Korean J Sports Med.
2016 Jun;34(1):1-9. 10.5763/kjsm.2016.34.1.1.
Regenerative Medicine in the Treatment of Sports Injuries: Prolotherapy and Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. coolkwon@cu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2361663
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5763/kjsm.2016.34.1.1
Abstract
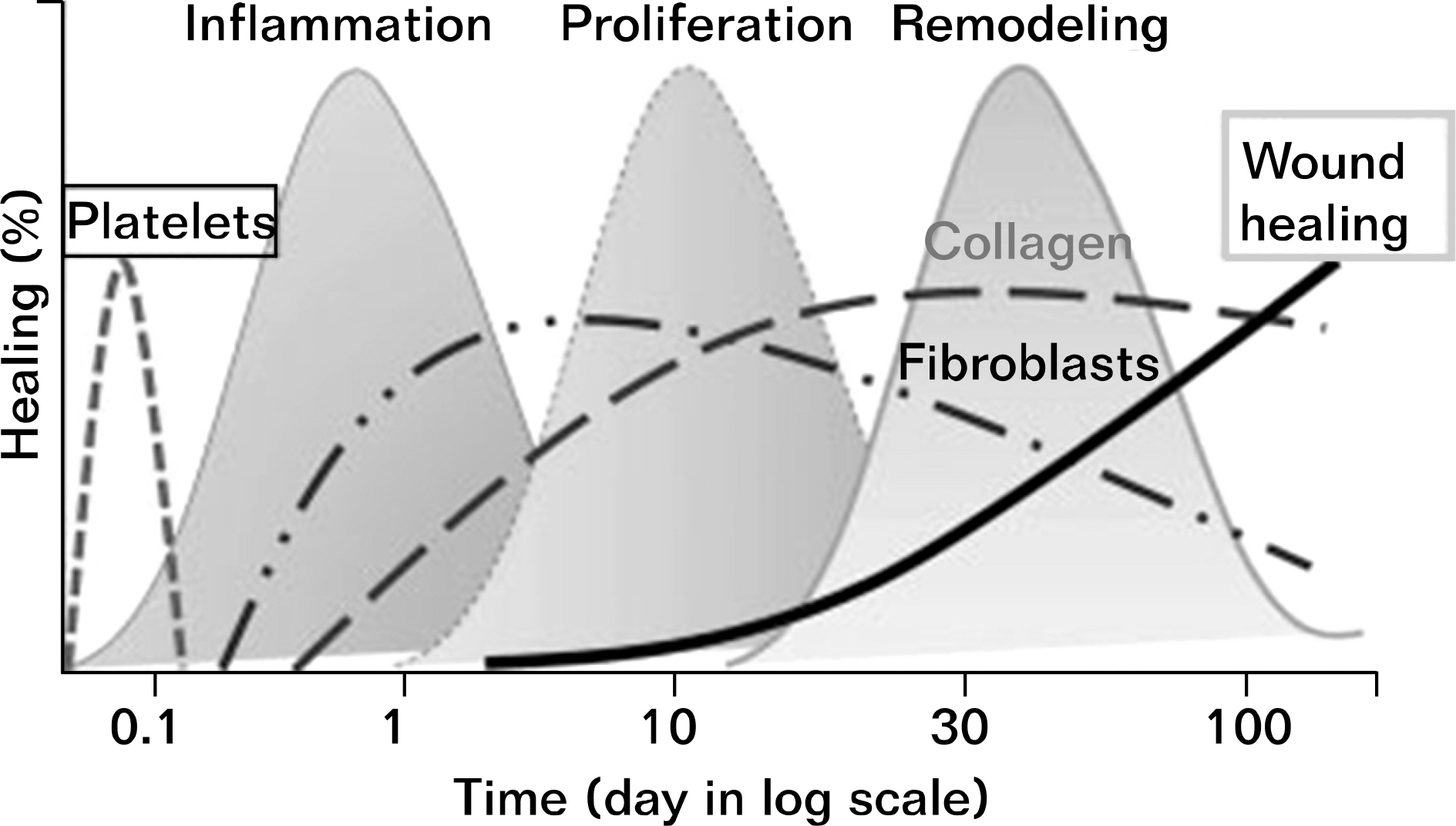
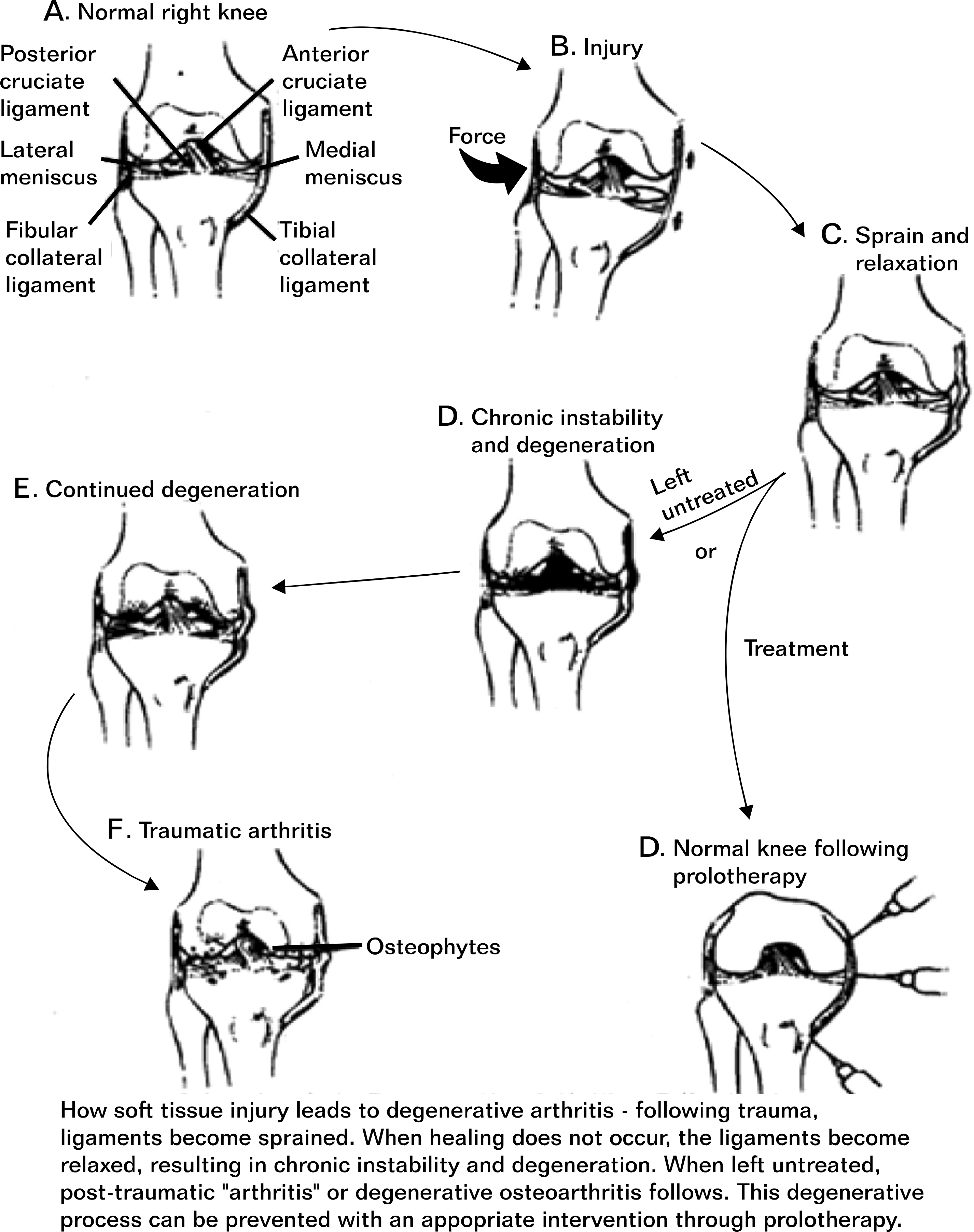
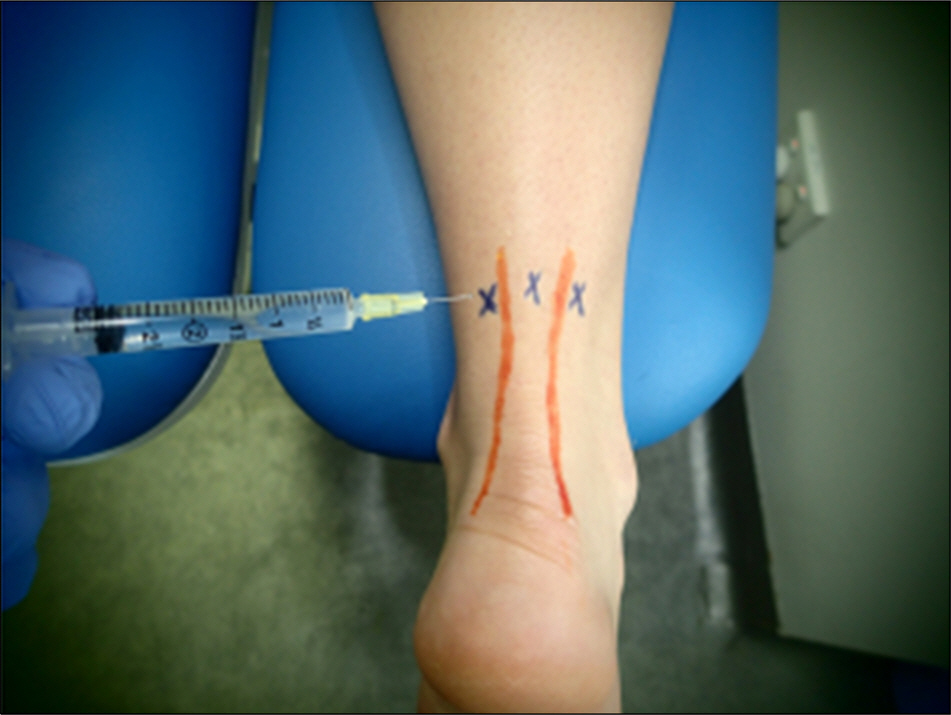
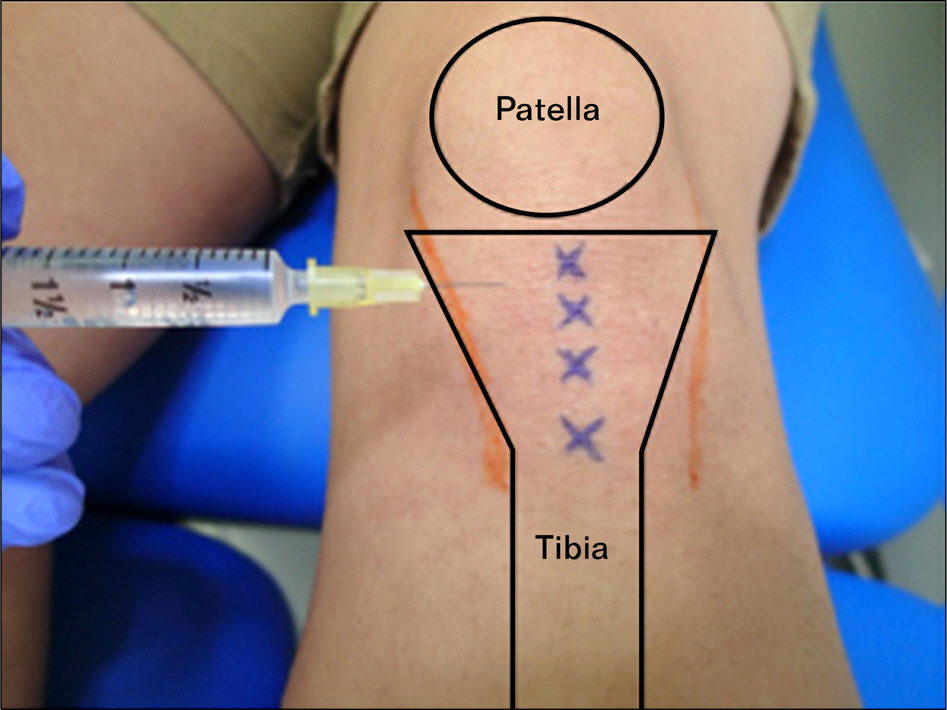
- The treatment of sports injuries traditionally has included the use of the PRICE principle (protection, rest, ice/cold, compression, and elevation), analgesics/nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and, commonly, corticosteroids. Although NSAIDs, modalities, and corticosteroids may be helpful for short-term pain reduction and early recovery of function, they do not typically reverse the structural changes associated with degenerative conditions and may contribute to even worse long-term outcomes by potentially interfering with tissue healing. Regenerative interventions, including prolotherapy and extracorporeal shock wave therapy, recently have been used to treat refractory painful conditions such as chronic tendinopathies because of the potential of these interventions to facilitate tissue healing. The true utility of prolotherapy and regenerative medicine for sports injuries will become clearer as more high-quality research is published.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Hur NW., Choi CB., Uhm WS., Bae SC. The prevalence and trend of arthritis in Korea: results from Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2008. 15:11–26.
Article2.Jung CK., Park JY., Kim NS., Park HY. Status of chronic pain prevalence in the Korean adults. Public Health Wkly Rep. 2015. 8:728–34.3.Jarvinen TA., Jarvinen TL., Kaariainen M., Kalimo H., Jarvinen M. Muscle injuries: biology and treatment. Am J Sports Med. 2005. 33:745–64.4.Weiler JM. Medical modifiers of sports injury: the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in sports soft-tissue injury. Clin Sports Med. 1992. 11:625–44.5.Coombes BK., Bisset L., Brooks P., Khan A., Vicenzino B. Effect of corticosteroid injection, physiotherapy, or both on clinical outcomes in patients with unilateral lateral epicondylalgia: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2013. 309:461–9.6.Guo S., Dipietro LA. Factors affecting wound healing. J Dent Res. 2010. 89:219–29.
Article7.Gulotta LV., Rodeo SA. Growth factors for rotator cuff repair. Clin Sports Med. 2009. 28:13–23.
Article8.Anitua E., Andia I., Sanchez M, et al. Autologous preparations rich in growth factors promote proliferation and induce VEGF and HGF production by human tendon cells in culture. J Orthop Res. 2005. 23:281–6.
Article9.Molloy T., Wang Y., Murrell G. The roles of growth factors in tendon and ligament healing. Sports Med. 2003. 33:381–94.
Article10.Schultz LW. A treatment for subluxation of the temporomandibular joint. JAMA. 1937. 109:1032–5.
Article11.Hackett GS. Ligament and tendon relaxation treated by prolotherapy. 3rd ed.Springfield: Charles C Thomas;1956.12.Kim SR., Stitik TP., Foye PM., Greenwald BD., Campagnolo DI. Critical review of prolotherapy for osteoarthritis, low back pain, and other musculoskeletal conditions: a physiatric perspective. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2004. 83:379–89.13.Banks AR. A rationale for prolotherapy. J Orthop Med. 1991. 13:54–9.14.Reeves KD., Hassanein KM. Long-term effects of dextrose prolotherapy for anterior cruciate ligament laxity. Altern Ther Health Med. 2003. 9:58–62.15.Liu YK., Tipton CM., Matthes RD., Bedford TG., Maynard JA., Walmer HC. An in situ study of the influence of a sclerosing solution in rabbit medial collateral ligaments and its junction strength. Connect Tissue Res. 1983. 11:95–102.16.Yelland MJ., Sweeting KR., Lyftogt JA., Ng SK., Scuffham PA., Evans KA. Prolotherapy injections and eccentric loading exercises for painful Achilles tendinosis: a randomised trial. Br J Sports Med. 2011. 45:421–8.
Article17.Sanderson LM., Bryant A. Effectiveness and safety of prolotherapy injections for management of lower limb tendinopathy and fasciopathy: a systematic review. J Foot Ankle Res. 2015. 8:57.
Article18.Rabago D., Mundt M., Zgierska A., Grettie J. Hypertonic dextrose injection (prolotherapy) for knee osteoarthritis: long term outcomes. Complement Ther Med. 2015. 23:388–95.
Article19.Topol GA., Podesta LA., Reeves KD, et al. Chondrogenic effect of intra-articular hypertonic-dextrose (prolotherapy) in severe knee osteoarthritis. PM R. 2016 Apr 4. [Epub].http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.pmrj.2016.03.008.
Article20.Sit RW., VCh Chung., Reeves KD, et al. Hypertonic dextrose injections (prolotherapy) in the treatment of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2016. 6:25247.
Article21.Klein RG., Eek BC., DeLong WB., Mooney V. A randomized double-blind trial of dextrose-glycerine-phenol injections for chronic, low back pain. J Spinal Disord. 1993. 6:23–33.
Article22.Ongley MJ., Klein RG., Dorman TA., Eek BC., Hubert LJ. A new approach to the treatment of chronic low back pain. Lancet. 1987. 2:143–6.
Article23.Cusi M., Saunders J., Hungerford B., Wisbey-Roth T., Lucas P., Wilson S. The use of prolotherapy in the sacroiliac joint. Br J Sports Med. 2010. 44:100–4.
Article24.Kim WM., Lee HG., Jeong CW., Kim CM., Yoon MH. A randomized controlled trial of intra-articular prolotherapy versus steroid injection for sacroiliac joint pain. J Altern Complement Med. 2010. 16:1285–90.
Article25.Khan SA., Kumar A., Varshney MK., Trikha V., Yadav CS. Dextrose prolotherapy for recalcitrant coccygodynia. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2008. 16:27–9.
Article26.Miller MR., Mathews RS., Reeves KD. Treatment of painful advanced internal lumbar disc derangement with intradiscal injection of hypertonic dextrose. Pain Physician. 2006. 9:115–21.27.Rabago D., Lee KS., Ryan M, et al. Hypertonic dextrose and morrhuate sodium injections (prolotherapy) for lateral epicon-dylosis (tennis elbow): results of a single-blind, pilot-level, randomized controlled trial. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2013. 92:587–96.28.Ryan MB., Wong AD., Gillies JH., Wong J., Taunton JE. Sonographically guided intratendinous injections of hyperosmolar dextrose/lidocaine: a pilot study for the treatment of chronic plantar fasciitis. Br J Sports Med. 2009. 43:303–6.
Article29.Ogden JA., Toth-Kischkat A., Schultheiss R. Principles of shock wave therapy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001. 387:8–17.
Article30.Wang CJ. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy in musculoskeletal disorders. J Orthop Surg Res. 2012. 7:11.
Article31.Loew M., Daecke W., Kusnierczak D., Rahmanzadeh M., Ewerbeck V. Shock-wave therapy is effective for chronic calcifying tendinitis of the shoulder. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1999. 81:863–7.
Article32.Speed CA. Extracorporeal shock-wave therapy in the management of chronic soft-tissue conditions. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004. 86:165–71.
Article33.Schmitz C., Csaszar NB., Milz S, et al. Efficacy and safety of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for orthopedic conditions: a systematic review on studies listed in the PEDro database. Br Med Bull. 2015. 116:115–38.
Article34.Ramon S., Gleitz M., Hernandez L., Romero LD. Update on the efficacy of extracorporeal shockwave treatment for myofa-scial pain syndrome and fibromyalgia. Int J Surg. 2015. 24:201–6.
Article35.Park DS., Kwon DR., Park GY., Lee MY. Therapeutic effect of extracorporeal shock wave therapy according to treatment session on gastrocnemius muscle spasticity in children with spastic cerebral palsy: a pilot study. Ann Rehabil Med. 2015. 39:914–21.
Article36.Gollwitzer H., Saxena A., DiDomenico LA, et al. Clinically relevant effectiveness of focused extracorporeal shock wave therapy in the treatment of chronic plantar fasciitis: a randomized, controlled multicenter study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015. 97:701–8.37.Pettrone FA., McCall BR. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy without local anesthesia for chronic lateral epicondylitis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005. 87:1297–304.
Article38.Rompe JD., Kirkpatrick CJ., Kullmer K., Schwitalle M., Krischek O. Dose-related effects of shock waves on rabbit tendo Achillis: a sonographic and histological study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1998. 80:546–52.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Current Concepts in Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy
- Suggestions for Effective Extracorporeal Shock Wave Treatment Methods for Lateral Epicondylitis
- Treatment of Nonunion of Tibia with Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy: A Case Report
- Low Energy Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Stress Fracture of the Anterior Cortex of the Tibia
- Dose Related Effect of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy in Lateral Epicondylitis