Endocrinol Metab.
2016 Sep;31(3):439-445. 10.3803/EnM.2016.31.3.439.
Correlation of Glypican-4 Level with Basal Active Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Level in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea. salee@jejunu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Anesthesiology, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea.
- KMID: 2352984
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.3.439
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Previous studies have reported that glypican-4 (GPC4) regulates insulin signaling by interacting with insulin receptor and through adipocyte differentiation. However, GPC4 has not been studied with regard to its effects on clinical factors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). We aimed to identify factors associated with GPC4 level in T2DM.
METHODS
Between January 2010 and December 2013, we selected 152 subjects with T2DM and collected serum and plasma into tubes pretreated with aprotinin and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor to preserve active gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1). GPC4, active GLP-1, active GIP, and other factors were measured in these plasma samples. We performed a linear regression analysis to identify factors associated with GPC4 level.
RESULTS
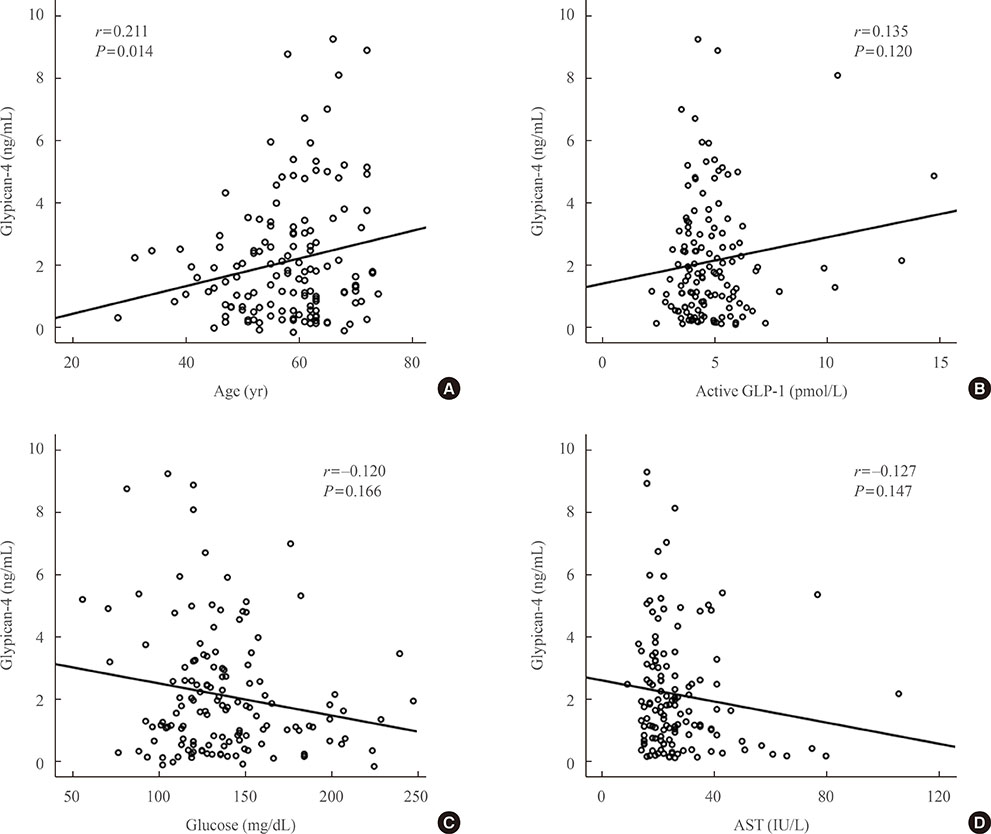
The subjects had a mean age of 58.1 years, were mildly obese (mean body mass index [BMI], 26.1 kg/m2), had T2DM of long-duration (mean, 101.3 months), glycated hemoglobin 7.5%, low insulin secretion, and low insulin resistance (mean homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance [HOMA-IR], 1.2). Their mean GPC4 was 2.0±0.2 ng/mL. In multivariate analysis, GPC4 was independently associated with age (β=0.224, P=0.009), and levels of active GLP-1 (β=0.171, P=0.049) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST; β=-0.176, P=0.043) after being adjusted for other clinical factors.
CONCLUSION
GPC4 was independently associated with age, active GLP-1, and AST in T2DM patients, but was not associated with HOMA-IR and BMI, which are well known factors related to GPC4. Further study is needed to identify the mechanisms of the association between GPC4 and basal active GLP-1 levels.
MeSH Terms
-
Adipocytes
Aprotinin
Aspartate Aminotransferases
Body Mass Index
Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2*
Gastric Inhibitory Polypeptide
Glucagon-Like Peptide 1*
Glypicans*
Hemoglobin A, Glycosylated
Humans
Insulin
Insulin Resistance
Linear Models
Multivariate Analysis
Plasma
Receptor, Insulin
Aprotinin
Aspartate Aminotransferases
Gastric Inhibitory Polypeptide
Glucagon-Like Peptide 1
Glypicans
Insulin
Receptor, Insulin
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lillioja S, Mott DM, Spraul M, Ferraro R, Foley JE, Ravussin E, et al. Insulin resistance and insulin secretory dysfunction as precursors of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Prospective studies of Pima Indians. N Engl J Med. 1993; 329:1988–1992.2. Chen KW, Boyko EJ, Bergstrom RW, Leonetti DL, Newell-Morris L, Wahl PW, et al. Earlier appearance of impaired insulin secretion than of visceral adiposity in the pathogenesis of NIDDM. 5-Year follow-up of initially nondiabetic Japanese-American men. Diabetes Care. 1995; 18:747–753.3. Hurt RT, Kulisek C, Buchanan LA, McClave SA. The obesity epidemic: challenges, health initiatives, and implications for gastroenterologists. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2010; 6:780–792.4. Fico A, Maina F, Dono R. Fine-tuning of cell signaling by glypicans. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011; 68:923–929.5. Gesta S, Bluher M, Yamamoto Y, Norris AW, Berndt J, Kralisch S, et al. Evidence for a role of developmental genes in the origin of obesity and body fat distribution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006; 103:6676–6681.6. Ussar S, Bezy O, Bluher M, Kahn CR. Glypican-4 enhances insulin signaling via interaction with the insulin receptor and serves as a novel adipokine. Diabetes. 2012; 61:2289–2298.7. Liu L, Gu H, Zhao Y, An L, Yang J. Glypican 4 may be involved in the adipose tissue redistribution in high-fat feeding C57BL/6J mice with peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor γ agonist rosiglitazone treatment. Exp Ther Med. 2014; 8:1813–1818.8. Yoo HJ, Hwang SY, Cho GJ, Hong HC, Choi HY, Hwang TG, et al. Association of glypican-4 with body fat distribution, insulin resistance, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013; 98:2897–2901.9. Li K, Xu X, Hu W, Li M, Yang M, Wang Y, et al. Glypican-4 is increased in human subjects with impaired glucose tolerance and decreased in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. Acta Diabetol. 2014; 51:981–990.10. Zhu HJ, Pan H, Cui Y, Wang XQ, Wang LJ, Li NS, et al. The changes of serum glypican4 in obese patients with different glucose metabolism status. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014; 99:E2697–E2701.11. Laakso M, Zilinskaite J, Hansen T, Boesgaard TW, Vanttinen M, Stancakova A, et al. Insulin sensitivity, insulin release and glucagon-like peptide-1 levels in persons with impaired fasting glucose and/or impaired glucose tolerance in the EU-GENE2 study. Diabetologia. 2008; 51:502–511.12. Smushkin G, Sathananthan A, Man CD, Zinsmeister AR, Camilleri M, Cobelli C, et al. Defects in GLP-1 response to an oral challenge do not play a significant role in the pathogenesis of prediabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012; 97:589–598.13. Faerch K, Torekov SS, Vistisen D, Johansen NB, Witte DR, Jonsson A, et al. GLP-1 response to oral glucose is reduced in prediabetes, screen-detected type 2 diabetes, and obesity and influenced by sex: the ADDITION-PRO study. Diabetes. 2015; 64:2513–2525.14. Lastya A, Saraswati MR, Suastika K. The low level of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is a risk factor of type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMC Res Notes. 2014; 7:849.15. Toft-Nielsen MB, Damholt MB, Madsbad S, Hilsted LM, Hughes TE, Michelsen BK, et al. Determinants of the impaired secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1 in type 2 diabetic patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001; 86:3717–3723.16. Nathan DM. Clinical practice. Initial management of glycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 2002; 347:1342–1349.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Correlations between Glucagon Stimulated C-peptide Levels and Microvascular Complications in Type 2 Diabetes Patients
- Clinical Efficacy of Glucagon Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Analogues
- Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association
- New Potential Targets of Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists in Pancreatic β-Cells and Hepatocytes
- Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Agonist