Ann Lab Med.
2015 Jan;35(1):128-131. 10.3343/alm.2015.35.1.128.
Submicroscopic Deletions of Immunoglobulin Heavy Chain Gene (IGH) in Precursor B Lymphoblastic Leukemia with IGH Rearrangements
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. JungWonH@ewha.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2363160
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2015.35.1.128
Abstract
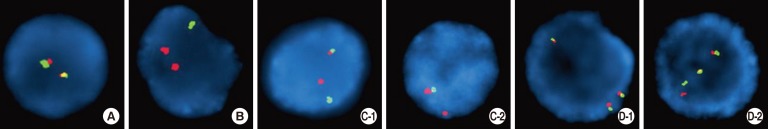
- Translocations leading to fusions between the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene (IGH) and various partner genes have been reported in B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL). However, submicroscopic deletions within IGH in B-ALL have not been rigorously assessed. In this study, we investigated characteristics of IGH submicroscopic deletions, by FISH, in B-ALL with IGH rearrangements. FISH was performed by using commercially available IGH dual-color break-apart rearrangement probes (Abbott/Vysis, Downers Grove, IL, USA; Kreatech, Amsterdam, Netherlands). The study group included seven B-ALL patients with IGH rearrangements, observed by FISH. Among them, two exhibited deletion of the 5' variable region of IGH by FISH. The B-ALL in these two patients included two kinds of abnormal cells; one had an IGH rearrangement without any IGH submicroscopic deletion, while the other had an IGH submicroscopic deletion, which showed that one normal fusion signal and one 3' IGH signal were detected. Thus, submicroscopic deletion of the IGH 5' variable region may have occurred in either the native or rearranged chromosome 14. These findings indicate that B-ALL with IGH rearrangements may be accompanied by submicroscopic deletions of the IGH 5' variable region, which can be detected by FISH. The clinical significance of such deletions is unclear, but the loss of part of the IGH gene in B-ALL warrants further study.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, editors. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Lyon: IARC;2008.2. Meloni-Ehrig A. The cytogenetics of hematologic neoplasms. In : Gersen SL, Keagle MB, editors. The principles of clinical cytogenetics. 3rd ed. New York: Springer;2013. p. 309–370.3. Dyer MJ, Akasaka T, Capasso M, Dusanjh P, Lee YF, Karran EL, et al. Immunoglobulin heavy chain locus chromosomal translocations in B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia: rare clinical curios or potent genetic drivers? Blood. 2010; 115:1490–1499. PMID: 20042721.
Article4. Akasaka T, Balasas T, Russell LJ, Sugimoto KJ, Majid A, Walewska R, et al. Five members of the CEBP transcription factor family are targeted by recurrent IGH translocations in B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (BCP-ALL). Blood. 2007; 109:3451–3461. PMID: 17170124.
Article5. Harrison CJ. Cytogenetics of paediatric and adolescent acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2009; 144:147–156. PMID: 19006567.
Article6. Chapiro E, Radford-Weiss I, Cung HA, Dastugue N, Nadal N, Taviaux S, et al. Chromosomal translocations involving the IGH@ locus in B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia: 29 new cases and a review of the literature. Cancer Genet. 2013; 206:162–173. PMID: 23827691.
Article7. Moorman AV, Schwab C, Ensor HM, Russell LJ, Morrison H, Jones L, et al. IGH@ translocations, CRLF2 deregulation, and microdeletions in adolescents and adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2012; 30:3100–3108. PMID: 22851563.
Article8. Wlodarska I, Matthews C, Veyt E, Pospisilova H, Catherwood MA, Poulsen TS, et al. Telomeric IGH losses detectable by fluorescence in situ hybridization in chronic lymphocytic leukemia reflect somatic VH recombination events. J Mol Diagn. 2007; 9:47–54. PMID: 17251335.
Article9. Trakhtenbrot L, Hardan I, Koren-Michowitz M, Oren S, Yshoev G, Rechavi G, et al. Correlation between losses of IGH or its segments and deletions of 13q14 in t(11;14) (q13;q32) multiple myeloma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2010; 49:17–27. PMID: 19787791.10. Fink SR, Paternoster SF, Smoley SA, Flynn HC, Geyer SM, Shanafelt TD, et al. Fluorescent-labeled DNA probes applied to novel biological aspects of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk Res. 2005; 29:253–262. PMID: 15661260.
Article11. Hwang Y, Lee JY, Mun YC, Seong CM, Chung WS, Huh J. Various patterns of IgH deletion identified by FISH using combined IgH and IgH/CCND1 probes in multiple myeloma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Int J Lab Hematol. 2011; 33:299–304. PMID: 21272268.
Article12. Quintero-Rivera F, Nooraie F, Rao PN. Frequency of 5' IGH deletions in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2009; 190:33–39. PMID: 19264231.13. Hutspardol S, Pakakasama S, Kanta K, Nuntakarn L, Anurathapan U, Sirachainan N, et al. Interphase-FISH screening for eight common rearrangements in pediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Int J Lab Hematol. 2013; 35:406–415. PMID: 23190578.
Article14. Dyer MJ, Heward JM, Zani VJ, Buccheri V, Catovsky D. Unusual deletions within the immunoglobulin heavy-chain locus in acute leukemias. Blood. 1993; 82:865–871. PMID: 8338950.
Article15. Paulsson K, Heidenblad M, Mörse H, Borg A, Fioretos T, Johansson B. Identification of cryptic aberrations and characterization of translocation breakpoints using array CGH in high hyperdiploid childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 2006; 20:2002–2007. PMID: 16990785.
Article16. Shaffer LG, Jordan JM, Schmid M, editors. An international System for human cytogenetic nomenclature. Basel: S. Karger;2013.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Characterization of clonal immunoglobulin heavy (IGH) V-D-J gene rearrangements and the complementarity-determining region in South Indian patients with precursor B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Non-Radioactive Detection of Clonality in Malignant Lymphoid Neoplasms using the Polymerase Chain Reaction
- Detection of Immunoglobulin Heavy Chain Gene Clonality by Next-Generation Sequencing for Minimal Residual Disease Monitoring in B-Lymphoblastic Leukemia
- Comparison of the Rate of Detection of Immunoglobulin Heavy Chain Gene Rearrangement by Fluoresecence In Situ Hybridization Probes in Multiple Myeloma
- Polymerase Chain Reaction and Sequencing of Immunoglobulin Heavy Chain Gene Rearrangement in Formalin Fixed, Paraffin-embedded Tissue of Patients with B Cell Lymphoma