Yonsei Med J.
2015 Jan;56(1):196-203. 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.1.196.
Attenuation of Peripheral Regulatory T-Cell Suppression of Skin-Homing CD8+T Cells in Atopic Dermatitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Yidu Central Hospital, Weifang Medical University, Weifang, P.R. China.
- 2Department of Health Statistics, Public Health College of Weifang Medical University, Weifang, P.R. China.
- 3Department of Clinical Laboratory, Yidu Central Hospital, Weifang Medical University, Weifang, P.R. China.
- 4Department of Dermatology, Weifang Skin Disease Hospital, Weifang, P.R. China.
- 5Department of Stomatology, Yidu Central Hospital, Weifang Medical University, Weifang, P.R. China. dentistdg@sina.com
- KMID: 2352807
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2015.56.1.196
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Cutaneous lymphocyte-associated antigen (CLA)-expressing CD8+T cells have been known to play an important role in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis (AD). However, the mechanisms underlying the loss of self-tolerance remain unclear. Regulatory T cells (Tregs) play a key role in the development of homeostasis in the immune system. We, therefore, hypothesized that a reduced ability of Tregs to inhibit autologous CD8+CLA+T cells might be underlying mechanism in AD.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
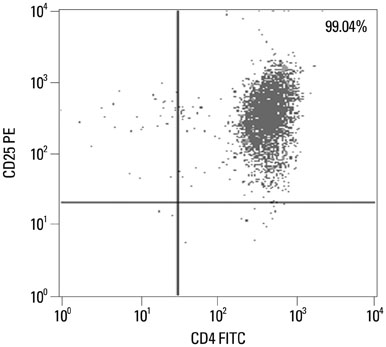
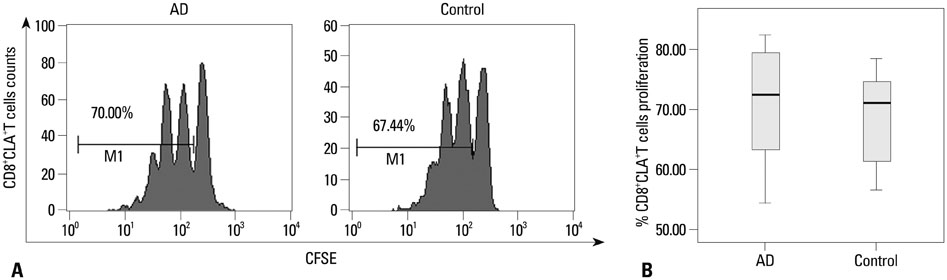
CD8+CLA+T cells and Tregs were obtained from the peripheral blood of AD patients and control volunteers. The frequencies of CD8+CLA+T cells were evaluated. The proliferative responses of CD8+CLA+T cells were assessed by flow cytometry, and the levels of transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1) and interleukin-10 (IL-10) in culture supernatants were detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
RESULTS
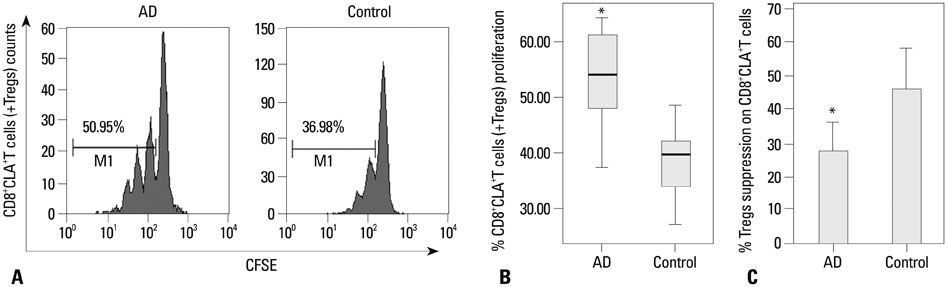
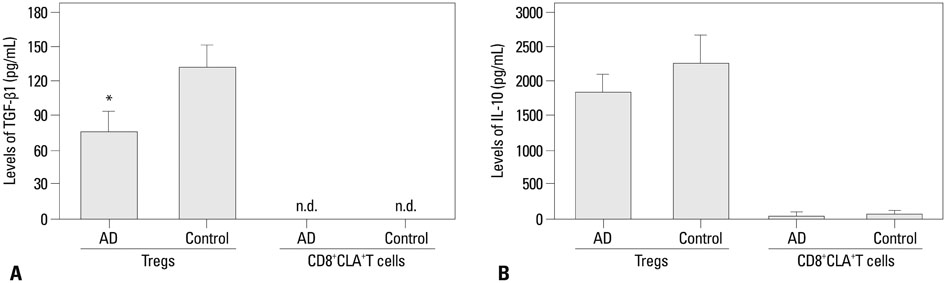
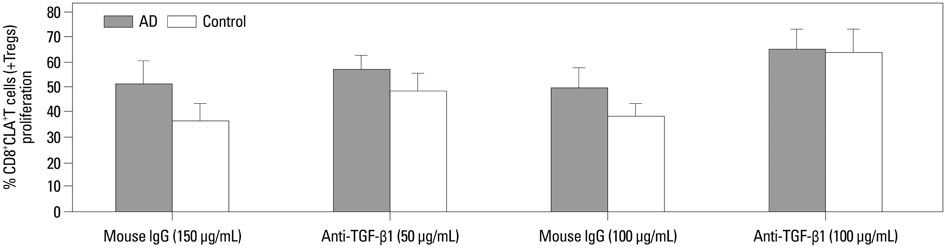
Our results revealed higher frequency and increased expression of perforin and granzyme-B in peripheral CD8+CLA+T cells in AD, and lower inhibitory ability of Tregs on proliferation of CD8+CLA+T cells in AD. Meanwhile, the levels of TGF-beta1 produced by Tregs were significantly lower in AD, and anti-TGF-beta1 abolished such suppression.
CONCLUSION
The attenuated inhibitory ability of Tregs on hyper-activated autologous CD8+CLA+T cells, mediated by TGF-beta1, plays an important role in the pathogenesis of AD.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
CD8-Positive T-Lymphocytes/drug effects/*immunology
Case-Control Studies
Cell Proliferation
Cell Separation
Dermatitis, Atopic/*immunology/pathology
Female
Granzymes/metabolism
Humans
Interleukin-10/metabolism
Lymphocyte Count
Male
Perforin/metabolism
Skin/*immunology/pathology
T-Lymphocytes, Cytotoxic/drug effects/immunology
T-Lymphocytes, Regulatory/drug effects/*immunology
Transforming Growth Factor beta1/pharmacology
Granzymes
Interleukin-10
Perforin
Transforming Growth Factor beta1
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bieber T. Atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2008; 358:1483–1494.
Article2. Hennino A, Jean-Decoster C, Giordano-Labadie F, Debeer S, Vanbervliet B, Rozières A, et al. CD8+ T cells are recruited early to allergen exposure sites in atopy patch test reactions in human atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 127:1064–1067.
Article3. Hennino A, Vocanson M, Toussaint Y, Rodet K, Benetière J, Schmitt AM, et al. Skin-infiltrating CD8+ T cells initiate atopic dermatitis lesions. J Immunol. 2007; 178:5571–5577.
Article4. Sallusto F, Lenig D, Förster R, Lipp M, Lanzavecchia A. Two subsets of memory T lymphocytes with distinct homing potentials and effector functions. Nature. 1999; 401:708–712.
Article5. Akdis M, Simon HU, Weigl L, Kreyden O, Blaser K, Akdis CA. Skin homing (cutaneous lymphocyte-associated antigen-positive) CD8+ T cells respond to superantigen and contribute to eosinophilia and IgE production in atopic dermatitis. J Immunol. 1999; 163:466–475.6. Teraki Y, Hotta T, Shiohara T. Increased circulating skin-homing cutaneous lymphocyte-associated antigen (CLA)+ type 2 cytokine-producing cells, and decreased CLA+ type 1 cytokine-producing cells in atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 2000; 143:373–378.
Article7. Sakaguchi S. Naturally arising CD4+ regulatory t cells for immunologic self-tolerance and negative control of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004; 22:531–562.8. Loser K, Hansen W, Apelt J, Balkow S, Buer J, Beissert S. In vitro-generated regulatory T cells induced by Foxp3-retrovirus infection control murine contact allergy and systemic autoimmunity. Gene Ther. 2005; 12:1294–1304.
Article9. Fontenot JD, Gavin MA, Rudensky AY. Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol. 2003; 4:330–336.
Article10. Hori S, Nomura T, Sakaguchi S. Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3. Science. 2003; 299:1057–1061.
Article11. Verhagen J, Akdis M, Traidl-Hoffmann C, Schmid-Grendelmeier P, Hijnen D, Knol EF, et al. Absence of T-regulatory cell expression and function in atopic dermatitis skin. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006; 117:176–183.
Article12. Caproni M, Antiga E, Torchia D, Volpi W, Barletta E, Gitti G, et al. FoxP3-expressing T regulatory cells in atopic dermatitis lesions. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2007; 28:525–528.
Article13. Schnopp C, Rad R, Weidinger A, Weidinger S, Ring J, Eberlein B, et al. Fox-P3-positive regulatory T cells are present in the skin of generalized atopic eczema patients and are not particularly affected by medium-dose UVA1 therapy. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2007; 23:81–85.
Article14. Szegedi A, Baráth S, Nagy G, Szodoray P, Gál M, Sipka S, et al. Regulatory T cells in atopic dermatitis: epidermal dendritic cell clusters may contribute to their local expansion. Br J Dermatol. 2009; 160:984–993.
Article15. Hanifin JM, Rajka G. Diagnostic features of atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol (Stockh 92). 1980; Suppl 92. 44–47.16. Sigmundsdóttir H, Gudjónsson JE, Jónsdóttir I, Lúdvíksson BR, Valdimarsson H. The frequency of CLA+ CD8+ T cells in the blood of psoriasis patients correlates closely with the severity of their disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 2001; 126:365–369.
Article17. Yano S, Nakamura K, Okochi H, Tamaki K. Analysis of the expression of cutaneous lymphocyte-associated antigen on the peripheral blood and cutaneous lymphocytes of alopecia areata patients. Acta Derm Venereol. 2002; 82:82–85.
Article18. Santamaria Babi LF, Picker LJ, Perez Soler MT, Drzimalla K, Flohr P, Blaser K, et al. Circulating allergen-reactive T cells from patients with atopic dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis express the skin-selective homing receptor, the cutaneous lymphocyte-associated antigen. J Exp Med. 1995; 181:1935–1940.
Article19. Akdis M, Akdis CA, Weigl L, Disch R, Blaser K. Skin-homing, CLA+ memory T cells are activated in atopic dermatitis and regulate IgE by an IL-13-dominated cytokine pattern: IgG4 counter-regulation by CLA- memory T cells. J Immunol. 1997; 159:4611–4619.20. Leung DY, Gately M, Trumble A, Ferguson-Darnell B, Schlievert PM, Picker LJ. Bacterial superantigens induce T cell expression of the skin-selective homing receptor, the cutaneous lymphocyte-associated antigen, via stimulation of interleukin 12 production. J Exp Med. 1995; 181:747–753.
Article21. Yawalkar N, Schmid S, Braathen LR, Pichler WJ. Perforin and granzyme B may contribute to skin inflammation in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 2001; 144:1133–1139.
Article22. Pastore S, Mascia F, Girolomoni G. The contribution of keratinocytes to the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. Eur J Dermatol. 2006; 16:125–131.23. Akdis M, Trautmann A, Klunker S, Daigle I, Kucuksezer UC, Deglmann W, et al. T helper (Th) 2 predominance in atopic diseases is due to preferential apoptosis of circulating memory/effector Th1 cells. FASEB J. 2003; 17:1026–1035.
Article24. Hilchey SP, Bernstein SH. Use of CFSE to monitor ex vivo regulatory T-cell suppression of CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell proliferation within unseparated mononuclear cells from malignant and non-malignant human lymph node biopsies. Immunol Invest. 2007; 36:629–648.
Article25. Toubi E. The role of CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells in autoimmune diseases. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2008; 34:338–344.
Article26. Costantino CM, Baecher-Allan CM, Hafler DA. Human regulatory T cells and autoimmunity. Eur J Immunol. 2008; 38:921–924.
Article27. Sugiyama H, Gyulai R, Toichi E, Garaczi E, Shimada S, Stevens SR, et al. Dysfunctional blood and target tissue CD4+CD25high regulatory T cells in psoriasis: mechanism underlying unrestrained pathogenic effector T cell proliferation. J Immunol. 2005; 174:164–173.
Article28. Antiga E, Quaglino P, Volpi W, Pierini I, Del Bianco E, Bianchi B, et al. Regulatory T cells in skin lesions and blood of patients with bullous pemphigoid. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013; [Epub ahead of print].
Article29. Lili Y, Yi W, Ji Y, Yue S, Weimin S, Ming L. Global activation of CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes correlates with an impairment in regulatory T cells in patients with generalized vitiligo. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e37513.
Article30. Umetsu DT, Akbari O, Dekruyff RH. Regulatory T cells control the development of allergic disease and asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 112:480–487.
Article31. Goodman WA, Cooper KD, McCormick TS. Regulation generation: the suppressive functions of human regulatory T cells. Crit Rev Immunol. 2012; 32:65–79.
Article32. Nakamura K, Kitani A, Strober W. Cell contact-dependent immunosuppression by CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells is mediated by cell surface-bound transforming growth factor beta. J Exp Med. 2001; 194:629–644.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Increased Cutaneous Lymphocyte Antigen (CLA) +T Cells in the Peripheral Blood of Children with Severe Atopic Dermatitis
- Quantitation of T Lymphocytes and T Subsets Peripheral Blood and Cutaneous Lesion in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis
- A Study of the T cell Subset of Atopic Dermatitis
- Changes in Peripheral Blood T Cells after Treatment of Cyclosporine in Children with Severe Atopic Dermatitis
- A Case of Atopic Dermatitis with Psoriasis