J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2018 Jun;59(6):537-542. 10.3341/jkos.2018.59.6.537.
Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Measured by Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography in Healthy Koreans
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. bjcho@kuh.ac.kr
- KMID: 2413816
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2018.59.6.537
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To determine normal retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness by age and to investigate the relationships of the RNFL with clinical variables using spectral domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) in healthy Koreans.
METHODS
The peripapillary RNFL thicknesses were measured around the optic disc using consecutive circular B-scans with 3.5 mm diameter and automatically calculated using a SD-OCT.
RESULTS
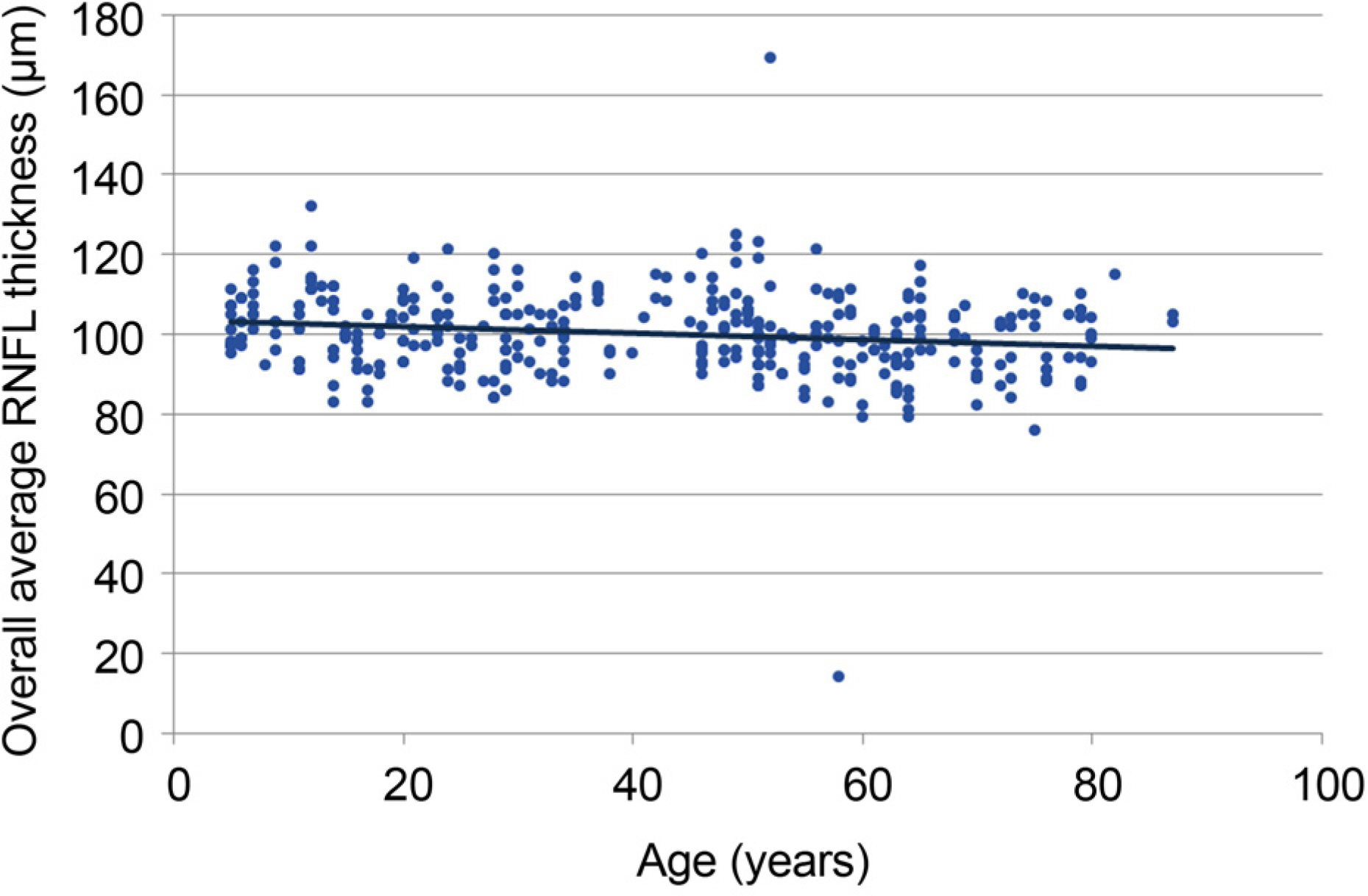
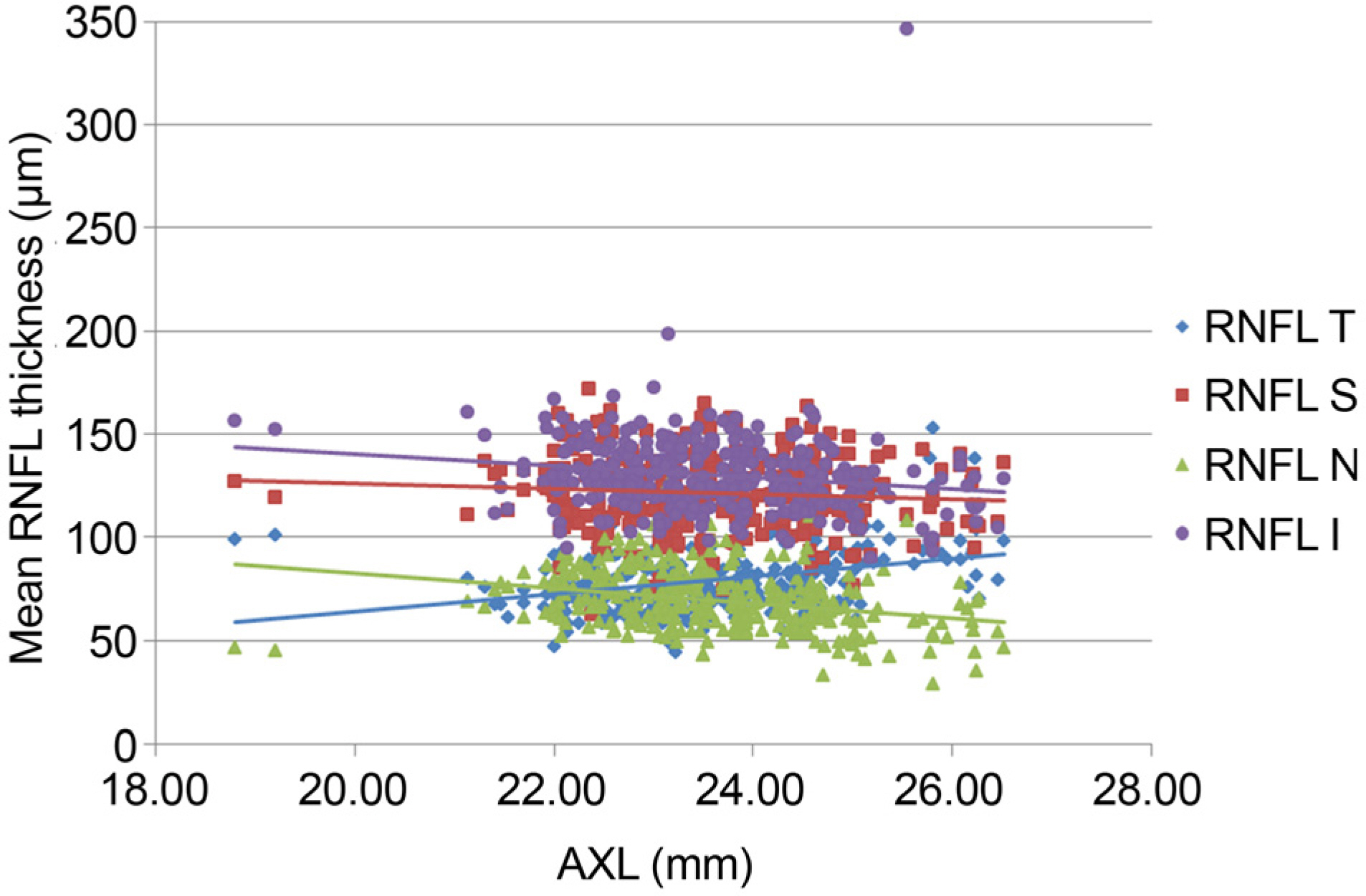
Three hundreds fifty-two eyes of 205 healthy subjects were included in the study and RNFL thickness were measured by SD-OCT. Overall average RNFL thickness was 100.2 ± 10.9 µm, and significantly and negatively correlated with age (r = −0.164, p = 0.002). The overall average RNFL thickness decrease per decade was 0.8 µm (95% confidence interval, −0.3 to −1.3, p = 0.019). Mean RNFL thickness of each quadrant was significantly correlated with axial length except in the superior quadrant.
CONCLUSIONS
This study describes the normal RNFL thickness values of Koreans as determined by SD-OCT. Furthermore, age was found to be correlated with normal RNFL thickness, however age-related changes were not uniform across every region.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Klaver CC, Wolfs RC, Vingerling JR, et al. Age-specific prevalence and causes of blindness and visual impairment in an older abdominal: the Rotterdam Study. Arch Ophthalmol. 1998; 116:653–58.2. Sommer A, Miller NR, Pollack I, et al. The nerve fiber layer in the diagnosis of glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 1977; 95:2149–56.
Article3. Quigley HA, Katz J, Derick RJ, et al. An evaluation of optic disc and nerve fiber layer examinations in monitoring progression of early glaucoma damage. Ophthalmology. 1992; 99:19–28.
Article4. Sommer A, Katz J, Quigley HA, et al. Clinically detectable nerve fiber atrophy precedes the onset of glaucomatous field loss. Arch Ophthalmol. 1991; 109:77–83.
Article5. Leung CK, Cheung CY, Weinreb RN, et al. Retinal nerve fiber abdominal imaging with spectraldomain optical coherence tomography: a variability and diagnostic performance study. Ophthalmology. 2009; 116:1257–63. 1263.e1–2.6. Kim JS, Ishikawa H, Sung KR, et al. Retinal nerve fibre layer thickness measurement reproducibility improved with spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Br J Ophthalmol. 2009; 93:1057–63.
Article7. Mwanza JC, Chang RT, Budenz DL, et al. Reproducibility of abdominal retinal nerve fiber layer thickness and optic nerve head parameters measured with cirrus HD-OCT in glaucomatous eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010; 51:5724–30.8. Lisboa R, Leite MT, Zangwill LM, et al. Diagnosing preperimetric glaucoma with spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology. 2012; 119:2261–9.
Article9. Budenz DL, Andersoon DR, Varma R, et al. Determinants of abdominal retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measured by Stratus OCT. Ophthalmology. 2007; 114:1046–52.10. Alasil T, Wang K, Keane PA, et al. Analysis of normal retinal nerve fiber layer thickness by age, sex, and race using spectral domain optical coherence tomography. J Glaucoma. 2013; 22:532–41.
Article11. Hyung SM, Kim DM, Hong C, Youn DH. Optic disc of the myopic eye: relationship between refractive errors and morphometric characteristics. Korean J Ophthalmol. 1992; 6:32–5.
Article12. Savini G, Zanini M, Carelli V, et al. Correlation between retinal nerve fibre layer thickness and optic nerve head size: an optical abdominal tomography study. Br J Ophthalmol. 2005; 89:489–92.13. Hougaard JL, Ostenfeld C, Heijl A, Bengtsson B. Modelling the normal retinal nerve fibre layer thickness as measured by Stratus optical coherence tomography. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2006; 244:1607–14.
Article14. Leung MM, Huang RY, Lam AK. Retinal nerve fiber layer abdominal in normal Hong Kong chinese children measured with optical coherence tomography. J Glaucoma. 2010; 19:95–9.15. Knight OJ, Chang RT, Feuer WJ, Budenz DL. Comparison of retinal nerve fiber layer measurements using time domain and spectral abdominal optical coherent tomography. Ophthalmology. 2009; 116:1271–7.16. Hirasawa H, Tomidokoro A, Araie M, et al. Peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer thickness determined by spectraldomain optical coherence tomography in ophthalmologically normal eyes. Arch Ophthalmol. 2010; 128:1420–6.
Article17. Lee JY, Hwang YH, Lee SM, Kim YY. Age and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measured by spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2012; 26:163–8.
Article18. Leung CK, Mohamed S, Leung KS, et al. Retinal nerve fiber layer measurements in myopia: An optical coherence tomography study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006; 47:5171–6.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography Findings in Acute Central Retinal Artery Occlusion
- Influence of Epiretinal Membranes on the Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Measured by Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography in Glaucoma
- Comparison of OCT Parameters between the Dominant and Nondominant Eye
- Comparison of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Measured by Spectral-Domain and Time-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography
- Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Measurement Comparison Using Spectral Domain and Swept Source Optical Coherence Tomography