Ann Lab Med.
2015 Nov;35(6):657-659. 10.3343/alm.2015.35.6.657.
Campylobacter hyointestinalis Isolated From a Human Stool Specimen
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine and Research Institute of Bacterial Resistance, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. leekcp@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2363274
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2015.35.6.657
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
-
Aged, 80 and over
Anti-Bacterial Agents/pharmacology
Campylobacter hyointestinalis/drug effects/*genetics/isolation & purification
Diarrhea/diagnosis/microbiology
Feces/*microbiology
Gastroenteritis/diagnosis/microbiology
Humans
Male
Microbial Sensitivity Tests
RNA, Ribosomal, 16S/analysis/genetics/metabolism
Sequence Analysis, DNA
Spectrometry, Mass, Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption-Ionization
Anti-Bacterial Agents
RNA, Ribosomal, 16S
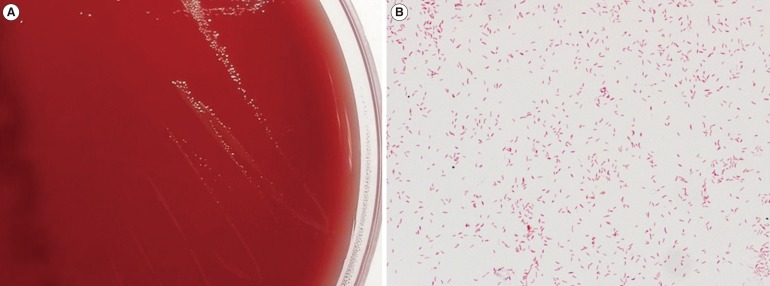
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fitzgerald C, Nachamkin I. Camphylobacter and Arcobacter. Manual of clinical microbiology. 10th ed. Washington DC: ASM press;2011. p. 885–899.2. Gebart CJ, Ward GE, Chang K, Kurtz HJ. Campylobacter hyointestinalis (new species) isolated from swine with lesions of proliferative ileitis. Am J Vet Res. 1983; 44:361–367. PMID: 6838031.3. Fennell CL, Rompalo AM, Totten PA, Bruch KL, Flores BM, Stamm WE. Isolation of "Campylobacter hyointestinalis" from a human. J Clin Microbiol. 1986; 24:146–148. PMID: 3722361.4. Edmonds P, Patton CM, Griffin PM, Barrett TJ, Schmid GP, Baker CN, et al. Campylobacter hyointestinalis associated with human gastrointestinal disease in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 1987; 25:685–691. PMID: 3571477.5. Chung Y, Lee K, et al. Diagnostic Microbiology. 5th ed. Seoul: Seoheung;2014. p. 374–385.6. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Methods for antimicrobial dilution and disk susceptibility testing of infrequently isolated or fastidious bacteria; approved guideline. M45-A2. 2nd ed. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2010.7. Alispahic M, Hummel K, Jandreski-Cvetkovic D, Nöbauer K, Razzazi-Fazeli E, Hess M, et al. Species-specific identification and differentiation of Arcobacter, Helicobacter and Campylobacter by full-spectral matrix-associated laser desorption/ionization time of flight mass spectrometry analysis. J Med Microbiol. 2010; 59:295–301. PMID: 19959629.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pyogenic arthritis of the hip due to Campylobacter fetus: a case report
- Detection of Campylobacter jejuni by Multiplex PCR and Patterns of Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis
- A Study on Effectiveness of Stool Culture
- A Case of Escherichia coli O157 and Campylobacter species Gastroenteritis
- Prevalence of Bacteria in the Nationwide Survey of Stool Culture Performed in 2015, Korea.