J Korean Acad Nurs.
2015 Dec;45(6):939-948. 10.4040/jkan.2015.45.6.939.
Applying the Flipped Learning Model to an English-Medium Nursing Course
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Nursing and the Research Institute of Nursing Science, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. hchoi20@snu.ac.kr
- 2College of Nursing, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2363117
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.6.939
Abstract
- PURPOSE
An emerging trend in Asian higher education is English-medium instruction (EMI), which uses English as the primary instructional language. EMI prepares domestic students for international leadership; however, students report difficulty in learning, and educators have raised questions concerning the effectiveness of EMI. The flipped learning model (FLM), in which lecture and homework activities for a course are reversed, was applied to an English-medium course offered by a college of nursing in Korea. The aims of this study were to: 1) revise an existing English-medium nursing course using the FLM; 2) explore students' learning experiences and their acceptance of the FLM; and 3) identify key factors in the success of FLM.
METHODS
We used a descriptive, cross-sectional, mixed-methods design and the participants were students at one nursing school in Korea. A series of course development meetings with faculties from the nursing school and the center for teaching and learning were used to develop the course format and content. We conducted course evaluations using the Flipped Course Evaluation Questionnaire with open-ended questions and focus group interviews.
RESULTS
Students (N=75) in a 15-week nursing course responded to a survey after completing the course. Among them, seven students participated in one of two focus groups. Overall, students accepted and favored the flipped learning strategy, and indicated that the method enhanced lecture content and their understanding of it. Factors associated with effective instruction included structured monitoring systems and motivational environments.
CONCLUSION
The FLM requires sufficient preparation to facilitate student motivation and maximize learning outcomes.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
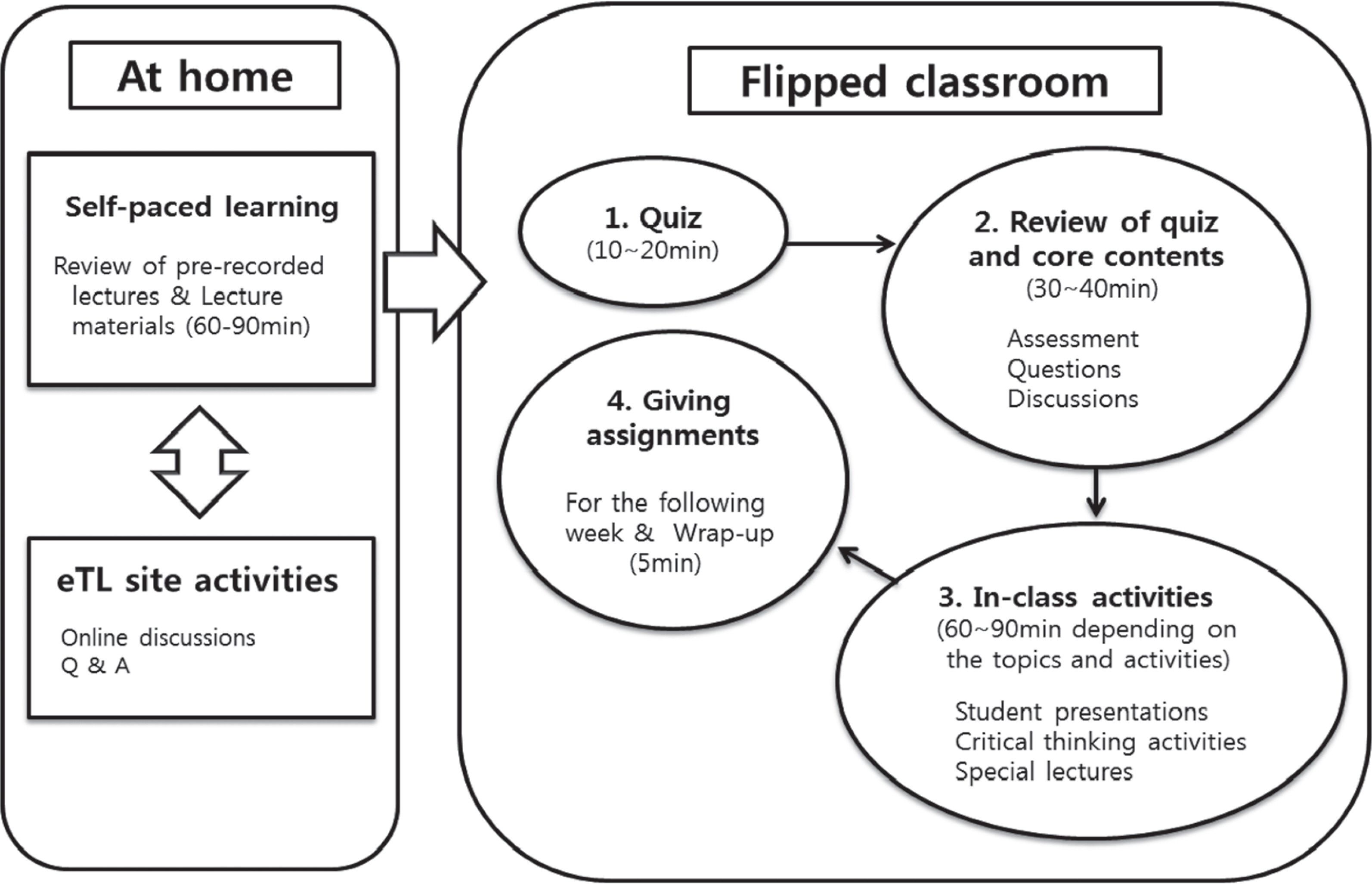
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Byun K, Chu H, Kim M, Park I, Kim S, Jung J. English-medium teaching in Korean higher education: Policy debates and reality. Higher Education. 2011; 62(4):431–449. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10734-010-9397-4.
Article2. Manh LD. English as a medium of instruction in Asian universities: The case of Vietnam. Language Education in Asia. 2012; 3(2):263–267. http://dx.doi.org/10.5746/LEiA/12/V3/I2/A14/Manh.
Article3. Kang HS. English-only instruction at Korean universities: Help or hindrance to higher learning? English Today. 2012; 28(1):29–34. http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S0266078411000654.
Article4. Kim KR. Korean professor and student perceptions of the efficacy of English-medium instruction. Linguistic Research. 2011; 28(3):711–741.5. Joongangilbo. The Joongang daily university ranking [Internet]. Seoul: Author;2013. [cited 2014 September 21]. Available from:. http://univ.joongang.co.kr/university/totalRankingReport.asp.6. Joe YJ, Lee HK. Does English-medium instruction benefit students in EFL contexts? A case study of medical students in Korea. The Asia-Pacific Education Researcher. 2013; 22(2):201–207. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s40299-012-0003-7.
Article7. Chang YY. English-medium instruction for subject courses in tertiary education: Reactions from Taiwanese undergraduate students. Taiwan International ESP Journal. 2010; 2(1):55–84.8. Kim M. Korean students’ responses to English-medium classes and their implications. Studies in English Education. 2009; 14(1):30–50.9. Bergmann J, Sams A. Flip your classroom: Reach every student in every class every day [Internet]. Washington, DC: International Society for Technology in Education;2012. [cited 2014 August 25]. Available from:. http://www.ascd.org/publications/books/112060.aspx.10. Kim MK, Kim SM, Khera O, Getman J. The experience of three flipped classrooms in an urban university: An exploration of design principles. The Internet and Higher Education. 2014; 22:37–50. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2014.04.003.
Article11. McLaughlin JE, Griffin LM, Esserman DA, Davidson CA, Glatt DM, Roth MT, et al. Pharmacy student engagement, performance, and perception in a flipped satellite classroom. American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education. 2013; 77(9):196. http://dx.doi.org/10.5688/ajpe779196.
Article12. McLaughlin JE, Roth MT, Glatt DM, Gharkholonarehe N, Davidson CA, Griffin LM, et al. The flipped classroom: A course redesign to foster learning and engagement in a health professions school. Academic Medicine. 2014; 89(2):236–243. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/acm.0000000000000086.13. Pierce R, Fox J. Vodcasts and active-learning exercises in a “flipped classroom” model of a renal pharmacotherapy module. American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education. 2012; 76(10):196. http://dx.doi.org/10.5688/ajpe7610196.
Article14. Missildine K, Fountain R, Summers L, Gosselin K. Flipping the classroom to improve student performance and satisfaction. The Journal of Nursing Education. 2013; 52(10):597–599. http://dx.doi.org/10.3928/01484834-20130919-03.
Article15. Schwartz TA. Flipping the statistics classroom in nursing education. The Journal of Nursing Education. 2014; 53(4):199–206. http://dx.doi.org/10.3928/01484834-20140325-02.
Article16. Critz CM, Knight D. Using the flipped classroom in graduate nursing education. Nurse Educator. 2013; 38(5):210–213. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/NNE.0b013e3182a0e56a.
Article17. O'Flaherty J, Phillips C. The use of flipped classrooms in higher education: A scoping review. The Internet and Higher Education. 2015; 25:85–95. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2015.02.002.18. Moraros J, Islam A, Yu S, Banow R, Schindelka B. Flipping for success: Evaluating the effectiveness of a novel teaching approach in a graduate level setting. BMC Medical Education. 2015; 15:27. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12909-015-0317-2.
Article19. Simpson V, Richards E. Flipping the classroom to teach population health: Increasing the relevance. Nurse Education in Practice. 2015; 15(3):162–167. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nepr.2014.12.001.
Article20. Ferreri SP, O'Connor SK. Redesign of a large lecture course into a small-group learning course. American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education. 2013; 77(1):13. http://dx.doi.org/10.5688/ajpe77113.
Article21. Maher ML, Lipford H, Singh V. Flipped classroom strategies using online videos [Internet]. Charlotte, NC: University of North Carolina;2014. [cited 2014 November 25]. Available from:. http://cei.uncc.edu/sites/default/files/CEI%20Tech%20Report%203.pdf.22. Ginsberg MB, Wlodkowski RJ. Diversity and motivation: Culturally responsive teaching in college. 2nd ed.San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass;2009.23. Tajvidi M, Ghiyasvandian S, Salsali M. Probing concept of critical thinking in nursing education in Iran: A concept analysis. Asian Nursing Research. 2014; 8(2):158–164. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.anr.2014.02.005.24. Hamdan N, McKnight P, McKnight K, Arfstrom KM. The flipped learning model: A white paper based on the literature review titled “a review of flipped learning” [Internet]. Lake Forest, IL: Flipped Learning Network;2013. [cited 2014 December 2]. Available from:. http://www.flippedlearning.org/cms/lib07/VA01923112/Centricity/Domain/41/WhitePaper_FlippedLearning.pdf.25. Lage MJ, Platt GJ, Treglia M. Inverting the classroom: A gateway to creating an inclusive learning environment. The Journal of Economic Education. 2000; 31(1):30–43.
Article26. Boucher B, Robertson E, Wainner R, Sanders B. “Flipping” Texas state university's physical therapist musculoskeletal curriculum: Implementation of a hybrid learning model. Journal of Physical Therapy Education. 2013; 27(3):72–77.
Article27. Gilboy MB, Heinerichs S, Pazzaglia G. Enhancing student engagement using the flipped classroom. Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior. 2015; 47(1):109–114. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jneb.2014.08.008.
Article28. Moffett J. Twelve tips for “flipping” the classroom. Medical Teacher. 2015; 37(4):331–336. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/0142159x.2014.943710.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Flipped Learning on the Critical Thinking Disposition, Academic Achievement and Academic Self-efficacy of Nursing Students: A Mixed Methods Study
- Effect of flipped learning-based smoking cessation intervention education program for nursing students in South Korea
- The effect of case-based learning based on flipped learning for nursing students
- Effects of Flipped Learning Using Online Materials in a Surgical Nursing Practicum: A Pilot Stratified Group-Randomized Trial
- The Effect of the Flipped Learning on Self-efficacy, Critical Thinking Disposition, and Communication Competence of Nursing Students