Korean J Sports Med.
2011 Dec;29(2):122-125. 10.5763/kjsm.2011.29.2.122.
Low Energy Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Stress Fracture of the Anterior Cortex of the Tibia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. jhlee.hwang@samsung.com
- KMID: 1987193
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5763/kjsm.2011.29.2.122
Abstract
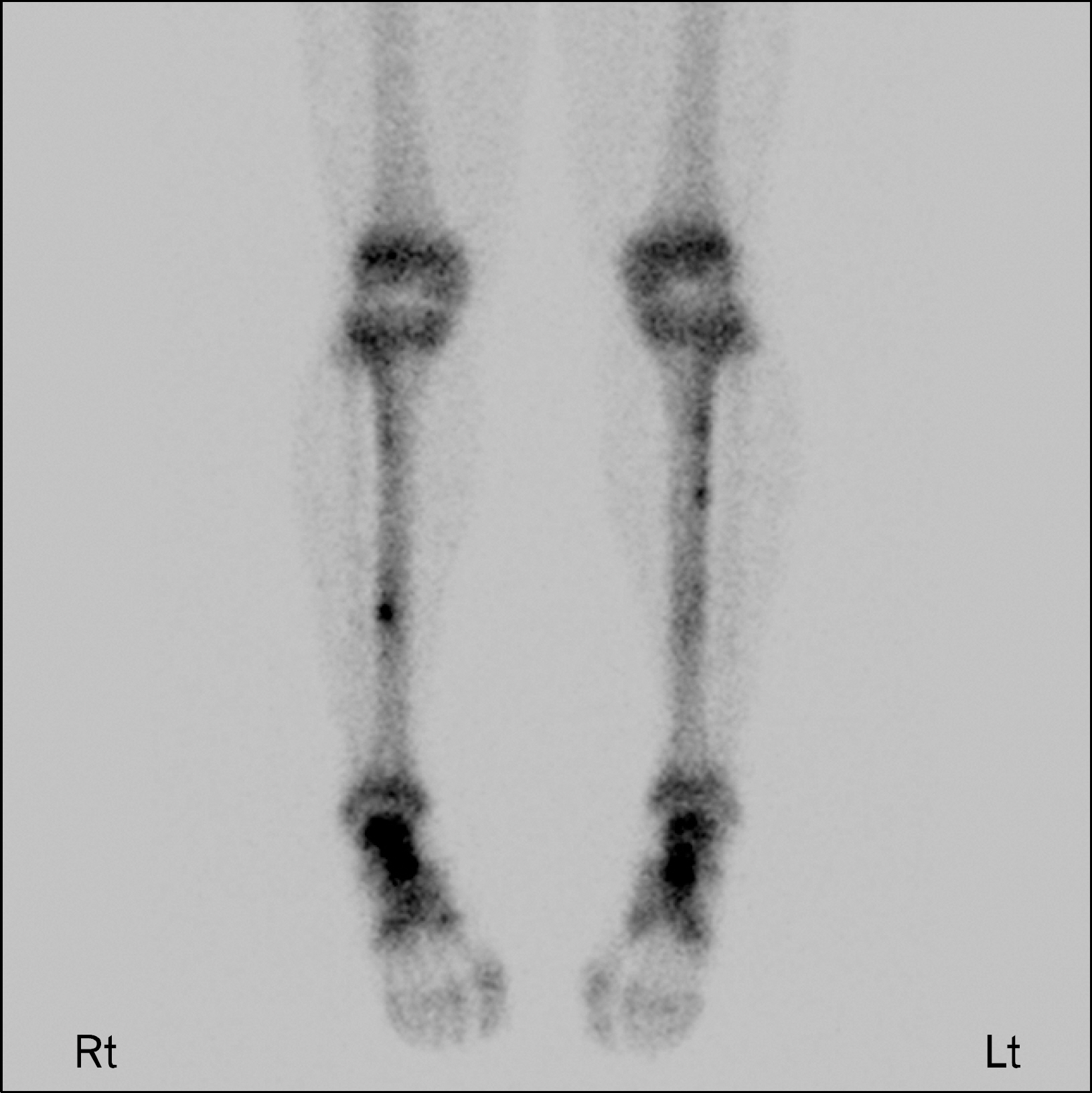
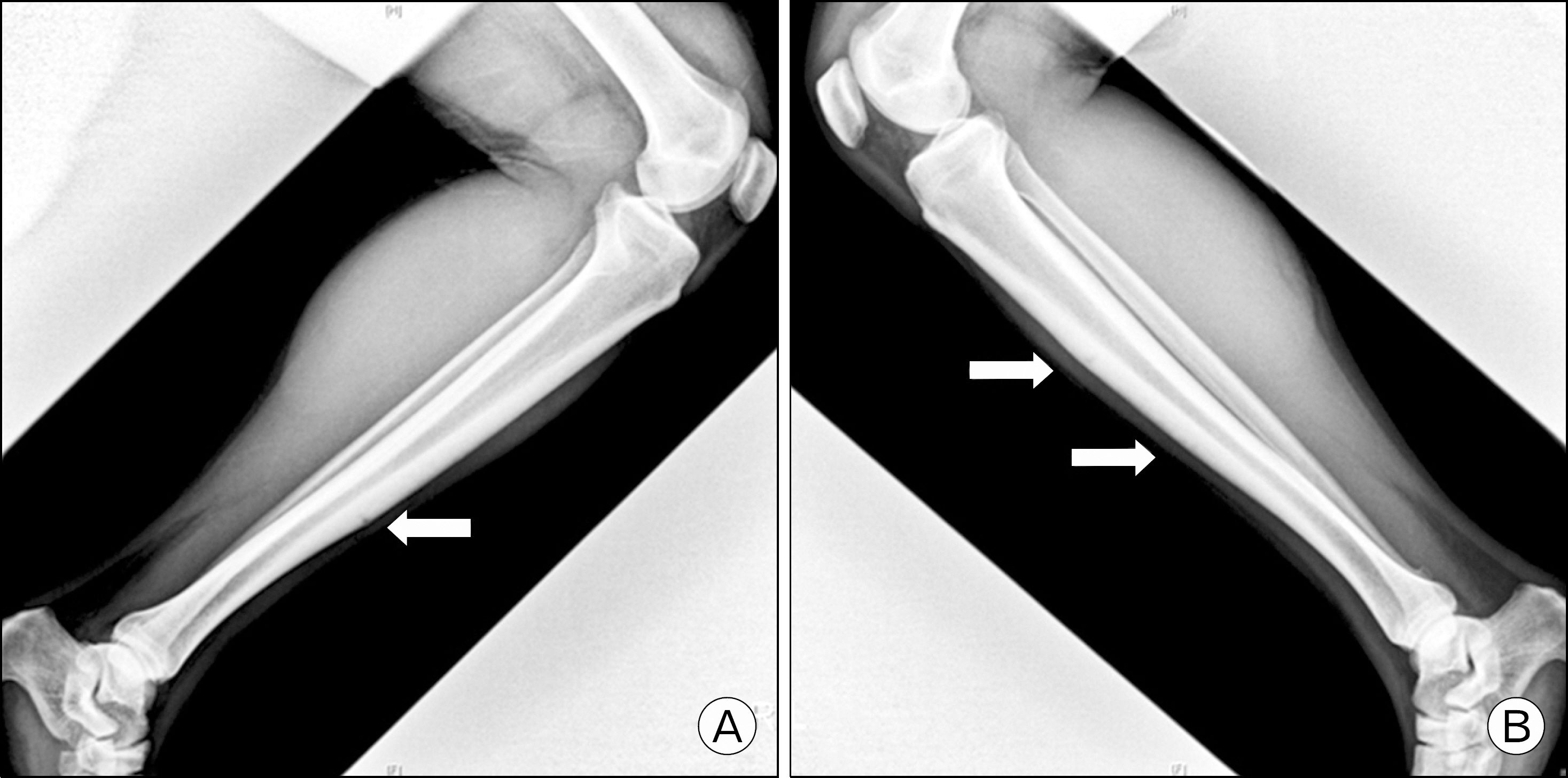
- Anterior cortex of the tibia is one of the intractable stress fracture sites ocurring in athletes, which are result of repetitive use damage that exceeds the intrinsic ability of the bone to repair itself. It is sometimes difficulty to repair the anterior cortical stress fracture, which result in delayed union or nonunion. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) can be an useful method in the management of stress fracture of the anterior cortex of the tibia. We present a case of an young athlete affected by chronic stress fractures of the anterior cortex of the tibia that received low energy ESWT. The clinical result was excellent and he was able to gradually return to sports activities.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Raasch WG, Hergan DJ. Treatment of stress fractures: the fundamentals. Clin Sports Med. 2006; 25:29–36. vii.
Article2. Bennell KL, Brukner PD. Epidemiology and site specificity of stress fractures. Clin Sports Med. 1997; 16:179–96.
Article3. Batt ME, Kemp S, Kerslake R. Delayed union stress fractures of the anterior tibia: conservative management. Br J Sports Med. 2001; 35:74–7.
Article4. Chang PS, Harris RM. Intramedullary nailing for chronic tibial stress fractures. A review of five cases. Am J Sports Med. 1996; 24:688–92.5. Moretti B, Notarnicola A, Garofalo R, et al. Shock waves in the treatment of stress fractures. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2009; 35:1042–9.
Article6. Taki M, Iwata O, Shiono M, Kimura M, Takagishi K. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for resistant stress fracture in athletes: a report of 5 cases. Am J Sports Med. 2007; 35:1188–92.7. Rettig AC, Shelbourne KD, McCarroll JR, Bisesi M, Watts J. The natural history and treatment of delayed union stress fractures of the anterior cortex of the tibia. Am J Sports Med. 1988; 16:250–5.
Article8. Young AJ, McAllister DR. Evaluation and treatment of tibial stress fractures. Clin Sports Med. 2006; 25:117–28. x.
Article9. Haupt G. Use of extracorporeal shock waves in the treatment of pseudarthrosis, tendinopathy and other orthopedic diseases. J Urol. 1997; 158:4–11.
Article10. Speed CA. Extracorporeal shock-wave therapy in the management of chronic soft-tissue conditions. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004; 86:165–71.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment of Nonunion of Tibia with Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy: A Case Report
- Current Concepts in Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy
- Suggestions for Effective Extracorporeal Shock Wave Treatment Methods for Lateral Epicondylitis
- Effects of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithortripsy Experimentally Induced Cholelithiasis and Organs in the Dog
- Tension Band Plating for a Stress Fracture of the Anterior Tibial Cortex in a Basketball Player: A Case Report