burton PR, Pemberton PJ, Stanley F. Predictors of neonatal encephalopathy in full-term infants. BMJ. 1995; 311:598–602.
Article3. Johnston MV, Fatemi A, Wilson MA, Northington F. Treatment advances in neonatal neuroprotection and neurointensive care. Lancet Neurol. 2011; 10:372–382.
Article4. El Shimi MS, Awad HA, Hassanein SM, Gad GI, Imam SS, Shaaban HA, et al. Single dose recombinant erythropoietin versus moderate hypothermia for neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy in low resource settings. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2014; 27:1295–1300.
Article5. Nordberg A, Miniscalco C, Lohmander A, Himmelmann K. Speech problems affect more than one in two children with cerebral palsy: Swedish population-based study. Acta Paediatr. 2013; 102:161–166.
Article6. Bhatia M, Joseph B. Rehabilitation of cerebral palsy in a developing country: the need for comprehensive assessment. Pediatr Rehabil. 2000; 4:83–86.
Article7. Guekht AB, Moessler H, Novak PH, Gusev EI. Cerebrolysin Investigators. Cerebrolysin in vascular dementia: improvement of clinical outcome in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled multicenter trial. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2011; 20:310–318.
Article8. Alvarez XA, Cacabelos R, Laredo M, Couceiro V, Sampedro C, Varela M, et al. A 24-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of three dosages of Cerebrolysin in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease. Eur J Neurol. 2006; 13:43–54.
Article9. Chen H, Tung YC, Li B, Iqbal K, Grundke-Iqbal I. Trophic factors counteract elevated FGF-2-induced inhibition of adult neurogenesis. Neurobiol Aging. 2007; 28:1148–1162.
Article10. Deigner HP, Haberkorn U, Kinscherf R. Apoptosis modulators in the therapy of neurodegenerative diseases. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2000; 9:747–764.
Article11. Rockenstein E, Mallory M, Mante M, Alford M, Windisch M, Moessler H, et al. Effects of Cerebrolysin on amyloid-beta deposition in a transgenic model of Alzheimer's disease. J Neural Transm Suppl. 2002; (62):327–336.
Article12. Rockenstein E, Adame A, Mante M, Moessler H, Windisch M, Masliah E. The neuroprotective effects of Cerebrolysin in a transgenic model of Alzheimer's disease are associated with improved behavioral performance. J Neural Transm. 2003; 110:1313–1327.
Article13. Zhang C, Chopp M, Cui Y, Wang L, Zhang R, Zhang L, et al. Cerebrolysin enhances neurogenesis in the ischemic brain and improves functional outcome after stroke. J Neurosci Res. 2010; 88:3275–3281.
Article14. Shankaran S, Laptook AR, Ehrenkranz RA, Tyson JE, McDonald SA, Donovan EF, et al. Whole-body hypothermia for neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. N Engl J Med. 2005; 353:1574–1584.
Article15. Wetherby AM, Prizant BM. CSBS DP manual: communication and symbolic behavior scales developmental profile. 1st ed. Baltimore: Paul H. Brookes;2002.16. Iznak AF, Iznak EV, Zavadenko NN, Guzilova LS. [Neurophysiological indices of the CNS plasticity in the course of treatment of craniocerebral trauma in adolescents]. Fiziol Cheloveka. 2008; 34:23–29.17. Wetherby AM, Allen L, Cleary J, Kublin K, Goldstein H. Validity and reliability of the communication and symbolic behavior scales developmental profile with very young children. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2002; 45:1202–1218.
Article18. McCathren RB, Yoder PJ, Warren SF. The relationship between prelinguistic vocalization and later expressive vocabulary in young children with developmental delay. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 1999; 42:915–924.
Article19. Watt N, Wetherby A, Shumway S. Prelinguistic predictors of language outcome at 3 years of age. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2006; 49:1224–1237.
Article20. Peeters M, Verhoeven L, de Moor J. Predictors of verbal working memory in children with cerebral palsy. Res Dev Disabil. 2009; 30:1502–1511.
Article21. Voorman JM, Dallmeijer AJ, Van Eck M, Schuengel C, Becher JG. Social functioning and communication in children with cerebral palsy: association with disease characteristics and personal and environmental factors. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2010; 52:441–447.
Article22. Ladurner G, Kalvach P, Moessler H. Cerebrolysin Study Group. Neuroprotective treatment with cerebrolysin in patients with acute stroke: a randomised controlled trial. J Neural Transm. 2005; 112:415–428.
Article23. Alvarez XA, Lombardi VR, Fernández-Novoa L, García M, Sampedro C, Cagiao A, et al. Cerebrolysin reduces microglial activation in vivo and in vitro: a potential mechanism of neuroprotection. J Neural Transm Suppl. 2000; 59:281–292.24. Birch AM, Kelly ÁM. Chronic intracerebroventricular infusion of nerve growth factor improves recognition memory in the rat. Neuropharmacology. 2013; 75:255–261.
Article25. Schauer E, Wronski R, Patockova J, Moessler H, Doppler E, Hutter-Paier B, et al. Neuroprotection of cerebrolysin in tissue culture models of brain ischemia: post lesion application indicates a wide therapeutic window. J Neural Transm. 2006; 113:855–868.
Article26. Alvarez XA, Cacabelos R, Sampedro C, Aleixandre M, Linares C, Granizo E, et al. Efficacy and safety of Cerebrolysin in moderate to moderately severe Alzheimer's disease: results of a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial investigating three dosages of Cerebrolysin. Eur J Neurol. 2011; 18:59–68.
Article27. Chen CC, Wei ST, Tsaia SC, Chen XX, Cho DY. Cerebrolysin enhances cognitive recovery of mild traumatic brain injury patients: double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized study. Br J Neurosurg. 2013; 27:803–807.
Article28. Gorbachevskaya N, Bashina V, Gratchev V, Iznak A. Cerebrolysin therapy in Rett syndrome: clinical and EEG mapping study. Brain Dev. 2001; 23:Suppl 1. S90–S93.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- MR findings of brain damage due to perinatal hypoxia
- Therapeutic Hypothermia for Perinatal Asphyxia
- Perinatal Hypoxic-lschemic Brain Injury: MR Findings
- Effects of Antenatal Exposure to Magnesium Sulfate on Neuroprotection in Preterm Infants
- Efficacy and safety of rapid intermittent bolus compared with slow continuous infusion in patients with severe hypernatremia (SALSA II trial): a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial