J Korean Fract Soc.
2012 Oct;25(4):323-326. 10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.4.323.
Tension Band Plating for a Stress Fracture of the Anterior Tibial Cortex in a Basketball Player: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Seoul Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. leewoochun@gmail.com
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 1434074
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.4.323
Abstract
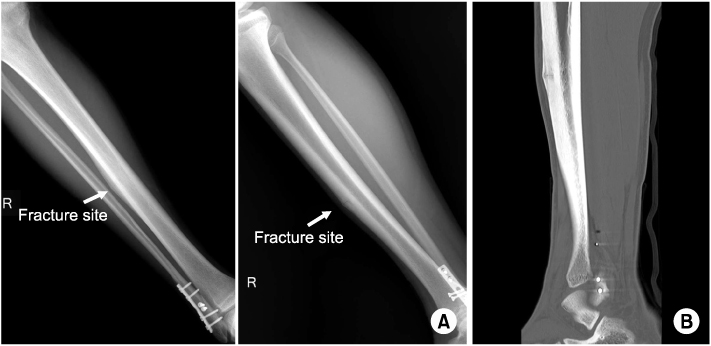
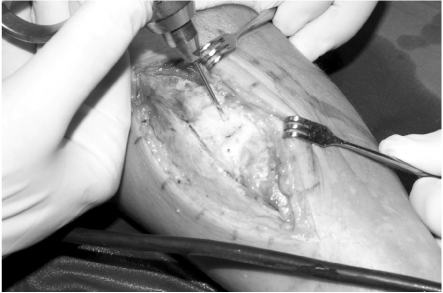
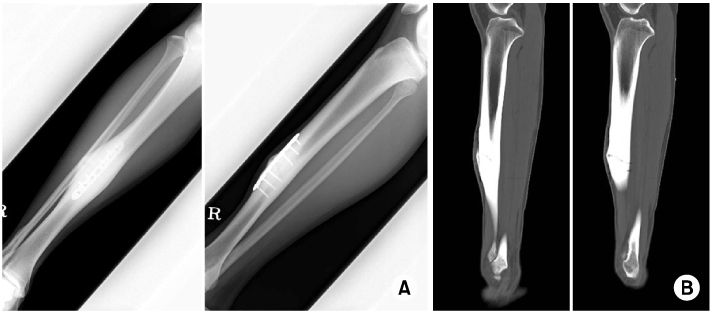
- Stress fractures of the anterior tibial cortex are prone to complete fracture because these stress fractures occur on the tension side of the bone. Recently, surgical treatments are preferred in high-performance athletes requiring rapid return to sports. We report our experience of a case in which stress fracture of the anterior tibial cortex was treated using anterior tension band plating in a male athlete and successful bony union and rapid return to sports were achieved.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Barrick EF, Jackson CB. Prophylactic intramedullary fixation of the tibia for stress fracture in a professional athlete. J Orthop Trauma. 1992. 6:241–244.
Article2. Batt ME, Kemp S, Kerslake R. Delayed union stress fractures of the anterior tibia: conservative management. Br J Sports Med. 2001. 35:74–77.
Article3. Baublitz SD, Shaffer BS. Acute fracture through an intramedullary stabilized chronic tibial stress fracture in a basketball player: a case report and literature review. Am J Sports Med. 2004. 32:1968–1972.
Article4. Beals RK, Cook RD. Stress fractures of the anterior tibial diaphysis. Orthopedics. 1991. 14:869–875.
Article5. Boden BP, Osbahr DC. High-risk stress fractures: evaluation and treatment. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2000. 8:344–353.
Article6. Borens O, Sen MK, Huang RC, et al. Anterior tension band plating for anterior tibial stress fractures in high-performance female athletes: a report of 4 cases. J Orthop Trauma. 2006. 20:425–430.
Article7. Burrows HJ. Fatigue infraction of the middle of the tibia in ballet dancers. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1956. 38-B:83–94.
Article8. Choo SK, Oh HK, Choi HW, Song JG. Anterior knee pain after intramedullary nailing for tibial shaft fractures. J Korean Fract Soc. 2011. 24:28–32.
Article9. Court-Brown CM, Gustilo T, Shaw AD. Knee pain after intramedullary tibial nailing: its incidence, etiology, and outcome. J Orthop Trauma. 1997. 11:103–105.
Article10. Harmon KG. Lower extremity stress fractures. Clin J Sport Med. 2003. 13:358–364.
Article11. Rettig AC, Shelbourne KD, McCarroll JR, Bisesi M, Watts J. The natural history and treatment of delayed union stress fractures of the anterior cortex of the tibia. Am J Sports Med. 1988. 16:250–255.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment for the Stress Fracture of the Proximal Phalanx of the Great Toe in a Basketball Player with Hallux Valgus (A Case Report)
- Serial Radiographs Showing Progression of a Patellar Stress Fracture and Beneficial Surgical Technique for a Displaced Patellar Stress Fracture
- Tension Band Fixation in the Treatment of the Olecranon Fracture
- Tension band wiring and Modified tension band wiring in the Operative Treatment of Patella Fracture
- Nonunion of a Stress Fracture Through the Olecranon Epiphyseal Plate in an Adolescent Judo Player: A Case Report