J Korean Med Sci.
2016 Feb;31(2):315-320. 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.2.315.
Isolation of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus from a Patient of the 2015 Korean Outbreak
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. mdohmd@snu.ac.kr
- 2Laboratory of Infection & Immunity, Seoul National University Hospital Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Macrogen, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2360059
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.2.315
Abstract
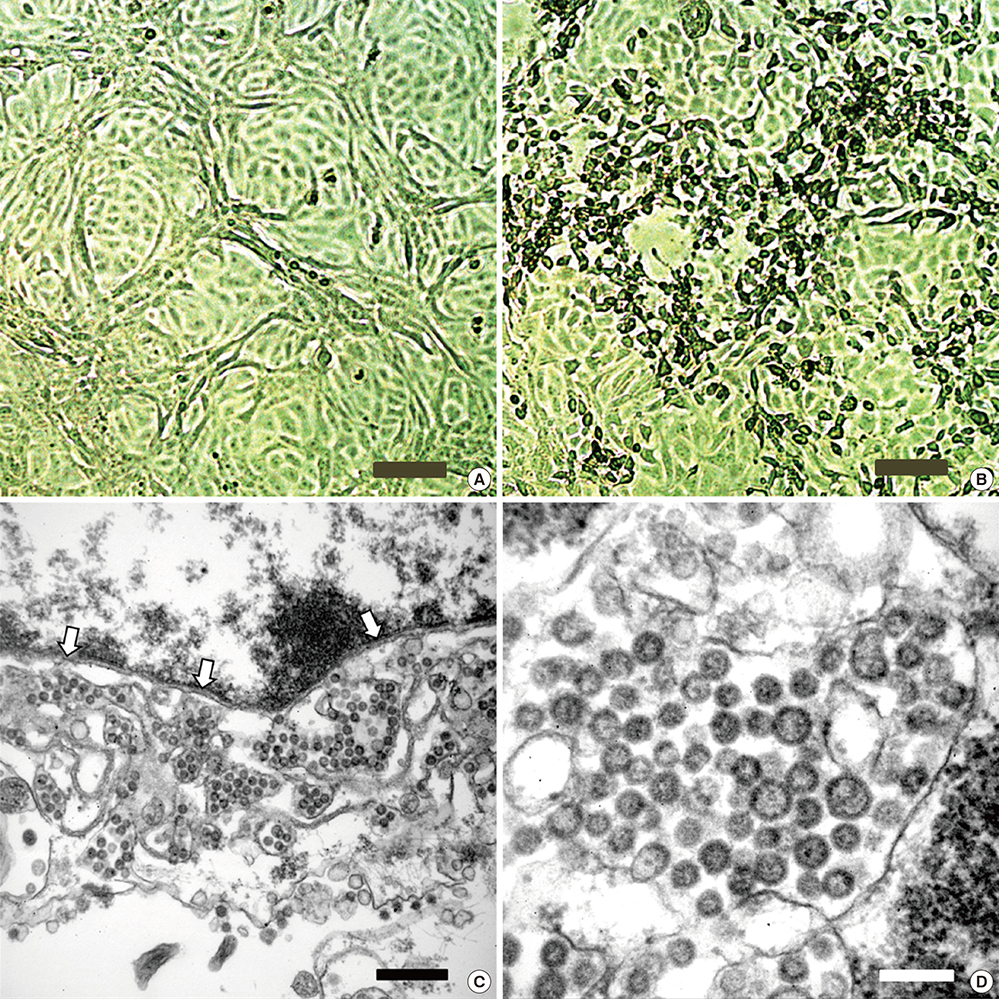
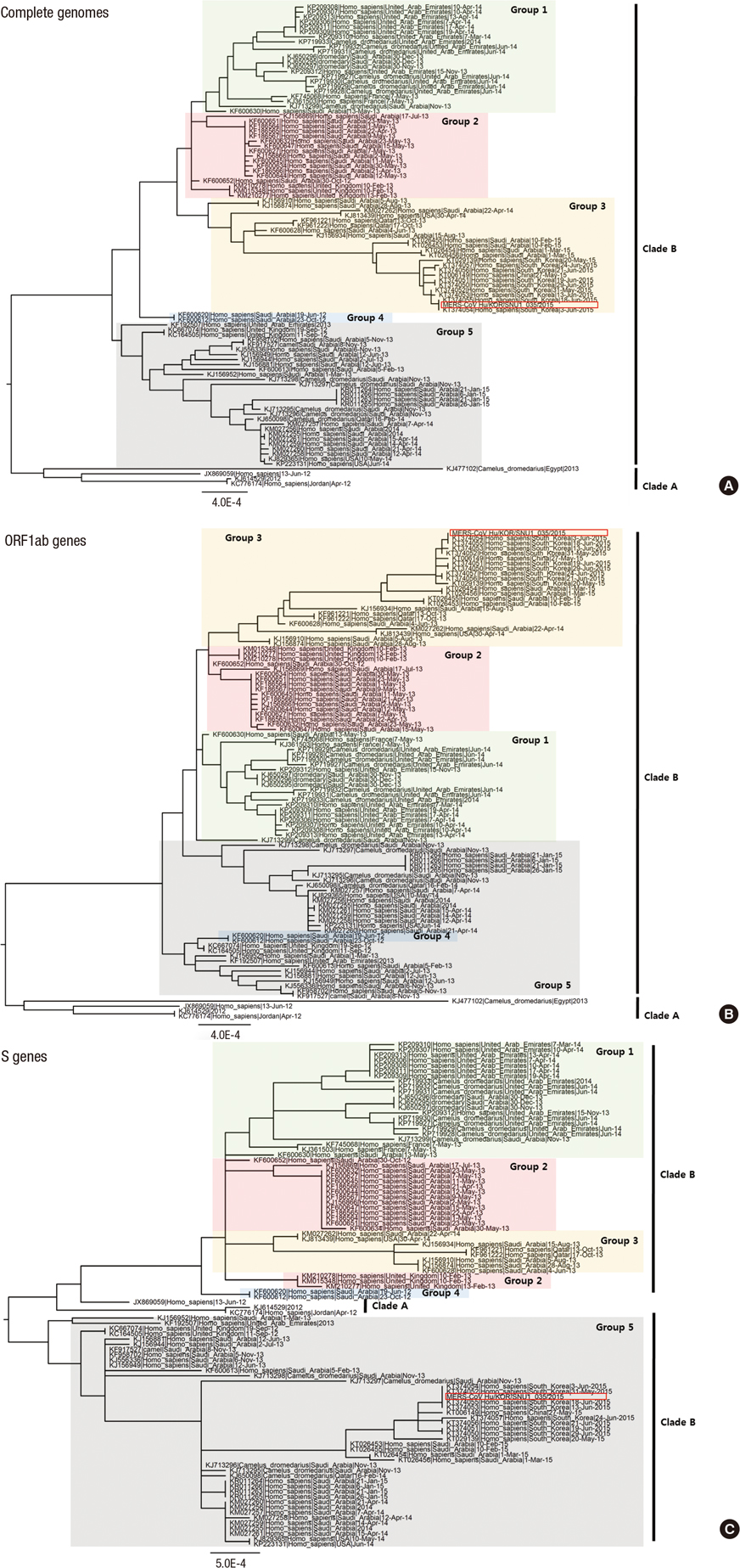
- During the 2015 outbreak of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) in Korea, 186 persons were infected, resulting in 38 fatalities. We isolated MERS-CoV from the oropharyngeal sample obtained from a patient of the outbreak. Cytopathic effects showing detachment and rounding of cells were observed in Vero cell cultures 3 days after inoculation of the sample. Spherical virus particles were observed by transmission electron microscopy. Full-length genome sequence of the virus isolate was obtained and phylogenetic analyses showed that it clustered with clade B of MERS-CoV.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Cercopithecus aethiops
Coronavirus Infections/*diagnosis/epidemiology/*virology
Disease Outbreaks
Humans
Microscopy, Electron
Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus/classification/genetics/*isolation & purification/ultrastructure
Phylogeny
Polymerase Chain Reaction
RNA, Viral/analysis/chemistry/metabolism
Republic of Korea/epidemiology
Sequence Analysis, RNA
Vero Cells
RNA, Viral
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Virus Isolation from the First Patient with SARS-CoV-2 in Korea
Wan Beom Park, Nak-Jung Kwon, Su-Jin Choi, Chang Kyung Kang, Pyoeng Gyun Choe, Jin Yong Kim, Jiyoung Yun, Gir-Won Lee, Moon-Woo Seong, Nam Joong Kim, Jeong-Sun Seo, Myoung-don Oh
J Korean Med Sci. 2020;35(7):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e84.
Reference
-
1. Chan JF, Lau SK, To KK, Cheng VC, Woo PC, Yuen KY. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus: another zoonotic betacoronavirus causing SARS-like disease. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2015; 28:465–522.2. Zumla A, Hui DS, Perlman S. Middle East respiratory syndrome. Lancet. 2015; 386:995–1007.3. Zaki AM, van Boheemen S, Bestebroer TM, Osterhaus AD, Fouchier RA. Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N Engl J Med. 2012; 367:1814–1820.4. World Health Organization. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) - Saudi Arabia: disease outbreak news. updated on 4 December 2015. Available at http://www.who.int/csr/don/4-december-2015-mers-saudi-arabia/en/.5. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus outbreak in the Republic of Korea, 2015. Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2015; 6:269–278.6. Chowell G, Abdirizak F, Lee S, Lee J, Jung E, Nishiura H, Viboud C. Transmission characteristics of MERS and SARS in the healthcare setting: a comparative study. BMC Med. 2015; 13:210.7. Breban R, Riou J, Fontanet A. Interhuman transmissibility of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus: estimation of pandemic risk. Lancet. 2013; 382:694–699.8. Cotten M, Watson SJ, Kellam P, Al-Rabeeah AA, Makhdoom HQ, Assiri A, Al-Tawfiq JA, Alhakeem RF, Madani H, AlRabiah FA, et al. Transmission and evolution of the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus in Saudi Arabia: a descriptive genomic study. Lancet. 2013; 382:1993–2002.9. Edelstein M, Heymann DL. What needs to be done to control the spread of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus? Future Virol. 2015; 10:497–505.10. Oh MD, Choe PG, Oh HS, Park WB, Lee SM, Park J, Lee SK, Song JS, Kim NJ. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus superspreading Event Involving 81 Persons, Korea 2015. J Korean Med Sci. 2015; 30:1701–1705.11. Graham L, Orenstein JM. Processing tissue and cells for transmission electron microscopy in diagnostic pathology and research. Nat Protoc. 2007; 2:2439–2450.12. Cotten M, Lam TT, Watson SJ, Palser AL, Petrova V, Grant P, Pybus OG, Rambaut A, Guan Y, Pillay D, et al. Full-genome deep sequencing and phylogenetic analysis of novel human betacoronavirus. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013; 19:736–742B.13. Seong MW, Kim SY, Corman VM, Kim TS, Cho SI, Kim MJ, Lee SJ, Lee JS, Seo SH, Ahn JS, et al. Microevolution of outbreak-associated Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus, South Korea, 2015. Emerg Infect Dis. Forthcoming. 2016.14. Kim DW, Kim YJ, Park SH, Yun MR, Yang JS, Kang HJ, Han YW, Lee HS, Man Kim H, Kim H, et al. Variations in spike glycoprotein gene of MERS-CoV, South Korea, 2015. Emerg Infect Dis. 2016; 22:100–104.15. Wang Y, Liu D, Shi W, Lu R, Wang W, Zhao Y, Deng Y, Zhou W, Ren H, Wu J, et al. Origin and possible genetic recombination of the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus from the first imported case in China: phylogenetics and coalescence analysis. MBio. 2015; 6:e01280–15.16. Tamura K, Nei M. Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions in the control region of mitochondrial DNA in humans and chimpanzees. Mol Biol Evol. 1993; 10:512–526.17. Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2013; 30:2725–2729.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- An Unexpected Outbreak of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Infection in the Republic of Korea, 2015
- The Same Middle East Respiratory Syndrome-Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) yet Different Outbreak Patterns and Public Health Impacts on the Far East Expert Opinion from the Rapid Response Team of the Republic of Korea
- Costly Lessons From the 2015 Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Outbreak in Korea
- The Korean Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Outbreak and Our Responsibility to the Global Scientific Community
- Middle East respiratory syndrome: what we learned from the 2015 outbreak in the Republic of Korea