Yonsei Med J.
2012 Jan;53(1):231-235. 10.3349/ymj.2012.53.1.231.
Trichloroethylene Hypersensitivity Syndrome: A Disease of Fatal Outcome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul Paik Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. drhhkim@gmail.com
- KMID: 1779713
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2012.53.1.231
Abstract
- Trichloroethylene is commonly used as an industrial solvent and degreasing agent. The clinical features of acute and chronic intoxication with trichloroethylene are well-known and have been described in many reports, but hypersensitivity syndrome caused by trichloroethylene is rarely encountered. For managing patients with trichloroethylene hypersensitivity syndrome, avoiding trichloroethylene and initiating glucocorticoid have been generally accepted. Generally, glucocorticoid had been tapered as trichloroethylene hypersensitivity syndrome had ameliorated. However, we encountered a typical case of trichloroethylene hypersensitivity syndrome refractory to high dose glucocorticoid treatment. A 54-year-old Korean man developed jaundice, fever, red sore eyes, and generalized erythematous maculopapular rashes. A detailed history revealed occupational exposure to trichloroethylene. After starting intravenous methylprednisolone, his clinical condition improved remarkably, but we could not reduce prednisolone because his liver enzyme and total bilirubin began to rise within 2 days after reducing prednisolone under 60 mg/day. We recommended an extended admission for complete recovery, but the patient decided to leave the hospital against medical advice. The patient visited the emergency department due to pneumonia and developed asystole, which did not respond to resuscitation.
MeSH Terms
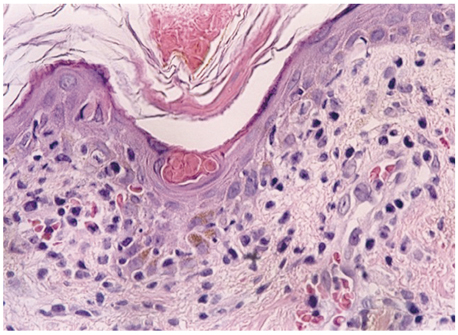
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Trichloroethylene Hypersensitivity Syndrome: Should Be Considered When Diagnosing DRESS Syndrome
Young Joong Kang, Jihye Lee, Jungho Ahn, Soonwoo Park, Mu Young Shin, Hye Won Lee
J Korean Med Sci. 2018;33(14):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2018.33.e106.Late-onset trichloroethylene-induced hypersensitivity syndrome after intermittent exposure to low-dose trichloroethylene
Seung Yun Lee, Se Hwan Oh, Hyuck Jae Choi, Woo Young Choi, Jee Young Han, Hong-Lyeol Lee, Cheol-Woo Kim
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2016;4(2):145-148. doi: 10.4168/aard.2016.4.2.145.
Reference
-
1. Kadry AM, Farghali H, Abdel-Rahman MS. Toxicity and metabolism of trichloroethylene in rat hepatocytes. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 1989. 18:888–894.
Article2. Goon AT, Lee LT, Tay YK, Yosipovitch G, Ng SK, Giam YC. A case of trichloroethylene hypersensitivity syndrome. Arch Dermatol. 2001. 137:274–276.3. Chae HB, Kim JA, Lee KS, Park SM, Yoon TY, Yoon SJ. A case of hepatitis after occupational exposure of trichloethylene. Korean J Hepatol. 1999. 5:59–64.4. Chae HJ, Lee SK, Lee KJ, Kim JY, Lee SC, Shin DH, et al. Exfoliative dermatitis and toxic hepatitis associated with occupational exposure to trichloroethylene. Korean J Occup Environ Med. 2003. 15:111–117.
Article5. Park JW, Chung JM, Jung KE, Jin WW, Kim MH, Cinn YW. A case of trichloroethylene hypersensitivity syndrome. Korean J Dermatol. 2008. 46:1561–1563.6. Ha JH, Lee CG, Yoon SH, Lee SI, Kwon YE. A case of hypersensitive exfoliative dermatitis with hepatitis after a occupational exposure to trichloroethylene. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009. 29:132–137.7. Kamijima M, Wang H, Huang H, Li L, Shibata E, Lin B, et al. Trichloroethylene causes generalized hypersensitivity skin disorders complicated by hepatitis. J Occup Health. 2008. 50:328–338.
Article8. Tanaka S, Ikeda M. A method for determination of trichloroethanol and trichloroacetic acid in urine. Br J Ind Med. 1968. 25:214–219.
Article9. Nakayama H, Kobayashi M, Takahashi M, Ageishi Y, Takano T. Generalized eruption with severe liver dysfunction associated with occupational exposure to trichloroethylene. Contact Dermatitis. 1988. 19:48–51.
Article10. Tang X, Que B, Song X, Li S, Yang X, Wang H, et al. Characterization of liver injury associated with hypersensitive skin reactions induced by trichloroethylene in the guinea pig maximization test. J Occup Health. 2008. 50:114–121.
Article11. Xu X, Yang R, Wu N, Zhong P, Ke Y, Zhou L, et al. Severe hypersensitivity dermatitis and liver dysfunction induced by occupational exposure to trichloroethylene. Ind Health. 2009. 47:107–112.
Article12. Dai Y, Leng S, Li L, Niu Y, Huang H, Liu Q, et al. Effects of genetic polymorphisms of N-Acetyltransferase on trichloroethylene-induced hypersensitivity dermatitis among exposed workers. Ind Health. 2009. 47:479–486.
Article13. Watanabe H, Tohyama M, Kamijima M, Nakajima T, Yoshida T, Hashimoto K, et al. Occupational trichloroethylene hypersensitivity syndrome with human herpesvirus-6 and cytomegalovirus reactivation. Dermatology. 2010. 221:17–22.
Article14. Huang H, Kamijima M, Wang H, Li S, Yoshikawa T, Lai G, et al. Human herpesvirus 6 reactivation in trichloroethylene-exposed workers suffering from generalized skin disorders accompanied by hepatic dysfunction. J Occup Health. 2006. 48:417–423.
Article15. Kamijima M, Hisanaga N, Wang H, Nakajima T. Occupational trichloroethylene exposure as a cause of idiosyncratic generalized skin disorders and accompanying hepatitis similar to drug hypersensitivities. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2007. 80:357–370.
Article16. Cheong HK, Kim EA, Choi JK, Choi SB, Suh JI, Choi DS, et al. Grand rounds: an outbreak of toxic hepatitis among industrial waste disposal workers. Environ Health Perspect. 2007. 115:107–112.
Article17. Bond GR. Hepatitis, rash and eosinophilia following trichloroethylene exposure: a case report and speculation on mechanistic similarity to halothane induced hepatitis. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 1996. 34:461–466.
Article18. Gut J, Christen U, Huwyler J. Mechanisms of halothane toxicity: novel insights. Pharmacol Ther. 1993. 58:133–155.
Article19. Smith GC, Kenna JG, Harrison DJ, Tew D, Wolf CR. Autoantibodies to hepatic microsomal carboxylesterase in halothane hepatitis. Lancet. 1993. 342:963–964.
Article20. Christen U, Quinn J, Yeaman SJ, Kenna JG, Clarke JB, Gandolfi AJ, et al. Identification of the dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase subunit of the human pyruvate dehydrogenase complex as an autoantigen in halothane hepatitis. Molecular mimicry of trifluoroacetyl-lysine by lipoic acid. Eur J Biochem. 1994. 223:1035–1047.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Late-onset trichloroethylene-induced hypersensitivity syndrome after intermittent exposure to low-dose trichloroethylene
- A Case of Trichloroethylene Hypersensitivity Syndrome
- Trichloroethylene Hypersensitivity Syndrome: Should Be Considered When Diagnosing DRESS Syndrome
- A Study on the Neuropsychiatric Symptom and Neurobehavioral Effects of Occupational Exposure to Trichloroethylene
- Health hazard of workers potentially exposed to trichloroethylene in the Inchon area