J Korean Med Sci.
2016 Feb;31(2):190-195. 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.2.190.
The Significance of Ectopic Germinal Centers in the Minor Salivary Gland of Patients with Sjogren's Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School & Hospital, Gwangju, Korea. shinseok@chonnam.ac.kr
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Chonnam National University Medical School & Hospital, Gwangju, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology Chonnam National University Medical School & Hospital, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 2360041
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.2.190
Abstract
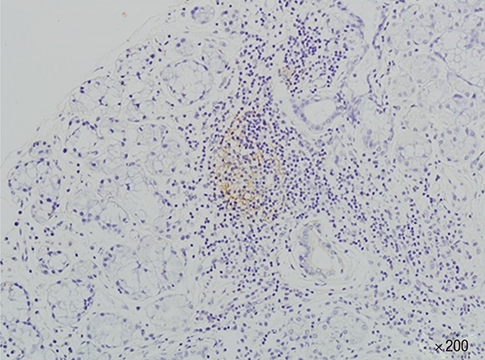
- We investigated the clinical and biological significance of germinal centers (GC) present in the minor salivary glands of patients with Sjogren's syndrome (SS). Minor salivary gland tissue biopsies from 93 patients with SS were used to identify GC-like structures, which were confirmed by CD21-positive follicular dendritic cell networks. Patients were compared based upon sociodemographics, glandular and extraglandular manifestations, and laboratory findings including autoantibody profiles, complement, and immunoglobulin levels; EULAR SS disease activity index (ESSDAI) and SS disease damage index (SSDDI) were also measured. GC-like structures were observed in 28 of 93 SS patients (30.1%). Mean focus scores and CRP levels were significantly higher in GC-positive patients than in GC-negative patients; GC-positive patients also exhibit a higher prevalence of rheumatoid factor and anti-SS-A/Ro antibodies compared to GC-negative patients. No differences in glandular or extra-glandular manifestations were evident between groups. In conclusion, SS patients with GC-like structures in the minor salivary glands exhibited laboratory profiles significantly different from those of their GC-negative counterparts. Long-term follow-up of these patients will be necessary to determine whether these laboratory abnormalities are predictive of clinical outcomes.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Autoantibodies/blood
C-Reactive Protein/analysis
Demography
Female
Germinal Center/*pathology
Humans
Immunohistochemistry
Male
Middle Aged
Receptors, Complement 3d/metabolism
Retrospective Studies
Salivary Glands, Minor/*pathology
Sjogren's Syndrome/immunology/metabolism/*pathology
Autoantibodies
C-Reactive Protein
Receptors, Complement 3d
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kassan SS, Moutsopoulos HM. Clinical manifestations and early diagnosis of Sjögren syndrome. Arch Intern Med. 2004; 164:1275–1284.2. Hansen A, Lipsky PE, Dörner T. Immunopathogenesis of primary Sjögren’s syndrome: implications for disease management and therapy. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2005; 17:558–565.3. Hagiwara E, Pando J, Ishigatsubo Y, Klinman DM. Altered frequency of type 1 cytokine secreting cells in the peripheral blood of patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome. J Rheumatol. 1998; 25:89–93.4. Mitsias DI, Tzioufas AG, Veiopoulou C, Zintzaras E, Tassios IK, Kogopoulou O, Moutsopoulos HM, Thyphronitis G. The Th1/Th2 cytokine balance changes with the progress of the immunopathological lesion of Sjogren’s syndrome. Clin Exp Immunol. 2002; 128:562–568.5. Bohnhorst JO, Bjørgan MB, Thoen JE, Jonsson R, Natvig JB, Thompson KM. Abnormal B cell differentiation in primary Sjögren’s syndrome results in a depressed percentage of circulating memory B cells and elevated levels of soluble CD27 that correlate with Serum IgG concentration. Clin Immunol. 2002; 103:79–88.6. Amft N, Curnow SJ, Scheel-Toellner D, Devadas A, Oates J, Crocker J, Hamburger J, Ainsworth J, Mathews J, Salmon M, et al. Ectopic expression of the B cell-attracting chemokine BCA-1 (CXCL13) on endothelial cells and within lymphoid follicles contributes to the establishment of germinal center-like structures in Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 2001; 44:2633–2641.7. Hansen A, Gosemann M, Pruss A, Reiter K, Ruzickova S, Lipsky PE, Dörner T. Abnormalities in peripheral B cell memory of patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 2004; 50:1897–1908.8. Hansen A, Odendahl M, Reiter K, Jacobi AM, Feist E, Scholze J, Burmester GR, Lipsky PE, Dörner T. Diminished peripheral blood memory B cells and accumulation of memory B cells in the salivary glands of patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 2002; 46:2160–2171.9. Szodoray P, Alex P, Jonsson MV, Knowlton N, Dozmorov I, Nakken B, Delaleu N, Jonsson R, Centola M. Distinct profiles of Sjögren’s syndrome patients with ectopic salivary gland germinal centers revealed by serum cytokines and BAFF. Clin Immunol. 2005; 117:168–176.10. Hansen A, Lipsky PE, Dörner T. B cells in Sjögren’s syndrome: indications for disturbed selection and differentiation in ectopic lymphoid tissue. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007; 9:218.11. Stott DI, Hiepe F, Hummel M, Steinhauser G, Berek C. Antigen-driven clonal proliferation of B cells within the target tissue of an autoimmune disease. The salivary glands of patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1998; 102:938–946.12. Jonsson MV, Skarstein K, Jonsson R, Brun JG. Serological implications of germinal center-like structures in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. J Rheumatol. 2007; 34:2044–2049.13. Jonsson MV, Skarstein K. Follicular dendritic cells confirm lymphoid organization in the minor salivary glands of primary Sjögren’s syndrome. J Oral Pathol Med. 2008; 37:515–521.14. Risselada AP, Looije MF, Kruize AA, Bijlsma JW, van Roon JA. The role of ectopic germinal centers in the immunopathology of primary Sjögren’s syndrome: a systematic review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2013; 42:368–376.15. Takemura S, Braun A, Crowson C, Kurtin PJ, Cofield RH, O’Fallon WM, Goronzy JJ, Weyand CM. Lymphoid neogenesis in rheumatoid synovitis. J Immunol. 2001; 167:1072–1080.16. Armengol MP, Juan M, Lucas-Martín A, Fernández-Figueras MT, Jaraquemada D, Gallart T, Pujol-Borrell R. Thyroid autoimmune disease: demonstration of thyroid antigen-specific B cells and recombination-activating gene expression in chemokine-containing active intrathyroidal germinal centers. Am J Pathol. 2001; 159:861–873.17. Sims GP, Shiono H, Willcox N, Stott DI. Somatic hypermutation and selection of B cells in thymic germinal centers responding to acetylcholine receptor in myasthenia gravis. J Immunol. 2001; 167:1935–1944.18. Serafini B, Rosicarelli B, Magliozzi R, Stigliano E, Aloisi F. Detection of ectopic B-cell follicles with germinal centers in the meninges of patients with secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. Brain Pathol. 2004; 14:164–174.19. Mazzucchelli L, Blaser A, Kappeler A, Schärli P, Laissue JA, Baggiolini M, Uguccioni M. BCA-1 is highly expressed in Helicobacter pylori-induced mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue and gastric lymphoma. J Clin Invest. 1999; 104:R49–54.20. Vinuesa CG, Sanz I, Cook MC. Dysregulation of germinal centres in autoimmune disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009; 9:845–857.21. Theander E, Vasaitis L, Baecklund E, Nordmark G, Warfvinge G, Liedholm R, Brokstad K, Jonsson R, Jonsson MV. Lymphoid organisation in labial salivary gland biopsies is a possible predictor for the development of malignant lymphoma in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011; 70:1363–1368.22. Manoussakis MN, Boiu S, Korkolopoulou P, Kapsogeorgou EK, Kavantzas N, Ziakas P, Patsouris E, Moutsopoulos HM. Rates of infiltration by macrophages and dendritic cells and expression of interleukin-18 and interleukin-12 in the chronic inflammatory lesions of Sjögren’s syndrome: correlation with certain features of immune hyperactivity and factors associated with high risk of lymphoma development. Arthritis Rheum. 2007; 56:3977–3988.23. Salomonsson S, Jonsson MV, Skarstein K, Brokstad KA, Hjelmström P, Wahren-Herlenius M, Jonsson R. Cellular basis of ectopic germinal center formation and autoantibody production in the target organ of patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 2003; 48:3187–3201.24. Jonsson MV, Szodoray P, Jellestad S, Jonsson R, Skarstein K. Association between circulating levels of the novel TNF family members APRIL and BAFF and lymphoid organization in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. J Clin Immunol. 2005; 25:189–201.25. Szyszko EA, Brokstad KA, Oijordsbakken G, Jonsson MV, Jonsson R, Skarstein K. Salivary glands of primary Sjögren’s syndrome patients express factors vital for plasma cell survival. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011; 13:R2.26. Reksten TR, Jonsson MV, Szyszko EA, Brun JG, Jonsson R, Brokstad KA. Cytokine and autoantibody profiling related to histopathological features in primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2009; 48:1102–1106.27. Aloisi F, Pujol-Borrell R. Lymphoid neogenesis in chronic inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006; 6:205–217.28. Barone F, Bombardieri M, Manzo A, Blades MC, Morgan PR, Challacombe SJ, Valesini G, Pitzalis C. Association of CXCL13 and CCL21 expression with the progressive organization of lymphoid-like structures in Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 2005; 52:1773–1784.29. Bombardieri M, Barone F, Humby F, Kelly S, McGurk M, Morgan P, Challacombe S, De Vita S, Valesini G, Spencer J, et al. Activation-induced cytidine deaminase expression in follicular dendritic cell networks and interfollicular large B cells supports functionality of ectopic lymphoid neogenesis in autoimmune sialoadenitis and MALT lymphoma in Sjögren’s syndrome. J Immunol. 2007; 179:4929–4938.30. Voulgarelis M, Dafni UG, Isenberg DA, Moutsopoulos HM. Malignant lymphoma in primary Sjögren’s syndrome: a multicenter, retrospective, clinical study by the European Concerted Action on Sjögren’s Syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1999; 42:1765–1772.31. Theander E, Henriksson G, Ljungberg O, Mandl T, Manthorpe R, Jacobsson LT. Lymphoma and other malignancies in primary Sjögren’s syndrome: a cohort study on cancer incidence and lymphoma predictors. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006; 65:796–803.32. Smedby KE, Hjalgrim H, Askling J, Chang ET, Gregersen H, Porwit-MacDonald A, Sundström C, Akerman M, Melbye M, Glimelius B, et al. Autoimmune and chronic inflammatory disorders and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma by subtype. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006; 98:51–60.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Sjogren Syndrome in Parotid Gland
- Update of Sjogren's Syndrome
- Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma of the Labial Minor Salivary Glands: Case Report
- A Case of Multiple Sialolithiasis in the Parotid Gland with Sjogren's Syndrome
- A Convenient and Less Invasive Technique of Labial Minor Salivary Gland Biopsy Using a Minimal Incision With a Needle Tip