J Clin Neurol.
2016 Jan;12(1):65-74. 10.3988/jcn.2016.12.1.65.
Bilaterally Abnormal Head Impulse Tests Indicate a Large Cerebellopontine Angle Tumor
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biomedical Laboratory Science, Kyungdong University, Goseong, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. jisookim@snu.ac.kr
- 3Department of Otolaryngology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 4Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2364921
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2016.12.1.65
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
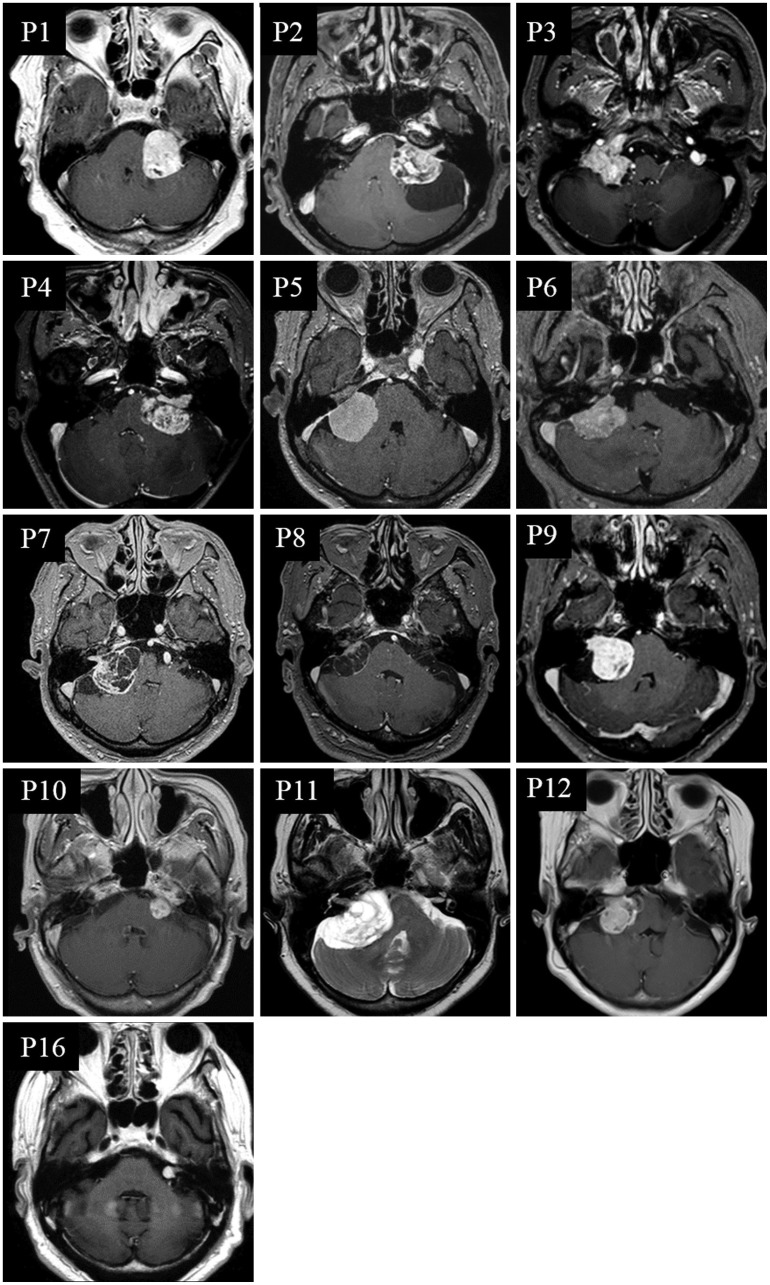
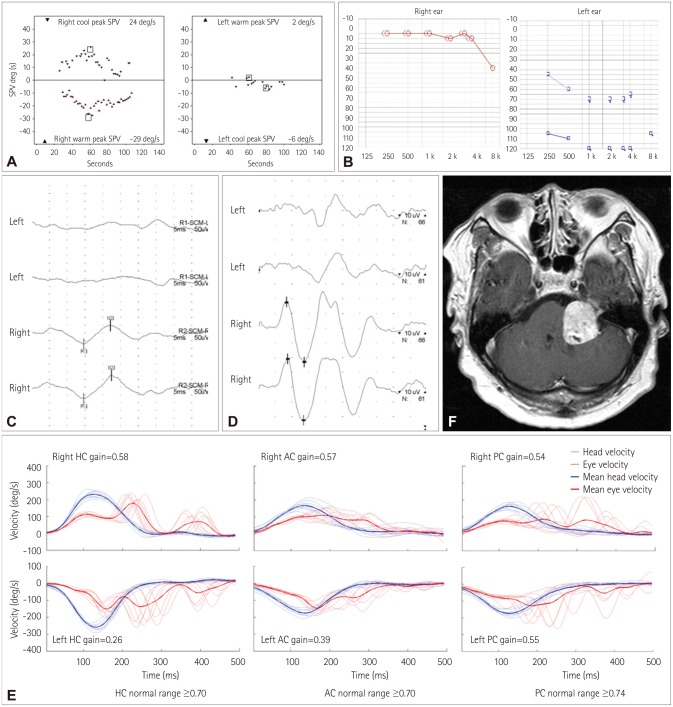
Tumors involving the cerebellopontine angle (CPA) pose a diagnostic challenge due to their diverse manifestations. Head impulse tests (HITs) have been used to evaluate vestibular function, but few studies have explored the head impulse gain of the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) in patients with a vestibular schwannoma. This study tested whether the head impulse gain of the VOR is an indicator of the size of a unilateral CPA tumor.
METHODS
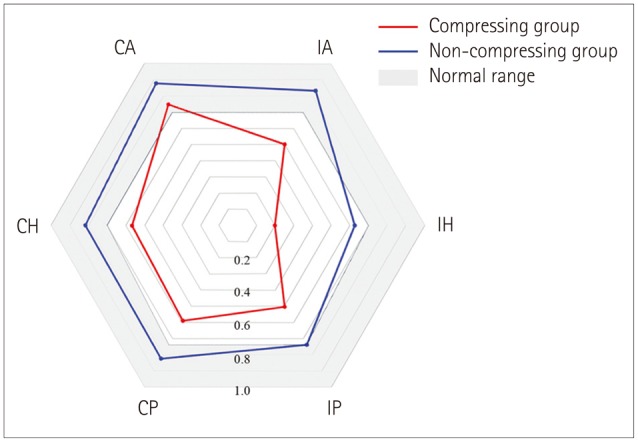
Twenty-eight patients (21 women; age=64+/-12 years, mean+/-SD) with a unilateral CPA tumor underwent a recording of the HITs using a magnetic search coil technique. Patients were classified into non-compressing (T1-T3) and compressing (T4) groups according to the Hannover classification.
RESULTS
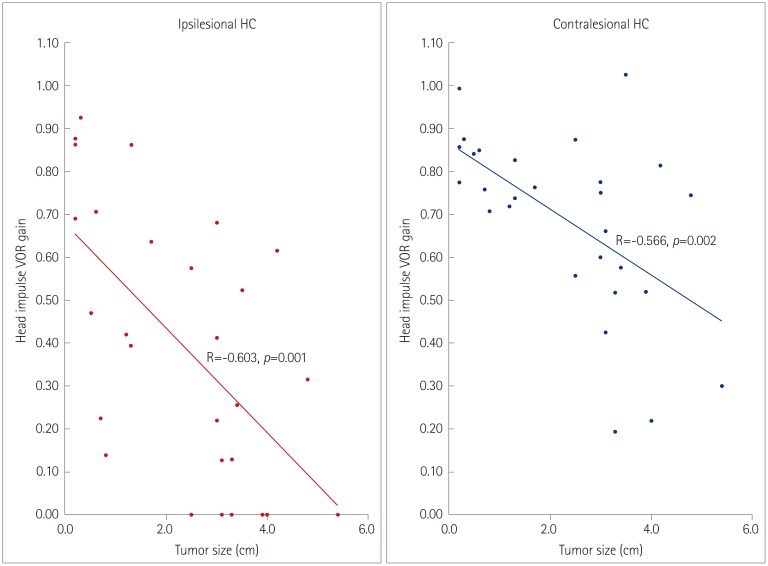
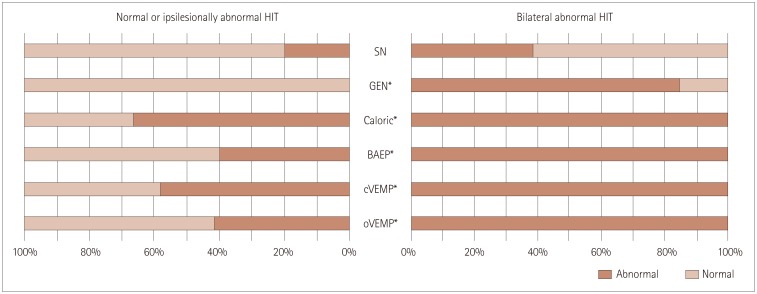
Most (23/28, 82%) of the patients showed abnormal HITs for the semicircular canals on the lesion side. The bilateral abnormality in HITs was more common in the compressing group than the non-compressing group (80% vs. 8%, Pearson's chi-square test: p<0.001). The tumor size was inversely correlated with the head impulse gain of the VOR in either direction.
CONCLUSIONS
Bilaterally abnormal HITs indicate that a patient has a large unilateral CPA tumor. The abnormal HITs in the contralesional direction may be explained either by adaptation or by compression and resultant dysfunction of the cerebellar and brainstem structures. The serial evaluation of HITs may provide information on tumor growth, and thereby reduce the number of costly brain scans required when following up patients with CPA tumors.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Normal Caloric Responses during Acute Phase of Vestibular Neuritis
Sun-Uk Lee, Seong-Ho Park, Hyo-Jung Kim, Ja-Won Koo, Ji-Soo Kim
J Clin Neurol. 2016;12(3):301-307. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2016.12.3.301.Relationship of Vertigo and Postural Instability in Patients With Vestibular Schwannoma
Gi-Sung Nam, Chan Min Jung, Ji Hyung Kim, Eun Jin Son
Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2018;11(2):102-108. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2017.01277.
Reference
-
1. Halmagyi GM, Curthoys IS. A clinical sign of canal paresis. Arch Neurol. 1988; 45:737–739. PMID: 3390028.
Article2. Jeong SH, Kim HJ, Kim JS. Vestibular neuritis. Semin Neurol. 2013; 33:185–194. PMID: 24057821.
Article3. Kattah JC, Talkad AV, Wang DZ, Hsieh YH, Newman-Toker DE. HINTS to diagnose stroke in the acute vestibular syndrome: three-step bedside oculomotor examination more sensitive than early MRI diffusion-weighted imaging. Stroke. 2009; 40:3504–3510. PMID: 19762709.5. Baek SH, Choi JY, Jung JM, Kwon do Y, Park MH, Choi J, et al. Abnormal head impulse test in a unilateral cerebellar lesion. J Clin Neurol. 2015; 11:279–282. PMID: 25749819.
Article6. Hitselberger WE. Tumors of the cerebellopontine angle in relation to vertigo. Arch Otolaryngol. 1967; 85:539–541. PMID: 5297882.
Article7. Lin C, Gong Q, Zuo W, Zhang R, Zhou A. The clinical characteristics and treatment for sudden sensorineural hearing loss with vestibular schwannoma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2015; 272:839–842. PMID: 24452772.
Article8. Choi KD, Kim JS, Kim HJ, Koo JW, Kim JH, Kim CY, et al. Hyperventilation-induced nystagmus in peripheral vestibulopathy and cerebellopontine angle tumor. Neurology. 2007; 69:1050–1059. PMID: 17785675.
Article9. Taylor RL, Kong J, Flanagan S, Pogson J, Croxson G, Pohl D, et al. Prevalence of vestibular dysfunction in patients with vestibular schwannoma using video head-impulses and vestibular-evoked potentials. J Neurol. 2015; 262:1228–1237. PMID: 25794859.
Article10. Newman-Toker DE, Kattah JC, Alvernia JE, Wang DZ. Normal head impulse test differentiates acute cerebellar strokes from vestibular neuritis. Neurology. 2008; 70(24 Pt 2):2378–2385. PMID: 18541870.
Article11. Newman-Toker DE, Saber Tehrani AS, Mantokoudis G, Pula JH, Guede CI, Kerber KA, et al. Quantitative video-oculography to help diagnose stroke in acute vertigo and dizziness: toward an ECG for the eyes. Stroke. 2013; 44:1158–1161. PMID: 23463752.12. Mangabeira Albernaz PL, Zuma E. The video head impulse test. Acta Otolaryngol. 2014; 134:1245–1250. PMID: 25399883.
Article13. Hirvonen M, Aalto H, Petteri Hirvonen T. Motorized head impulse rotator in patients with vestibular schwannoma. Acta Otolaryngol. 2008; 128:1215–1220. PMID: 18607973.
Article14. Blödow A, Blödow J, Bloching MB, Helbig R, Walther LE. Horizontal VOR function shows frequency dynamics in vestibular schwannoma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2015; 272:2143–2148. PMID: 24789061.
Article15. Huh YE, Kim JS. Bedside evaluation of dizzy patients. J Clin Neurol. 2013; 9:203–213. PMID: 24285961.
Article16. Choi KD, Oh SY, Kim HJ, Kim JS. The vestibulo-ocular reflexes during head impulse in Wernicke's encephalopathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2007; 78:1161–1162. PMID: 17578853.
Article17. Halmagyi GM, Aw ST, Cremer PD, Curthoys IS, Todd MJ. Impulsive testing of individual semicircular canal function. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001; 942:192–200. PMID: 11710461.
Article18. Chen L, Todd M, Halmagyi GM, Aw S. Head impulse gain and saccade analysis in pontine-cerebellar stroke and vestibular neuritis. Neurology. 2014; 83:1513–1522. PMID: 25253747.
Article19. Lehnen N, Aw ST, Todd MJ, Halmagyi GM. Head impulse test reveals residual semicircular canal function after vestibular neurectomy. Neurology. 2004; 62:2294–2296. PMID: 15210899.
Article20. Samii M, Matthies C. Management of 1000 vestibular schwannomas (acoustic neuromas): hearing function in 1000 tumor resections. Neurosurgery. 1997; 40:248–260. PMID: 9007856.
Article21. Kim HJ, Lee JH, Kim JS. Ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potentials to head tap and cervical vestibular evoked myogenic potentials to air-conducted sounds in isolated internuclear ophthalmoplegia. Clin Neurophysiol. 2014; 125:1042–1047. PMID: 24238926.
Article22. Choi KD, Oh SY, Kim HJ, Koo JW, Cho BM, Kim JS. Recovery of vestibular imbalances after vestibular neuritis. Laryngoscope. 2007; 117:1307–1312. PMID: 17603330.
Article23. Kim HJ, Lee SH, Park JH, Choi JY, Kim JS. Isolated vestibular nuclear infarction: report of two cases and review of the literature. J Neurol. 2014; 261:121–129. PMID: 24162036.
Article24. Park HK, Kim JS, Strupp M, Zee DS. Isolated floccular infarction: impaired vestibular responses to horizontal head impulse. J Neurol. 2013; 260:1576–1582. PMID: 23370610.
Article25. Baloh RW, Honrubia V, Konrad HR. Ewald's second law re-evaluated. Acta Otolaryngol. 1977; 83:475–479. PMID: 888682.
Article26. Zee DS, Yamazaki A, Butler PH, Gücer G. Effects of ablation of flocculus and paraflocculus of eye movements in primate. J Neurophysiol. 1981; 46:878–899. PMID: 7288469.
Article27. Lisberger SG, Miles FA, Zee DS. Signals used to compute errors in monkey vestibuloocular reflex: possible role of flocculus. J Neurophysiol. 1984; 52:1140–1153. PMID: 6335171.
Article28. Büttner-Ennever JA. Patterns of connectivity in the vestibular nuclei. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992; 656:363–378. PMID: 1599156.29. Galiana HL, Outerbridge JS. A bilateral model for central neural pathways in vestibuloocular reflex. J Neurophysiol. 1984; 51:210–241. PMID: 6608579.
Article30. Shin M, Moghadam SH, Sekirnjak C, Bagnall MW, Kolkman KE, Jacobs R, et al. Multiple types of cerebellar target neurons and their circuitry in the vestibulo-ocular reflex. J Neurosci. 2011; 31:10776–10786. PMID: 21795530.
Article31. Bronstein AM, Mossman S, Luxon LM. The neck-eye reflex in patients with reduced vestibular and optokinetic function. Brain. 1991; 114(Pt 1A):1–11. PMID: 1998877.32. Migliaccio AA, Halmagyi GM, McGarvie LA, Cremer PD. Cerebellar ataxia with bilateral vestibulopathy: description of a syndrome and its characteristic clinical sign. Brain. 2004; 127(Pt 2):280–293. PMID: 14607788.
Article33. Croxson GR, Moffat DA, Baguley D. Bruns bidirectional nystagmus in cerebellopontine angle tumours. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 1988; 13:153–157. PMID: 3262024.
Article34. Lloyd SK, Baguley DM, Butler K, Donnelly N, Moffat DA. Bruns' nystagmus in patients with vestibular schwannoma. Otol Neurotol. 2009; 30:625–628. PMID: 19471169.
Article35. Gait C, Frew EJ, Martin TP, Jowett S, Irving R. Conservative management, surgery and radiosurgery for treatment of vestibular schwannomas: a model-based approach to cost-effectiveness. Clin Otolaryngol. 2014; 39:22–31. PMID: 24313969.
Article36. Jethanamest D, Rivera AM, Ji H, Chokkalingam V, Telischi FF, Angeli SI. Conservative management of vestibular schwannoma: predictors of growth and hearing. Laryngoscope. 2015; 125:2163–2168. PMID: 25647714.
Article37. Tutar H, Duzlu M, Göksu N, Ustün S, Bayazit Y. Audiological correlates of tumor parameters in acoustic neuromas. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2013; 270:437–441. PMID: 22323104.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Four Cases of Large Cerebellopontine Angle Tumors Removed by Translabyrinthine Approach
- Conbined approach for large tumor of cerebellopontine angle
- Retroamstoid Suboccipital Approch to Cerebellopontine Angle Tumors
- Cystic Trigeminal Neurinoma at Cerebellopontine Angle
- Cerebellopontine Angle Medulloblastoma: Case Report