Blood Res.
2016 Sep;51(3):193-199. 10.5045/br.2016.51.3.193.
Bendamustine in heavily pre-treated multiple myeloma patients: Results of a retrospective analysis from the Korean Multiple Myeloma Working Party
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea.
- 4Division of Hematology, Department of Internal Medicine, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Hematology-Oncology Clinic, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea.
- 6Department of Oncology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Department of Hematology-Oncology, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Hwasun, Korea.
- 8Department of Internal Medicine, Gachon University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 9Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ssysmc@snu.ac.kr
- 10Division of Hematology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ckmin@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2353501
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/br.2016.51.3.193
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Bendamustine may be a potential treatment option for patients with myeloma, but little is known about the utility of bendamustine as a salvage treatment, especially in Asian patients.
METHODS
We performed a multicenter retrospective study of patients with relapsed or refractory myeloma who received bendamustine and prednisone.
RESULTS
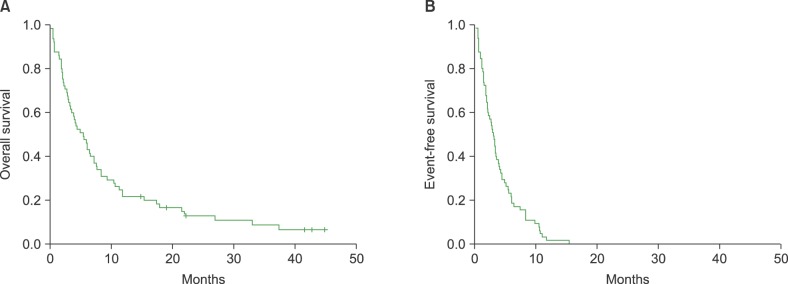
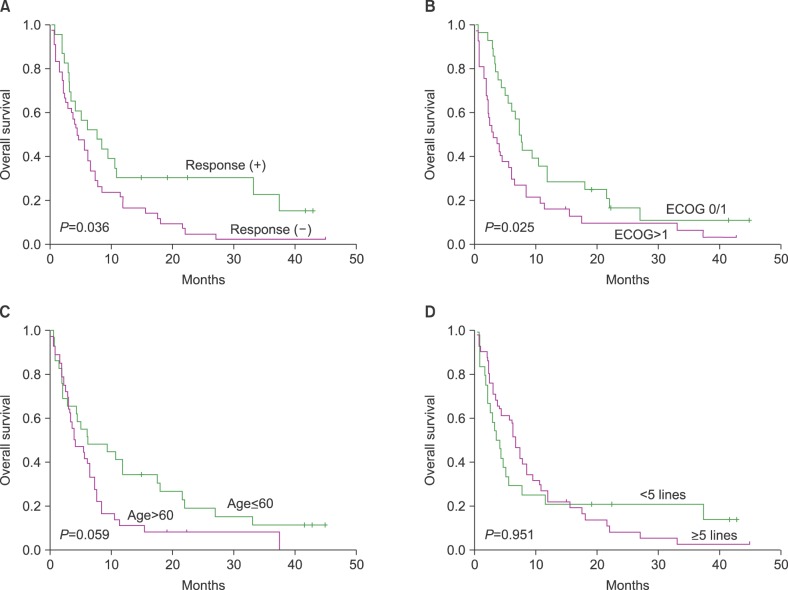
The records of 65 heavily pre-treated patients, who had undergone bortezomib and lenalidomide treatment (median number of previous treatments: 5), were analyzed. The median time from diagnosis to bendamustine treatment was 3.8 years, and the median patient age was 63 years (range, 38"’77 yr). The responses to the last treatment before bendamustine were refractory disease (N=52, 80%) or disease progression from partial response (N=13, 20%). Twenty-three patients responded to the treatment, with an overall response rate of 35% (23/65), and the median number of bendamustine treatment cycles was two (range, 1"’5 cycles). The median overall survival after bendamustine treatment was 5.5 months and the overall survival rate in responders to bendamustine was significantly better than that in non-responders (P=0.036).
CONCLUSION
Bendamustine may be a potential salvage treatment to extend survival in a select group of heavily pre-treated patients with relapsed or refractory myeloma.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Treatment of relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma
Ji Hyun Lee, Sung-Hyun Kim
Blood Res. 2020;55(Supplement):S43-S53. doi: 10.5045/br.2020.S008.Treatment of relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma
Ji Hyun Lee, Sung-Hyun Kim
Blood Res. 2020;55(S1):S43-S53. doi: 10.5045/br.2020.S008.Efficacy and Safety of Melphalan, Cyclophosphamide and Dexamethasone (MCD) as a Salvage Treatment for Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma
Seung-Shin Lee, Je-Jung Lee
Chonnam Med J. 2019;55(1):25-30. doi: 10.4068/cmj.2019.55.1.25.
Reference
-
1. Raab MS, Podar K, Breitkreutz I, Richardson PG, Anderson KC. Multiple myeloma. Lancet. 2009; 374:324–339. PMID: 19541364.
Article2. Kumar SK, Rajkumar SV, Dispenzieri A, et al. Improved survival in multiple myeloma and the impact of novel therapies. Blood. 2008; 111:2516–2520. PMID: 17975015.
Article3. Pulte D, Gondos A, Brenner H. Improvement in survival of older adults with multiple myeloma: results of an updated period analysis of SEER data. Oncologist. 2011; 16:1600–1603. PMID: 21968047.
Article4. Cavo M, Brioli A, Petrucci A, et al. Bortezomib with thalidomide plus dexamethasone compared with thalidomide plus dexamethasone as induction therapy before, and consolidation therapy after, double autologous stem-cell transplantation in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: a randomised phase 3 study. Lancet. 2010; 376:2075–2085. PMID: 21146205.
Article5. Kim HJ, Yoon SS, Eom HS, et al. Use of lenalidomide in the management of relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma: expert recommendations in Korea. Blood Res. 2015; 50:7–18. PMID: 25830125.
Article6. Kim SJ, Kim K, Kim BS, et al. Clinical features and survival outcomes in patients with multiple myeloma: analysis of web-based data from the Korean Myeloma Registry. Acta Haematol. 2009; 122:200–210. PMID: 19887776.
Article7. Lee JH, Lee DS, Lee JJ, et al. Multiple myeloma in Korea: past, present, and future perspectives. Experience of the Korean Multiple Myeloma Working Party. Int J Hematol. 2010; 92:52–57. PMID: 20544403.
Article8. Leoni LM, Bailey B, Reifert J, et al. Bendamustine (Treanda) displays a distinct pattern of cytotoxicity and unique mechanistic features compared with other alkylating agents. Clin Cancer Res. 2008; 14:309–317. PMID: 18172283.
Article9. Tageja N, Nagi J. Bendamustine: something old, something new. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2010; 66:413–423. PMID: 20376452.
Article10. Strumberg D, Harstrick A, Doll K, Hoffmann B, Seeber S. Bendamustine hydrochloride activity against doxorubicin-resistant human breast carcinoma cell lines. Anticancer Drugs. 1996; 7:415–421. PMID: 8826610.
Article11. Balfour JA, Goa KL. Bendamustine. Drugs. 2001; 61:631–638. discussion 639-40. PMID: 11368287.
Article12. Damaj G, Malard F, Hulin C, et al. Efficacy of bendamustine in relapsed/refractory myeloma patients: results from the French compassionate use program. Leuk Lymphoma. 2012; 53:632–634. PMID: 21916831.
Article13. Durie BG, Harousseau JL, Miguel JS, et al. International uniform response criteria for multiple myeloma. Leukemia. 2006; 20:1467–1473. PMID: 16855634.
Article14. Kyle RA, Rajkumar SV. Criteria for diagnosis, staging, risk stratification and response assessment of multiple myeloma. Leukemia. 2009; 23:3–9. PMID: 18971951.
Article15. Anderson KC, Kyle RA, Rajkumar SV, et al. Clinically relevant end points and new drug approvals for myeloma. Leukemia. 2008; 22:231–239. PMID: 17972944.
Article16. Lentzsch S, O'Sullivan A, Kennedy RC, et al. Combination of bendamustine, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (BLD) in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma is feasible and highly effective: results of phase 1/2 open-label, dose escalation study. Blood. 2012; 119:4608–4613. PMID: 22451423.
Article17. Ludwig H, Kasparu H, Leitgeb C, et al. Bendamustine-bortezomib-dexamethasone is an active and well-tolerated regimen in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. Blood. 2014; 123:985–991. PMID: 24227817.
Article