J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2016 Apr;57(4):628-633. 10.3341/jkos.2016.57.4.628.
Correlation between Visual Acuity and Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness in Optic Neuropathies
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea. kseeye@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2212798
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2016.57.4.628
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To assess the correlation between retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness measured by optical coherence tomography (OCT, Cirrus HD-OCT®) and visual acuity in optic neuritis, ischemic optic neuropathy and traumatic optic neuropathy.
METHODS
Thirty-eight patients were recruited. RNFL thickness and visual acuity in optic neuritis, ischemic optic neuropathy and traumatic optic neuropathy were measured at least 6 months after the event. The correlation between log MAR best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) and retinal nerve fiber thickness in each quadrant was analyzed.
RESULTS
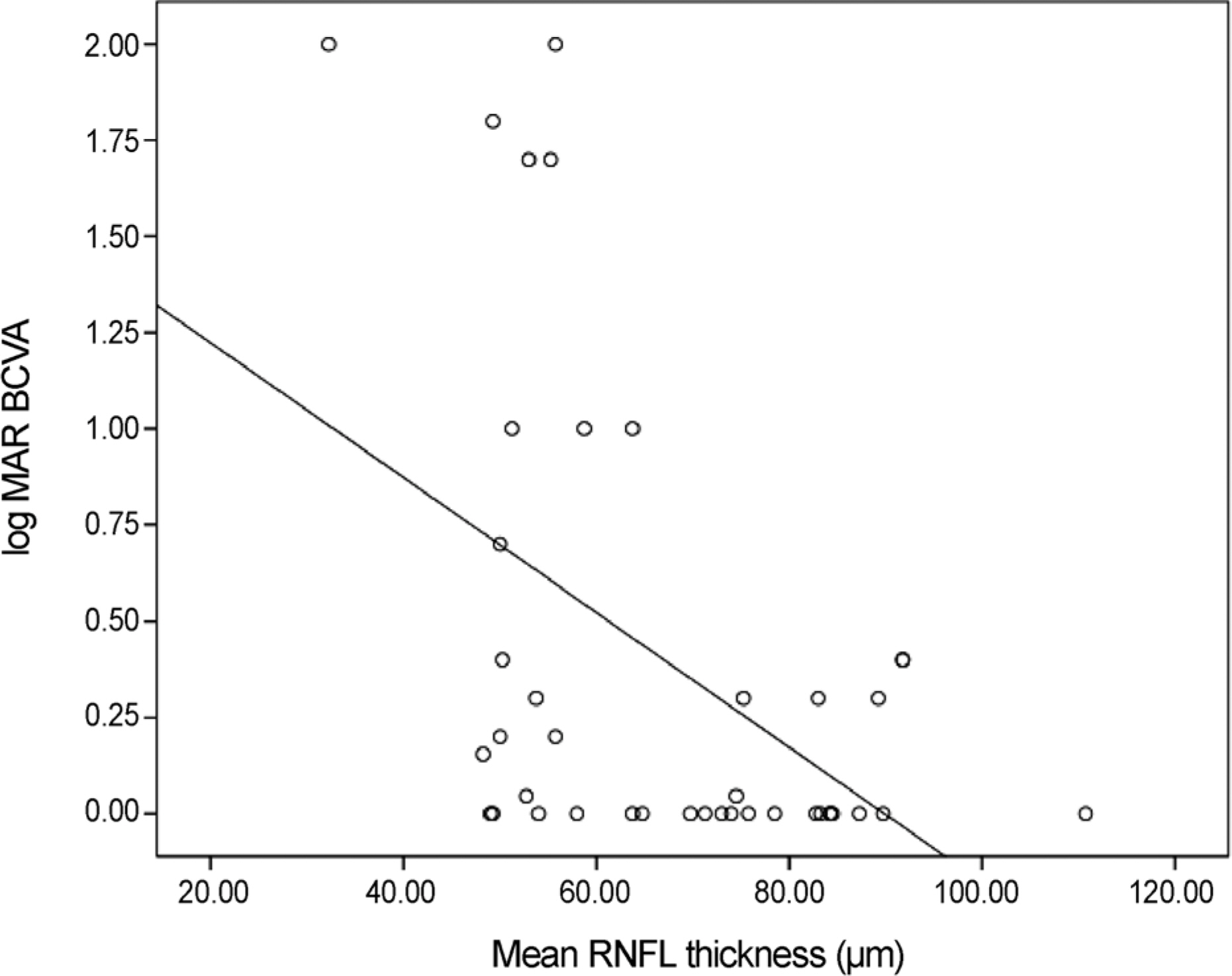
log MAR BCVA and RNFL thickness of each quadrant in optic neuropathy exhibited a statistically significant correlation. In optic neuritis, RNFL thickness of the superior quadrant was significantly thicker than in ischemic optic neuropathy and traumatic optic neuropathy (p = 0.009, 0.003). In addition, RNFL thickness of the inferior quadrant in optic neuritis was significantly thicker than in traumatic optic neuropathy (p = 0.012).
CONCLUSIONS
There was a statistically significant correlation between log MAR BCVA and RNFL thickness by OCT in patients with optic neuropathies. The RNFL thickness may predict visual acuity after an optic neuropathy attack and help to differentiate malingering patients with impaired vision loss.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Longitudinal Evaluation of Retinal Structure in Patients with Traumatic Optic Neuropathy Using Optical Coherence Tomography
Sung Ha Hwang, Jong Yeon Lee, Mijung Chi
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2018;59(1):73-80. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2018.59.1.73.
Reference
-
References
1. Thomas E. Ogden. Nerve fiber layer of the primate retina: thickness and glial content. Vision Res. 1983; 23:581–87.2. Blumenthal EZ, Williams JM, Weinreb RN, et al. Reproducibility of nerve fiber layer thickness measurements by use of optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology. 2000; 107:2278–82.3. Trip SA, Schlottmann PG, Jones SJ, et al. Retinal nerve fiber layer axonal loss and visual dysfunction in optic neuritis. Ann Neurol. 2005; 58:383–91.
Article4. Henderson AP, Altmann DR, Trip AS, et al. A serial study of retinal changes following optic neuritis with sample size estimates for acute neuroprotection trials. Brain. 2010; 133:2592–602.
Article5. Medeiros FA, Susanna R Jr. Retinal nerve fiber layer loss after traumatic optic neuropathy detected by scanning laser polarimetry. Arch Ophthalmol. 2001; 119:920–1.
Article6. Contreras I, Noval S, Rebolleda G, Muñoz-Negrete FJ. Follow-up of nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy with optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology. 2007; 114:2338–44.
Article7. Savini G, Zanini M, Carelli V, et al. Correlation between retinal nerve fiber layer thickness and optic nerve head size: an optical coherence tomography study. Br J Ophthalmol. 2005; 89:489–92.8. Ha DW, Sung K, Kim S, et al. Intraocular comparison of nerve fiber layer thickness and its relation with optic disc size in normal subjects. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2002; 16:8–12.9. Hayreh SS. Posterior ciliary artery circulation in health and disease: the Weisenfeld lecture. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004; 45:749–57. 748.
Article10. Hayreh SS. The blood supply of the optic nerve head and the evaluation of it - myth and reality. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2001; 20:563–93.
Article11. Omodaka K, Nakazawa T, Yokoyama Y, et al. Correlation between peripapillary macular fiber layer thickness and visual acuity in patients with open-angle glaucoma. Clin Ophthalmol. 2010; 4:629–35.12. Quigley HA, Davis EB, Anderson DR. Descending optic nerve degeneration in primates. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1977; 16:841–9.13. Hobom M, Storch MK, Weissert R, et al. Mechanisms and time course of neuronal degeneration in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Brain Pathol. 2004; 14:148–57.
Article14. Qi X, Lewin AS, Sun L, et al. Suppression of mitochondrial oxidative stress provides long-term neuroprotection in experimental optic neuritis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007; 48:681–91.
Article15. Fisher FB, Jacobs DA, Markowitz CE, et al. Relation of visual function to retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in multiple sclerosis. Ophthalmology. 2006; 113:324–32.
Article16. Noval S, Contreras I, Rebolleda G, et al. Optical coherence tomography versus automated perimetry for follow-up of optic neuritis. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2006; 84:790–4.
Article17. Barboni P, Savini G, Valentino ML, et al. Retinal nerve fiber layer evaluation by optical coherence tomography in Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy. Ophthalmology. 2005; 112:120–6.
Article18. Zoumalan CI, Agarwal M, Sadun AA. Optical coherence tomography can measure axonal loss in patients with ethambutol-induced optic neuropathy. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2005; 243:410–6.
Article19. Kanamori A, Escano MF, Eno A, et al. Evaluation of the effect of aging on retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measured by optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmologica. 2003; 217:273–8.
Article20. Evangelou N, Konz D, Esiri MM, et al. Size-selective neuronal changes in the anterior optic pathways suggest a differential susceptibility to injury in multiple sclerosis. Brain. 2001; 124(Pt 9):1813–20.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Thickness of Each Retinal Layer and Visual Acuity after Vitrectomy in Idiopathic Epiretinal Membrane
- Influence of RNFL Thickness on Visual Acuity and Visual Field in Bilateral Temporal Optic Atrophy
- Reproducibility of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Evaluation by Nerve Fiber Analyzer
- Two Cases of Topless Optic Disc Syndrome
- Differentiating Patients with Glaucoma from Glaucoma Suspects by Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Assessment Using Nerve Fiber Analyzer