Allergy Asthma Respir Dis.
2016 Mar;4(2):145-148. 10.4168/aard.2016.4.2.145.
Late-onset trichloroethylene-induced hypersensitivity syndrome after intermittent exposure to low-dose trichloroethylene
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Inha University Hospital, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. cwkim1805@inha.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Inha University Hospital, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2361288
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2016.4.2.145
Abstract
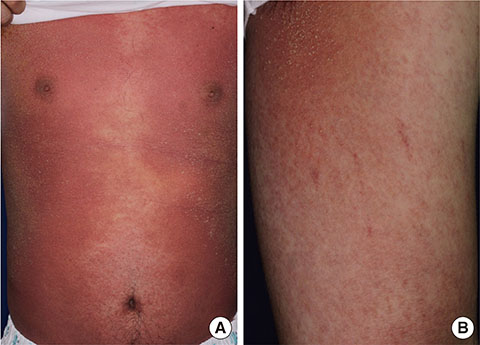
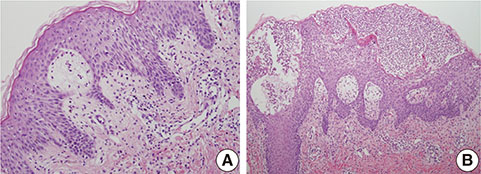
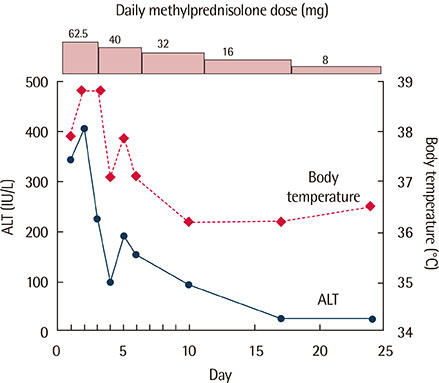
- Occupational exposure to trichloroethylene (TCE) can occasionally induce severe cutaneous disorders, including hypersensitivity syndrome and Stevens-Johnson syndrome. The clinical manifestation of TCE hypersensitivity syndrome is quite similar to that of drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome and includes skin lesions, hepatitis, fever, and lymphadenopathy. Almost all cases of TCE hypersensitivity syndrome developed within 2-8 weeks after the first exposure to TCE in an occupational setting. This typical course and clinical feature of hypersensitivity syndrome together with occupational history of TCE contact may lead to prompt diagnosis and treatment of this potentially fatal disease. This report describes a 32-year-old man who has been intermittently engaged in cleaning work using TCE for about 3 years, and then developed TCE hypersensitivity syndrome. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case of TCE hypersensitivity syndrome with a long duration of symptom onset due to intermittent exposure to TCE. Thus, physicians should take thorough occupational history when seeing a patient with hypersensitivity syndrome has neither history of drug intake nor regular exposure to TCE.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Trichloroethylene Hypersensitivity Syndrome: Should Be Considered When Diagnosing DRESS Syndrome
Young Joong Kang, Jihye Lee, Jungho Ahn, Soonwoo Park, Mu Young Shin, Hye Won Lee
J Korean Med Sci. 2018;33(14):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2018.33.e106.
Reference
-
1. Watanabe H. Hypersensitivity syndrome due to trichloroethylene exposure: a severe generalized skin reaction resembling drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome. J Dermatol. 2011; 38:229–235.
Article2. Watanabe H, Tohyama M, Kamijima M, Nakajima T, Yoshida T, Hashimoto K, et al. Occupational trichloroethylene hypersensitivity syndrome with human herpesvirus-6 and cytomegalovirus reactivation. Dermatology. 2010; 221:17–22.
Article3. Hong DP, Kim JS, Kim SH, Kim JM, Lee ES. A case of toxic erythema, toxic hepatitis and exfoliative deratitis due to trichloroethylene. Korean J Dermatol. 1985; 23:785–789.4. Jung HG, Kim HH, Song BG, Kim EJ. Trichloroethylene hypersensitivity syndrome: a disease of fatal outcome. Yonsei Med J. 2012; 53:231–235.
Article5. Lee SW, Kim EA, Kim DS, Koh DH, Kang SK, Kim BK, et al. Exposure level of trichloroethylene in Stevens-Johnson Syndrome due to occupational exposure: 3 case reports and a review of other cases. Korean J Occup Environ Med. 2008; 20:132–146.
Article6. Chae HB, Kim JA, Lee KS, Park SM, Yoon TY, Yoon SJ. A case of hepatitis after occupational exposure of trichloethylene. Korean J Hepatol. 1999; 5:59–64.7. Ha JH, Lee CG, Yoon SH, Lee SI, Kwon YE. A case of hypersensitive exfoliative dermatitis with hepatitis after a occupational exposure to trichloroethylene. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 29:132–137.8. Kim YJ, Hwang ED, Leem AY, Kang BD, Chang SY, Kim HK, et al. A case of occupational hypersensitivity pneumonitis associated with trichloroethylene. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2014; 76:75–79.
Article9. Chae HJ, Lee SK, Lee KJ, Kim JY, Lee SC, Shin DH, et al. Exfoliative dermatitis and toxic hepatitis associated with occupational exposure to trichloroethylene. Korean J Occup Environ Med. 2003; 15:111–117.
Article10. Park JW, Chung JM, Jung KE, Jin WW, Kim MH, Cinn YW. A case of trichloroethylene hypersensitivity syndrome. Korean J Dermatol. 2008; 46:1561–1563.11. Kamijima M, Hisanaga N, Wang H, Nakajima T. Occupational trichloroethylene exposure as a cause of idiosyncratic generalized skin disorders and accompanying hepatitis similar to drug hypersensitivities. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2007; 80:357–370.
Article12. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Toxicological review of trichloroethylene. Washington, DC: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency;2011. p. 2-15. p. 2-21. p. 5-22. p. 5-27.13. Xu X, Yang R, Wu N, Zhong P, Ke Y, Zhou L, et al. Severe hypersensitivity dermatitis and liver dysfunction induced by occupational exposure to trichloroethylene. Ind Health. 2009; 47:107–112.
Article14. Goon AT, Lee LT, Tay YK, Yosipovitch G, Ng SK, Giam YC. A case of trichloroethylene hypersensitivity syndrome. Arch Dermatol. 2001; 137:274–276.15. Tang X, Que B, Song X, Li S, Yang X, Wang H, et al. Characterization of liver injury associated with hypersensitive skin reactions induced by trichloroethylene in the guinea pig maximization test. J Occup Health. 2008; 50:114–121.
Article16. Huang H, Kamijima M, Wang H, Li S, Yoshikawa T, Lai G, et al. Human herpesvirus 6 reactivation in trichloroethylene-exposed workers suffering from generalized skin disorders accompanied by hepatic dysfunction. J Occup Health. 2006; 48:417–423.
Article17. Goh CL, Ng SK. A cutaneous manifestation of trichloroethylene toxicity. Contact Dermatitis. 1988; 18:59–61.
Article18. Conde-Salazar L, Guimaraens D, Romero LV, Sanchez Yus E. Subcorneal pustular eruption and erythema from occupational exposure to trichloroethylene. Contact Dermatitis. 1983; 9:235–237.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Trichloroethylene Hypersensitivity Syndrome
- Trichloroethylene Hypersensitivity Syndrome: A Disease of Fatal Outcome
- A Study on the Neuropsychiatric Symptom and Neurobehavioral Effects of Occupational Exposure to Trichloroethylene
- Health hazard of workers potentially exposed to trichloroethylene in the Inchon area
- Exfoliative Dermatitis and Toxic Hepatitis Associated with Occupational Exposure to Trichloroethylene