Korean J Crit Care Med.
2016 Aug;31(3):256-261. 10.4266/kjccm.2016.00213.
Use of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in a Fulminant Course of Amniotic Fluid Embolism Syndrome Immediately after Cesarean Delivery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. okabango21@gmail.com
- KMID: 2350911
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4266/kjccm.2016.00213
Abstract
- Amniotic fluid embolism is rare but is one of the most catastrophic complications in the peripartum period. This syndrome is caused by a maternal anaphylactic reaction to the introduction of fetal material into the pulmonary circulation. When amniotic fluid embolism is suspected, the immediate application of extracorporeal mechanical circulatory support such as veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) or cardiopulmonary bypass should be considered. Without the application of extracorporeal mechanical circulatory support, medical supportive care might not be sufficient to maintain cardiopulmonary stabilization in severe cases of amniotic fluid embolism. In this report, we present the case of a 36-year-old pregnant woman who developed an amniotic fluid embolism immediately after a cesarean section. Her catastrophic event started with the sudden onset of severe hypoxia, followed by circulatory collapse within 8 minutes. The veno-arterial mode of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation was initiated immediately. She was successfully resuscitated but with impaired cognitive function. Thus, urgent ECMO should be considered when amniotic fluid embolism syndrome is suspected in patients presenting acute cardiopulmonary collapse.
MeSH Terms
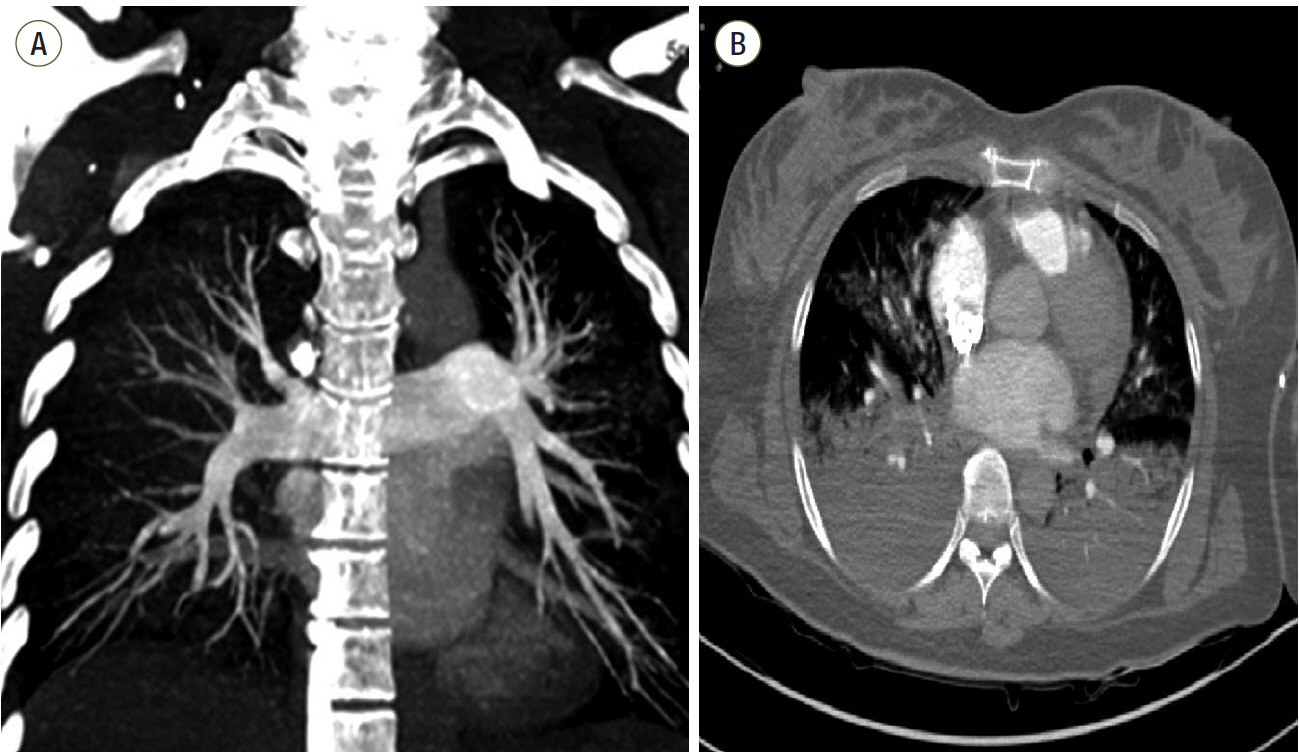
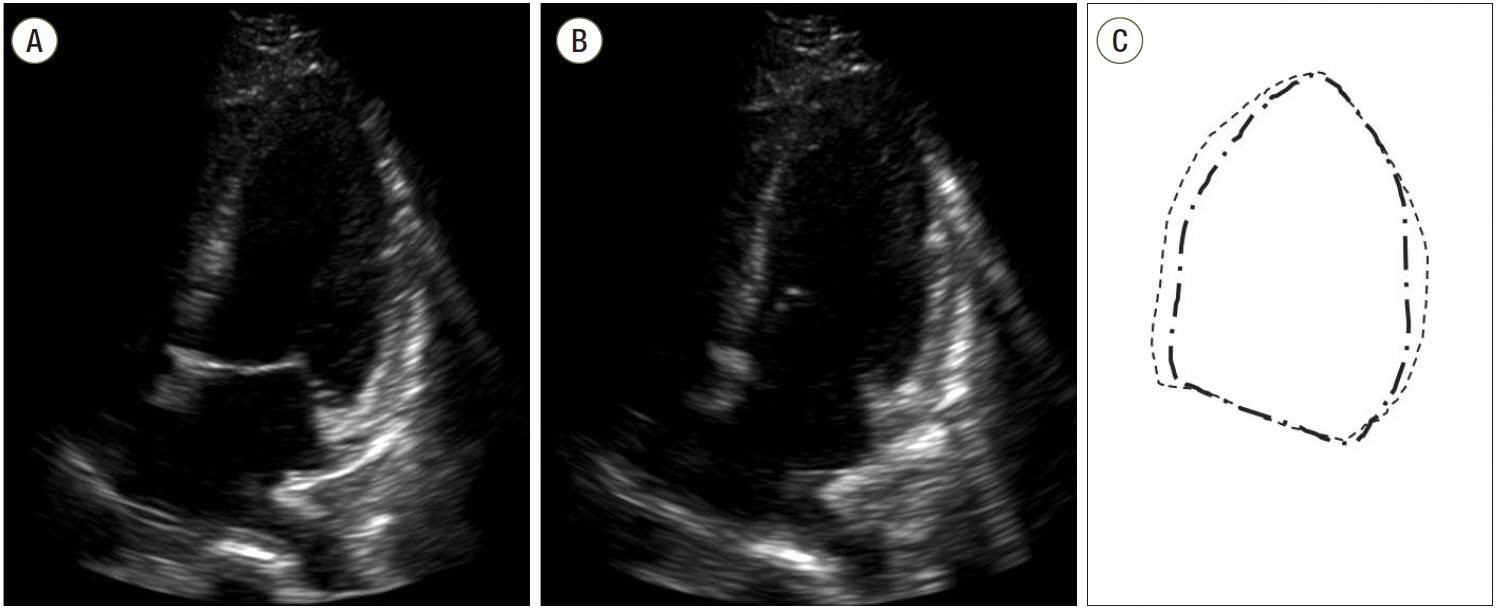
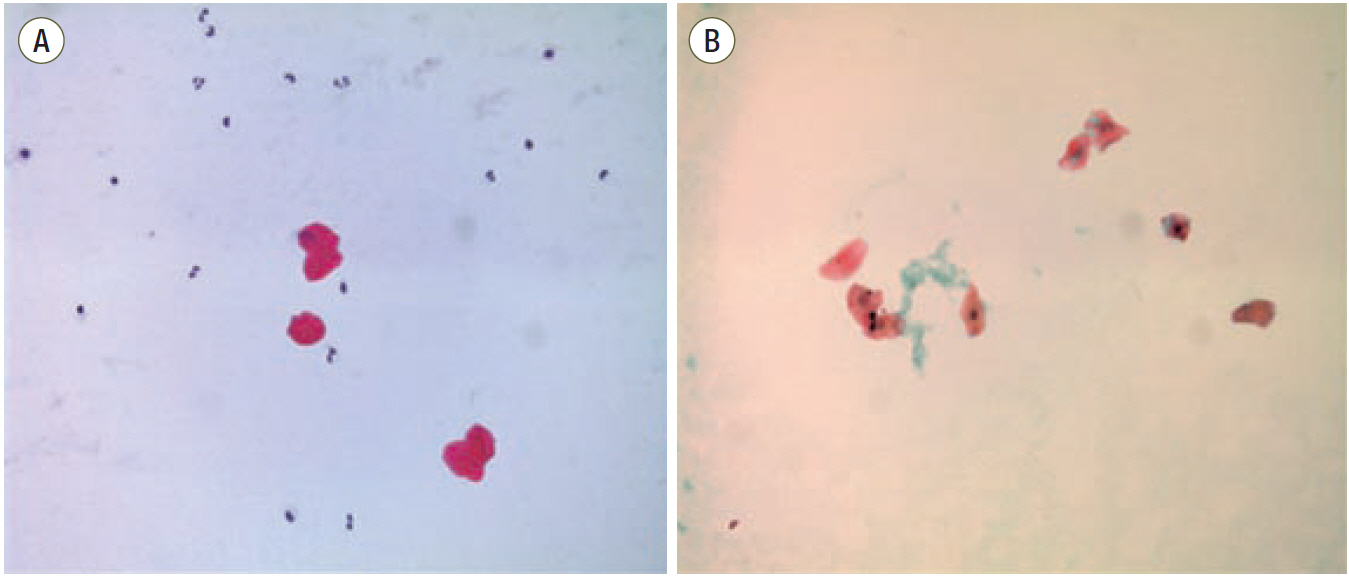
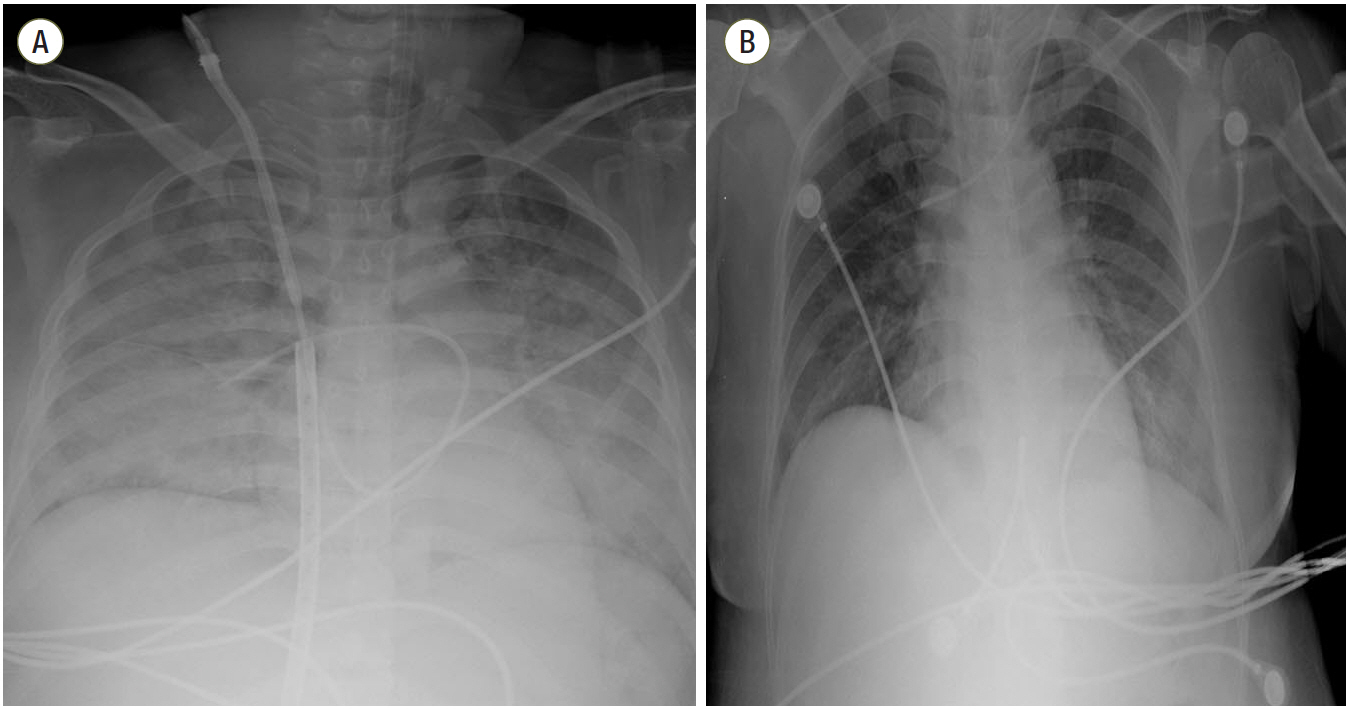
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Urgent Application of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in Amniotic Fluid Embolism
Moo Suk Park
Korean J Crit Care Med. 2016;31(3):179-180. doi: 10.4266/kjccm.2016.00745.
Reference
-
References
1. Clark SL, Hankins GD, Dudley DA, Dildy GA, Porter TF. Amniotic fluid mbolism: ional registry. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1995; 172:1158–67.2. Walsh SW, Wang Y, Jesse R. Peroxide induces vasoconstriction in the human placenta by stimulating thromboxane. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1993; 169:1007–12.
Article3. Ecker JL, Solt K, Fitzsimons MG, MacGillivray TE. Case 40-2012: a 43-year-old woman with cardiorespiratory arrest after a cesarean section. N Engl J Med. 2012; 367:2528–36.4. Price TM, Baker VV, Cefalo RC. Amniotic fluid embolism. Three case reports with a review of the literature. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 1985; 40:462–5.
Article5. Moore J, Baldisseri MR. Amniotic fluid embolism. Crit Care Med. 2005; 33:S279–85.
Article6. Stanten RD, Iverson LI, Daugharty TM, Lovett SM, Terry C, Blumenstock E. Amniotic fluid embolism causing catastrophic pulmonary vasoconstriction: diagnosis by transesophageal echocardiogram and treatment by cardiopulmonary bypass. Obstet Gynecol. 2003; 102:496–8.
Article7. Gist RS, Stafford IP, Leibowitz AB, Beilin Y. Amniotic fluid embolism. Anesth Analg. 2009; 108:1599–602.
Article8. Estellés A, Gilabert J, Andrés C, España F, Aznar J. Plasminogen activator inhibitors type 1 and type 2 and plasminogen activators in amniotic fluid during pregnancy. Thromb Haemost. 1990; 64:281–5.
Article9. Stoeger A, Daniaux M, Felber S, Stockhammer G, Aichner F, zur Nedden D. MRI findings in cerebral fat embolism. Eur Radiol. 1998; 8:1590–3.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Successful Application of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for a Patient with Clinical Amniotic Fluid Embolism
- Urgent Application of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in Amniotic Fluid Embolism
- Anesthetic experience using extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for cesarean section in the patient with peripartum cardiomyopathy: a case report
- Percutaneous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) for Acute Fulminant Myocarditis
- Venous Air Embolism Not Amniotic Fluid Embolism