Korean J Ophthalmol.
2016 Oct;30(5):335-343. 10.3341/kjo.2016.30.5.335.
Influence of Myopia on Size of Optic Nerve Head and Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Measured by Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. eyeyoung@hallym.or.kr
- 2Bundang Clean Eye Clinic, Seongnam, Korea.
- 3Somang Ophthalmic Clinic, Incheon, Korea.
- 4Haenam Kim's Eye Clinic, Haenam, Korea.
- 5Dain Eye Clinic, Incheon, Korea.
- 6Department of Ophthalmology, Armed Forces Capital Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 7Department of Ophthalmology, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 2353826
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2016.30.5.335
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To investigate optic nerve head size and retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness according to refractive status and axial length.
METHODS
In a cross-sectional study, 252 eyes of 252 healthy volunteers underwent ocular biometry measurement as well as optic nerve head and RNFL imaging by spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Correlation and linear regression analyses were performed for all subjects. The magnification effect was adjusted by the modified axial length method.
RESULTS
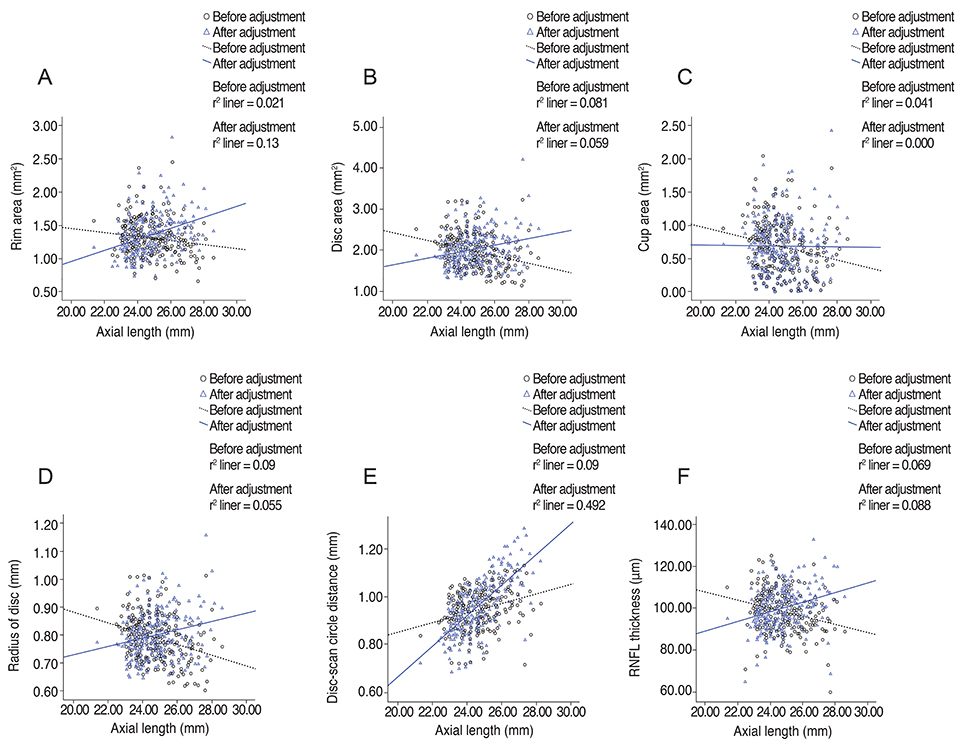
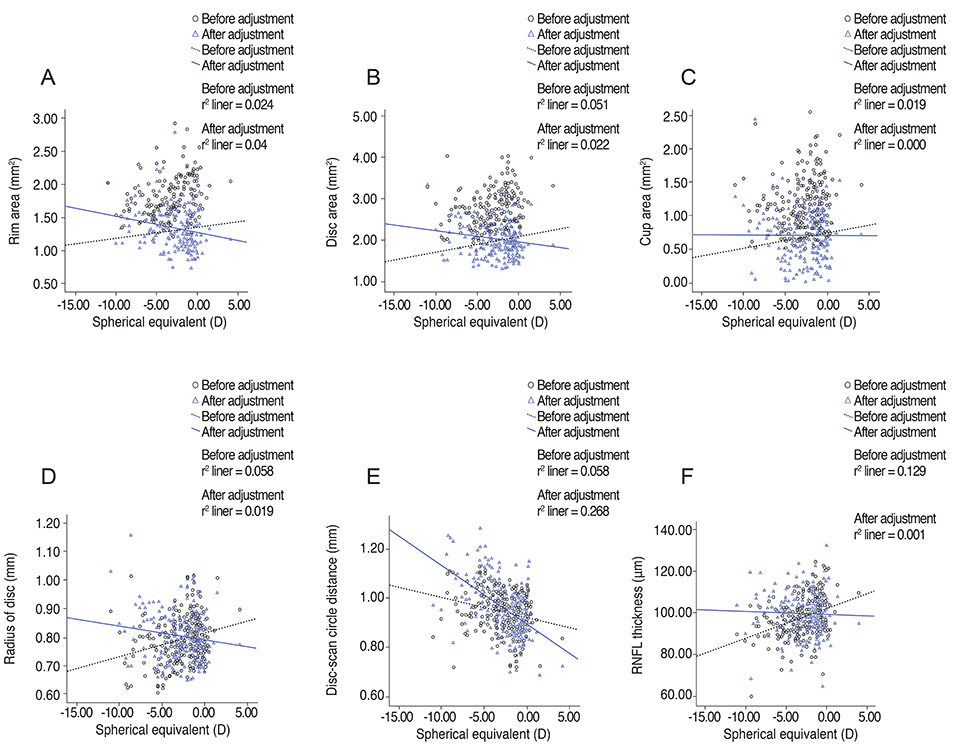
Disc area and spherical equivalent were positively correlated (r = 0.225, r² = 0.051, p = 0.000). RNFL thickness showed significant correlations with spherical equivalent (r = 0.359, r² = 0.129, p = 0.000), axial length (r = -0.262, r² = 0.069, p = 0.000), disc radius (r = 0.359, r² = 0.129, p = 0.000), and radius of the scan circle (r = -0.262, r² = 0.069, p = 0.000). After adjustment for the magnification effect, those relationships were reversed; RNFL thickness showed negative correlation with spherical equivalent and disc radius, and positive correlation with axial length and radius of the scan circle. The distance between the disc margin and the scan circle was closely correlated with RNFL thickness (r = -0.359, r² = 0.129, p = 0.000), which showed a negative correlation with axial length (r = -0.262, r² = 0.069, p = 0.000).
CONCLUSIONS
Optic disc radius and RNFL thickness decreased in more severely myopic eyes, but they increased after adjustment for magnification effect. The error due to the magnification effect and optic nerve head size difference might be factors that should be considered when interpreting optical coherence tomography results.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Effect of High Myopia on Optic Nerve Head by Confocal Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscopy in Nepalese Eyes
Sameer Bhaila, Sagun Narayan Joshi, Madhu Thapa, Gauri Shankar Shrestha
Korean J Ophthalmol. 2019;33(2):181-188. doi: 10.3341/kjo.2018.0098.
Reference
-
1. Hayreh SS. Optic disc changes in glaucoma. Br J Ophthalmol. 1972; 56:175–185.2. Lee KH, Park KH, Kim DM, Youn DH. Relationship between optic nerve head parameters of Heidelberg Retina Tomograph and visual field defects in primary open-angle glaucoma. Korean J Ophthalmol. 1996; 10:24–28.3. Chi T, Ritch R, Stickler D, et al. Racial differences in optic nerve head parameters. Arch Ophthalmol. 1989; 107:836–839.4. Mansour AM. Racial variation of optic disc size. Ophthalmic Res. 1991; 23:67–72.5. Varma R, Tielsch JM, Quigley HA, et al. Race-, age-, gender-, and refractive error-related differences in the normal optic disc. Arch Ophthalmol. 1994; 112:1068–1076.6. Tsai CS, Zangwill L, Gonzalez C, et al. Ethnic differences in optic nerve head topography. J Glaucoma. 1995; 4:248–257.7. Marsh BC, Cantor LB, WuDunn D, et al. Optic nerve head (ONH) topographic analysis by stratus OCT in normal subjects: correlation to disc size, age, and ethnicity. J Glaucoma. 2010; 19:310–318.8. Tomlinson A, Phillips CI. Ratio of optic cup to optic disc: in relation to axial length of eyeball and refraction. Br J Ophthalmol. 1969; 53:765–768.9. Jonas JB, Gusek GC, Naumann GO. Optic disk morphometry in high myopia. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1988; 226:587–590.10. Hyung SM, Kim DM, Hong C, Youn DH. Optic disc of the myopic eye: relationship between refractive errors and morphometric characteristics. Korean J Ophthalmol. 1992; 6:32–35.11. Samarawickrama C, Wang XY, Huynh SC, et al. Effects of refraction and axial length on childhood optic disk parameters measured by optical coherence tomography. Am J Ophthalmol. 2007; 144:459–461.12. Hoh ST, Lim MC, Seah SK, et al. Peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer thickness variations with myopia. Ophthalmology. 2006; 113:773–777.13. Melo GB, Libera RD, Barbosa AS, et al. Comparison of optic disk and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in nonglaucomatous and glaucomatous patients with high myopia. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006; 142:858–860.14. Uchida H, Yamamoto T, Araie M, et al. Topographic characteristics of the optic nerve head measured with scanning laser tomography in normal Japanese subjects. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2005; 49:469–476.15. Tay E, Seah SK, Chan SP, et al. Optic disk ovality as an index of tilt and its relationship to myopia and perimetry. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005; 139:247–252.16. Leung CK, Cheng AC, Chong KK, et al. Optic disc measurements in myopia with optical coherence tomography and confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscopy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007; 48:3178–3183.17. Kang SH, Hong SW, Im SK, et al. Effect of myopia on the thickness of the retinal nerve fiber layer measured by Cirrus HD optical coherence tomography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010; 51:4075–4083.18. Littmann H. Determination of the real size of an object on the fundus of the living eye. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 1982; 180:286–289.19. Bengtsson B, Krakau CE. Correction of optic disc measurements on fundus photographs. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1992; 230:24–28.20. Bennett AG, Rudnicka AR, Edgar DF. Improvements on Littmann's method of determining the size of retinal features by fundus photography. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1994; 232:361–367.21. Savini G, Barboni P, Parisi V, Carbonelli M. The influence of axial length on retinal nerve fibre layer thickness and optic-disc size measurements by spectral-domain OCT. Br J Ophthalmol. 2012; 96:57–61.22. Cheung CY, Chen D, Wong TY, et al. Determinants of quantitative optic nerve measurements using spectral domain optical coherence tomography in a population-based sample of non-glaucomatous subjects. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011; 52:9629–9635.23. Jonas JB. Optic disk size correlated with refractive error. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005; 139:346–348.24. Garway-Heath DF, Rudnicka AR, Lowe T, et al. Measurement of optic disc size: equivalence of methods to correct for ocular magnification. Br J Ophthalmol. 1998; 82:643–649.25. Jonas JB, Berenshtein E, Holbach L. Lamina cribrosa thickness and spatial relationships between intraocular space and cerebrospinal fluid space in highly myopic eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004; 45:2660–2665.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Normative Retinal and Choroidal Thicknesses of the Rabbit as Revealed by Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography
- Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Measured by Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography in Healthy Koreans
- Influence of Epiretinal Membranes on the Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Measured by Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography in Glaucoma
- Clinical Usefulness of Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography in Glaucoma and NAION
- Correlation between Visual Acuity and Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness in Optic Neuropathies