Ann Lab Med.
2015 Mar;35(2):269-271. 10.3343/alm.2015.35.2.269.
Two Cases of Shwachman-Diamond Syndrome in Adolescents Confirmed by Genetic Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, Seoul, Korea. suhbk@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, Seoul, Korea. microkim@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2363194
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2015.35.2.269
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Base Sequence
Bone Marrow Diseases/*diagnosis/diagnostic imaging/genetics
DNA Mutational Analysis
Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency/*diagnosis/diagnostic imaging/genetics
Humans
Lipomatosis/*diagnosis/diagnostic imaging/genetics
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Male
Mutation
Proteins/genetics
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Proteins
Figure
Reference
-
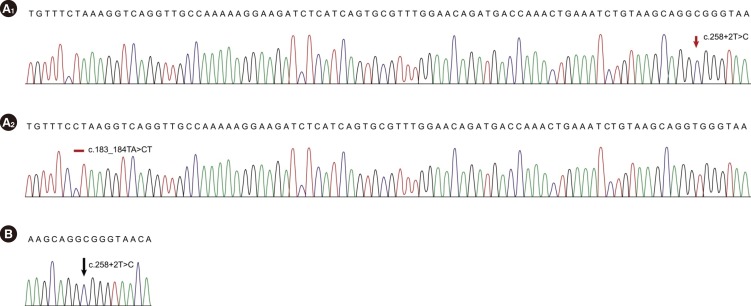
1. Minelli A, Maserati E, Nicolis E, Zecca M, Sainati L, Longoni D, et al. The isochromosome i(7)(q10) carrying c.258+2t>c mutation of the SBDS gene does not promote development of myeloid malignancies in patients with Shwachman syndrome. Leukemia. 2009; 23:708–711. PMID: 19148133.2. Park SY, Chae MB, Kwack YG, Lee MH, Kim I, Kim YS, et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in Shwachman-Diamond syndrome with malignant myeloid transformation. A case report. Korean J Intern Med. 2002; 17:204–206. PMID: 12298432.3. Kwak JW, Kim S, Lim YT. A case of Shwachman-Diamond syndrome. Korean J Pediatr. 2004; 47:900–903.4. Lee JH, Bae SH, Yu JJ, Lee R, Yun YM, Song EY. A case of Shwachman-Diamond syndrome confirmed with genetic analysis in a Korean child. J Korean Med Sci. 2008; 23:142–145. PMID: 18303216.
Article5. Nicolis E, Bonizzato A, Assael BM, Cipolli M. Identification of novel mutations in patients with Shwachman-Diamond syndrome. Hum Mutat. 2005; 25:410. PMID: 15776428.
Article6. Boocock GR, Morrison JA, Popovic M, Richards N, Ellis L, Durie PR, et al. Mutations in SBDS are associated with Shwachman-Diamond syndrome. Nat Genet. 2003; 33:97–101. PMID: 12496757.
Article7. den Dunnen JT, Antonarakis SE. Mutation nomenclature extensions and suggestions to describe complex mutations: a discussion. Hum Mutat. 2000; 15:7–12. PMID: 10612815.8. Toiviainen-Salo S, Mäyränpää MK, Durie PR, Richards N, Grynpas M, Ellis L, et al. Shwachman-Diamond syndrome is associated with low-turnover osteoporosis. Bone. 2007; 41:965–972. PMID: 17920346.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Genetics and genomics of bone marrow failure syndrome
- A Case of Shwachman-Diamond Syndrome
- A Case of Shwachman-Diamond Syndrome Confirmed with Genetic Analysis in a Korean Child
- Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplantation in Shwachman-Diamond Syndrome with Malignant Myeloid Transformation: A Case Report
- Current insights into inherited bone marrow failure syndromes