Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2015 Jun;8(2):117-122. 10.3342/ceo.2015.8.2.117.
Clinical Outcomes of Silk Patch in Acute Tympanic Membrane Perforation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Hallym University Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea. hlpch@paran.com
- 2Nano-Bio Regenerative Medical Institute, Hallym University, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Anyang, Korea. drran@hallym.or.kr
- KMID: 2360781
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2015.8.2.117
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
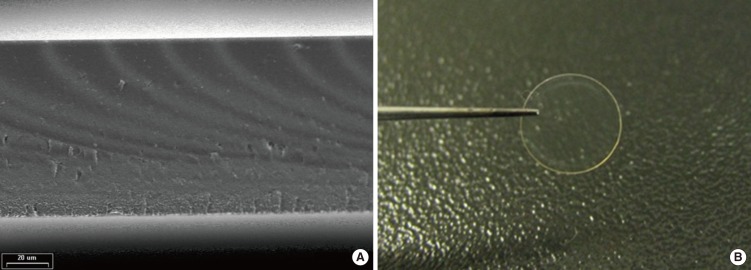
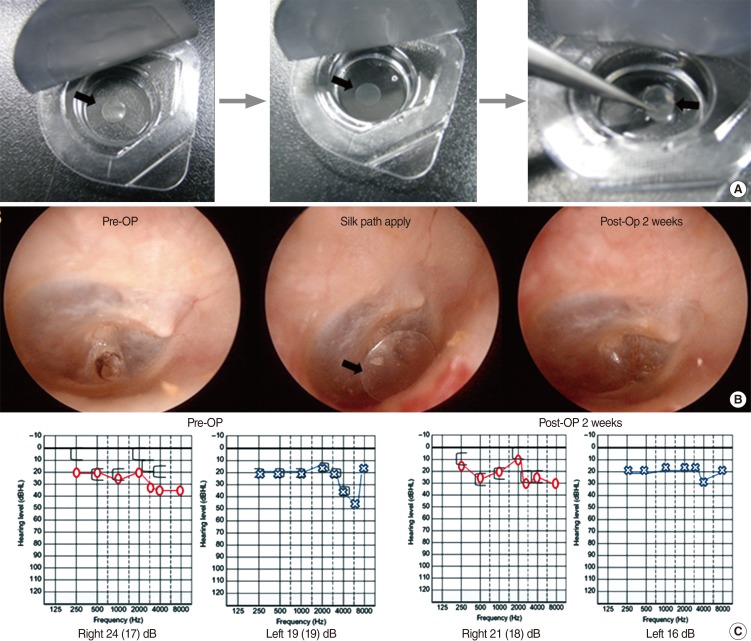
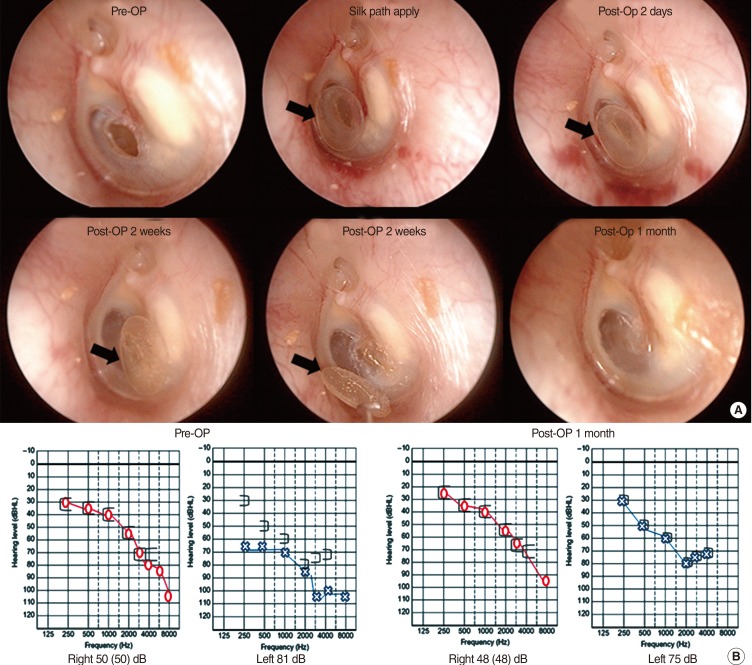
The silk patch is a thin transparent patch that is produced from silk fibroin. In this study, we investigated the treatment effects of the silk patch in patients with traumatic tympanic membrane perforation (TTMP).
METHODS
The closure rate, otorrhea rate, and closure time in all patients and the closure time in successful patients were compared between the paper patch and silk patch groups.
RESULTS
Demographic data (gender, site, age, traumatic duration, preoperative air-bone gap, and perforation size and location) were not significantly different between the two groups. The closure rate and otorrhea rate were not significantly different between the two groups. However, the closure time was different between the two groups (closure time of all patients, P=0.031; closure time of successful patients, P=0.037).
CONCLUSION
The silk patch which has transparent, elastic, adhesive, and hyper-keratinizing properties results in a more efficient closure time than the paper patch in the treatment of TTMP patients. We therefore believe that the silk patch should be recommended for the treatment of acute tympanic membrane perforation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Treatment for Acute Tympanic Membrane Perforation
Jian Yang, Zheng-Cai Lou
Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2016;9(3):284-285. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2015.01921.In Reply: Treatment for Acute Tympanic Membrane Perforation
Jun Ho Lee, Joong Seob Lee, Dong-Kyu Kim, Chan Hum Park, Hae Ran Lee
Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2016;9(4):386-386. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2016.00850.
Reference
-
1. da Lilly-Tariah OB, Somefun AO. Traumatic perforation of the tympanic membrane in University of Port Harcourt Teaching Hospital, Port Harcourt, Nigeria. Niger Postgrad Med J. 2007; 6. 14(2):121–124. PMID: 17599109.2. Orji FT, Agu CC. Determinants of spontaneous healing in traumatic perforations of the tympanic membrane. Clin Otolaryngol. 2008; 10. 33(5):420–426. PMID: 18983374.
Article3. Kristensen S. Spontaneous healing of traumatic tympanic membrane perforations in man: a century of experience. J Laryngol Otol. 1992; 12. 106(12):1037–1050. PMID: 1487657.
Article4. Teh BM, Marano RJ, Shen Y, Friedland PL, Dilley RJ, Atlas MD. Tissue engineering of the tympanic membrane. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2013; 4. 19(2):116–132. PMID: 23031158.
Article5. Levin B, Rajkhowa R, Redmond SL, Atlas MD. Grafts in myringoplasty: utilizing a silk fibroin scaffold as a novel device. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2009; 11. 6(6):653–664. PMID: 19911876.
Article6. Shen Y, Redmond SL, Teh BM, Yan S, Wang Y, Atlas MD, et al. Tympanic membrane repair using silk fibroin and acellular collagen scaffolds. Laryngoscope. 2013; 8. 123(8):1976–1982. PMID: 23536496.
Article7. Lee OJ, Lee JM, Kim JH, Kim J, Kweon H, Jo YY, et al. Biodegradation behavior of silk fibroin membranes in repairing tympanic membrane perforations. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2012; 8. 100(8):2018–2026. PMID: 22581612.
Article8. Kim J, Kim CH, Park CH, Seo JN, Kweon H, Kang SW, et al. Comparison of methods for the repair of acute tympanic membrane perforations: Silk patch vs. paper patch. Wound Repair Regen. 2010; Jan-Feb. 18(1):132–138. PMID: 20082686.
Article9. Park MK, Kim KH, Lee JD, Lee BD. Repair of large traumatic tympanic membrane perforation with a Steri-Strips patch. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2011; 10. 145(4):581–585. PMID: 21593464.
Article10. Saliba I. Hyaluronic acid fat graft myringoplasty: how we do it. Clin Otolaryngol. 2008; 12. 33(6):610–614. PMID: 19126140.
Article11. Mori H, Tsukada M. New silk protein: modification of silk protein by gene engineering for production of biomaterials. J Biotechnol. 2000; 8. 74(2):95–103. PMID: 11763506.
Article12. Horan RL, Antle K, Collette AL, Wang Y, Huang J, Moreau JE, et al. In vitro degradation of silk fibroin. Biomaterials. 2005; 6. 26(17):3385–3393. PMID: 15621227.
Article13. Meinel L, Hofmann S, Karageorgiou V, Kirker-Head C, McCool J, Gronowicz G, et al. The inflammatory responses to silk films in vitro and in vivo. Biomaterials. 2005; 1. 26(2):147–155. PMID: 15207461.
Article14. Mauney JR, Nguyen T, Gillen K, Kirker-Head C, Gimble JM, Kaplan DL. Engineering adipose-like tissue in vitro and in vivo utilizing human bone marrow and adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells with silk fibroin 3D scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2007; 12. 28(35):5280–5290. PMID: 17765303.
Article15. Kim JH, Choi SJ, Park JS, Lim KT, Choung PH, Kim SW, et al. Tympanic membrane regeneration using a water-soluble chitosan patch. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010; 1. 16(1):225–232. PMID: 19691425.
Article16. Altman GH, Diaz F, Jakuba C, Calabro T, Horan RL, Chen J, et al. Silk-based biomaterials. Biomaterials. 2003; 2. 24(3):401–416. PMID: 12423595.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment for Acute Tympanic Membrane Perforation
- The Effect of the Paper-patch Technique Trimmed with CO2 Laser on Treatment of Tympanic Membrane Perforation
- Therapeutic Effect of Multiple Paper Patching for Traumatic Tympanic Membrane Perforation-Trial of Quantitative Analysis Using Image Analyzer
- Clinical Analysis for Marginal Treatment of Tympanic Membrane Perforation with CO2 Laser Cauterization
- The Effect of the Amniotic Membrane on Treatment of Tympanic Membrane Perforation