Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2016 Sep;20(5):507-514. 10.4196/kjpp.2016.20.5.507.
Spatial reproducibility of complex fractionated atrial electrogram depending on the direction and configuration of bipolar electrodes: an in-silico modeling study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Yonsei University Health System, Seoul 03722, Korea. hnpak@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Mechanical and Biomedical Engineering, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon 24341, Korea. ebshim@kangwon.ac.kr
- KMID: 2350507
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2016.20.5.507
Abstract
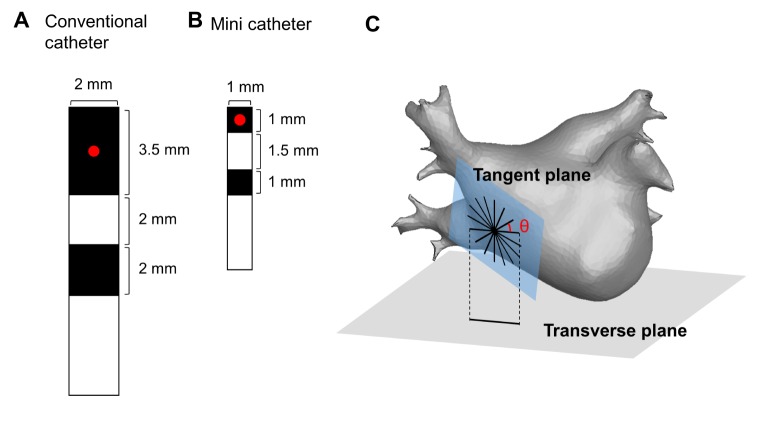
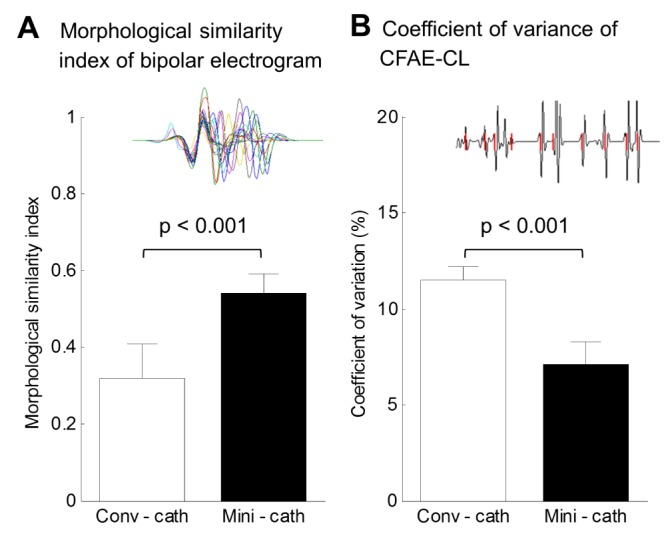
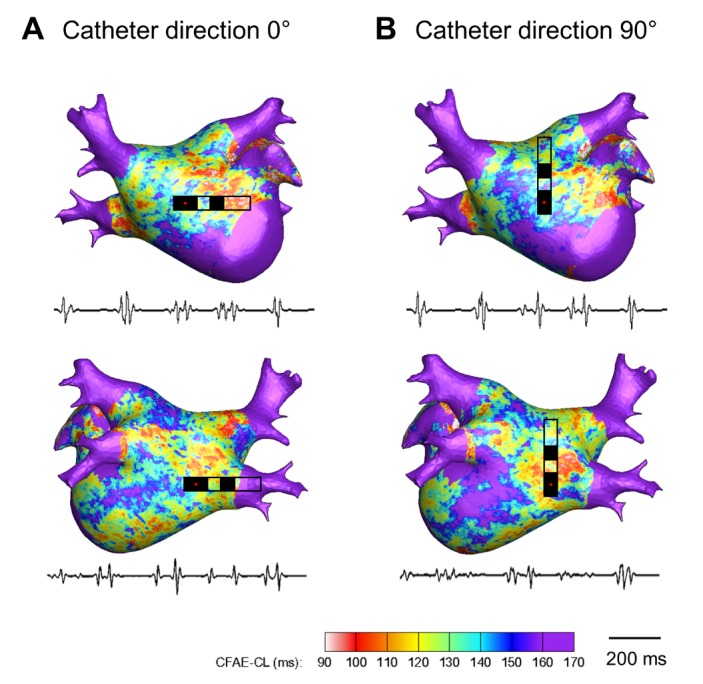
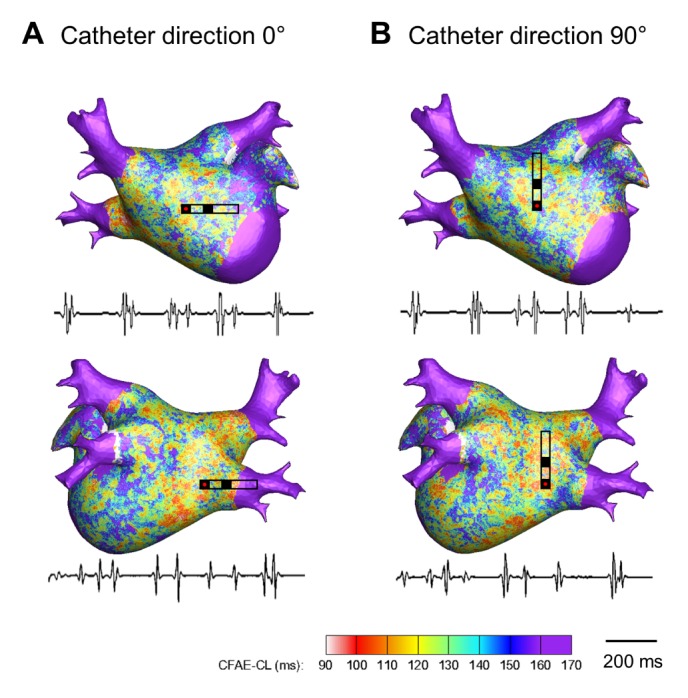
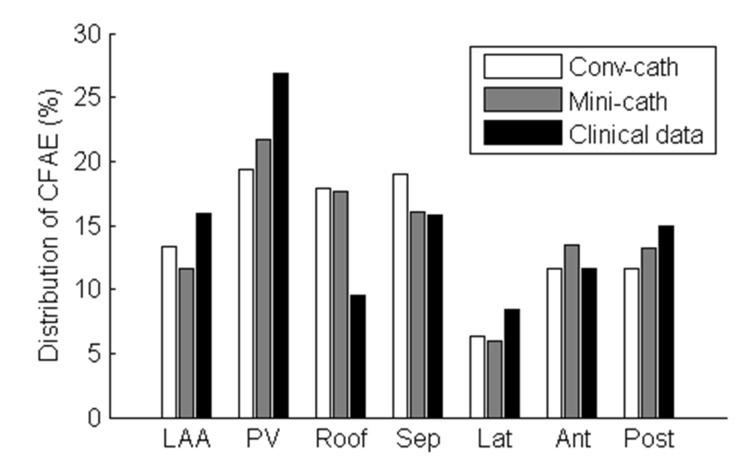
- Although 3D-complex fractionated atrial electrogram (CFAE) mapping is useful in radiofrequency catheter ablation for persistent atrial fibrillation (AF), the directions and configuration of the bipolar electrodes may affect the electrogram. This study aimed to compare the spatial reproducibility of CFAE by changing the catheter orientations and electrode distance in an in-silico left atrium (LA). We conducted this study by importing the heart CT image of a patient with AF into a 3D-homogeneous human LA model. Electrogram morphology, CFAE-cycle lengths (CLs) were compared for 16 different orientations of a virtual bipolar conventional catheter (conv-cath: size 3.5 mm, inter-electrode distance 4.75 mm). Additionally, the spatial correlations of CFAE-CLs and the percentage of consistent sites with CFAE-CL<120 ms were analyzed. The results from the conv-cath were compared with that obtained using a mini catheter (mini-cath: size 1 mm, inter-electrode distance 2.5 mm). Depending on the catheter orientation, the electrogram morphology and CFAE-CLs varied (conv-cath: 11.5±0.7% variation, mini-cath: 7.1±1.2% variation), however the mini-cath produced less variation of CFAE-CL than conv-cath (p<0.001). There were moderate spatial correlations among CFAE-CL measured at 16 orientations (conv-cath: r=0.3055±0.2194 vs. mini-cath: 0.6074±0.0733, p<0.001). Additionally, the ratio of consistent CFAE sites was higher for mini catheter than conventional one (38.3±4.6% vs. 22.3±1.4%, p<0.05). Electrograms and CFAE distribution are affected by catheter orientation and electrode configuration in the in-silico LA model. However, there was moderate spatial consistency of CFAE areas, and narrowly spaced bipolar catheters were less influenced by catheter direction than conventional catheters.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. January CT, Wann LS, Alpert JS, Calkins H, Cigarroa JE, Cleveland JC Jr, Conti JB, Ellinor PT, Ezekowitz MD, Field ME, Murray KT, Sacco RL, Stevenson WG, Tchou PJ, Tracy CM, Yancy CW. ACC/AHA Task Force Members. 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation. 2014; 130:e199–e267. PMID: 24682347.
Article2. Oral H, Knight BP, Tada H, Ozaydin M, Chugh A, Hassan S, Scharf C, Lai SW, Greenstein R, Pelosi F Jr, Strickberger SA, Morady F. Pulmonary vein isolation for paroxysmal and persistent atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2002; 105:1077–1081. PMID: 11877358.
Article3. Tilz RR, Chun KR, Schmidt B, Fuernkranz A, Wissner E, Koester I, Baensch D, Boczor S, Koektuerk B, Metzner A, Zerm T, Ernst S, Antz M, Kuck KH, Ouyang F. Catheter ablation of long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation: a lesson from circumferential pulmonary vein isolation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2010; 21:1085–1093. PMID: 20487116.
Article4. Nademanee K, McKenzie J, Kosar E, Schwab M, Sunsaneewitayakul B, Vasavakul T, Khunnawat C, Ngarmukos T. A new approach for catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: mapping of the electrophysiologic substrate. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004; 43:2044–2053. PMID: 15172410.
Article5. Brooks AG, Stiles MK, Laborderie J, Lau DH, Kuklik P, Shipp NJ, Hsu LF, Sanders P. Outcomes of long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation ablation: a systematic review. Heart Rhythm. 2010; 7:835–846. PMID: 20206320.
Article6. Oral H, Chugh A, Good E, Wimmer A, Dey S, Gadeela N, Sankaran S, Crawford T, Sarrazin JF, Kuhne M, Chalfoun N, Wells D, Frederick M, Fortino J, Benloucif-Moore S, Jongnarangsin K, Pelosi F Jr, Bogun F, Morady F. Radiofrequency catheter ablation of chronic atrial fibrillation guided by complex electrograms. Circulation. 2007; 115:2606–2612. PMID: 17502567.
Article7. Habel N, Znojkiewicz P, Thompson N, Müller JG, Mason B, Calame J, Calame S, Sharma S, Mirchandani G, Janks D, Bates J, Noori A, Karnbach A, Lustgarten DL, Sobel BE, Spector P. The temporal variability of dominant frequency and complex fractionated atrial electrograms constrains the validity of sequential mapping in human atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 2010; 7:586–593. PMID: 20156614.
Article8. Lau DH, Maesen B, Zeemering S, Verheule S, Crijns HJ, Schotten U. Stability of complex fractionated atrial electrograms: a systematic review. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2012; 23:980–987. PMID: 22554025.
Article9. Lin YJ, Tai CT, Kao T, Chang SL, Lo LW, Tuan TC, Udyavar AR, Wongcharoen W, Hu YF, Tso HW, Tsai WC, Chang CJ, Ueng KC, Higa S, Chen SA. Spatiotemporal organization of the left atrial substrate after circumferential pulmonary vein isolation of atrial fibrillation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2009; 2:233–241. PMID: 19808473.
Article10. Lin YJ, Tai CT, Kao T, Chang SL, Wongcharoen W, Lo LW, Tuan TC, Udyavar AR, Chen YJ, Higa S, Ueng KC, Chen SA. Consistency of complex fractionated atrial electrograms during atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 2008; 5:406–412. PMID: 18313599.
Article11. Blauer JJ, Swenson D, Higuchi K, Plank G, Ranjan R, Marrouche N, Macleod RS. Sensitivity and specificity of substrate mapping: an in silico framework for the evaluation of electroanatomical substrate mapping strategies. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2014; 25:774–780. PMID: 24762029.
Article12. Keller MW, Schuler S, Luik A, Seemann G, Schilling C, Schmitt C, Dössel O. Comparison of simulated and clinical intracardiac electrograms. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2013; 2013:6858–6861. PMID: 24111320.
Article13. Hwang M, Kwon SS, Wi J, Park M, Lee HS, Park JS, Lee YS, Shim EB, Pak HN. Virtual ablation for atrial fibrillation in personalized in-silico three-dimensional left atrial modeling: comparison with clinical catheter ablation. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2014; 116:40–47. PMID: 25261813.
Article14. Courtemanche M, Ramirez RJ, Nattel S. Ionic mechanisms underlying human atrial action potential properties: insights from a mathematical model. Am J Physiol. 1998; 275:H301–H321. PMID: 9688927.
Article15. Clayton RH, Bernus O, Cherry EM, Dierckx H, Fenton FH, Mirabella L, Panfilov AV, Sachse FB, Seemann G, Zhang H. Models of cardiac tissue electrophysiology: progress, challenges and open questions. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2011; 104:22–48. PMID: 20553746.
Article16. Brignole M, Menozzi C, Sartore B, Barra M, Monducci I. The use of atrial pacing to induce atrial fibrillation and flutter. Int J Cardiol. 1986; 12:45–54. PMID: 3733266.
Article17. Zozor S, Blanc O, Jacquemet V, Virag N, Vesin JM, Pruvot E, Kappenberger L, Henriquez C. A numerical scheme for modeling wavefront propagation on a monolayer of arbitrary geometry. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2003; 50:412–420. PMID: 12723052.
Article18. Yun Y, Hwang M, Park JH, Shin H, Shim EB, Pak HN. The relationship among complex fractionated electrograms, wavebreak, phase singularity, and local dominant frequency in fibrillation wave-dynamics: a modeling comparison study. J Korean Med Sci. 2014; 29:370–377. PMID: 24616586.
Article19. Potse M, Vinet A, Opthof T, Coronel R. Validation of a simple model for the morphology of the T wave in unipolar electrograms. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009; 297:H792–H801. PMID: 19465555.
Article20. Plonsey R, Barr RC. Current flow patterns in two-dimensional anisotropic bisyncytia with normal and extreme conductivities. Biophys J. 1984; 45:557–571. PMID: 6713068.
Article21. Faes L, Nollo G, Antolini R, Gaita F, Ravelli F. A method for quantifying atrial fibrillation organization based on wave-morphology similarity. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2002; 49:1504–1513. PMID: 12549732.
Article22. Park JH, Park SW, Kim JY, Kim SK, Jeoung B, Lee MH, Hwang C, Kim YH, Kim SS, Pak HN. Characteristics of complex fractionated atrial electrogram in the electroanatomically remodeled left atrium of patients with atrial fibrillation. Circ J. 2010; 74:1557–1563. PMID: 20562494.
Article23. Konings KT, Smeets JL, Penn OC, Wellens HJ, Allessie MA. Configuration of unipolar atrial electrograms during electrically induced atrial fibrillation in humans. Circulation. 1997; 95:1231–1241. PMID: 9054854.
Article24. Takahashi Y, O'Neill MD, Hocini M, Dubois R, Matsuo S, Knecht S, Mahapatra S, Lim KT, Jaïs P, Jonsson A, Sacher F, Sanders P, Rostock T, Bordachar P, Clémenty J, Klein GJ, Haïssaguerre M. Characterization of electrograms associated with termination of chronic atrial fibrillation by catheter ablation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008; 51:1003–1010. PMID: 18325439.
Article25. Lin J, Scherlag BJ, Zhou J, Lu Z, Patterson E, Jackman WM, Lazzara R, Po SS. Autonomic mechanism to explain complex fractionated atrial electrograms (CFAE). J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2007; 18:1197–1205. PMID: 17916143.
Article26. Atienza F, Calvo D, Almendral J, Zlochiver S, Grzeda KR, Martínez-Alzamora N, González-Torrecilla E, Arenal A, Fernández-Avilés F, Berenfeld O. Mechanisms of fractionated electrograms formation in the posterior left atrium during paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in humans. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011; 57:1081–1092. PMID: 21349400.
Article27. Jalife J, Berenfeld O, Mansour M. Mother rotors and fibrillatory conduction: a mechanism of atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc Res. 2002; 54:204–216. PMID: 12062327.
Article28. Jacquemet V, Henriquez CS. Genesis of complex fractionated atrial electrograms in zones of slow conduction: a computer model of microfibrosis. Heart Rhythm. 2009; 6:803–810. PMID: 19467508.
Article29. Zlochiver S, Yamazaki M, Kalifa J, Berenfeld O. Rotor meandering contributes to irregularity in electrograms during atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 2008; 5:846–854. PMID: 18534369.
Article30. Chen X, Hu Y, Fetics BJ, Berger RD, Trayanova NA. Unstable QT interval dynamics precedes ventricular tachycardia onset in patients with acute myocardial infarction: a novel approach to detect instability in QT interval dynamics from clinical ECG. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2011; 4:858–866. PMID: 21841208.31. Vadakkumpadan F, Arevalo H, Ceritoglu C, Miller M, Trayanova N. Image-based estimation of ventricular fiber orientations for personalized modeling of cardiac electrophysiology. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2012; 31:1051–1060. PMID: 22271833.
Article32. Ng J, Jacobson JT, Ng JK, Gordon D, Lee DC, Carr JC, Goldberger JJ. Virtual electrophysiological study in a 3-dimensional cardiac magnetic resonance imaging model of porcine myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012; 60:423–430. PMID: 22633654.
Article33. Ruchat P, Virag N, Dang L, Schlaepfer J, Pruvot E, Kappenberger L. A biophysical model of atrial fibrillation ablation: what can a surgeon learn from a computer model? Europace. 2007; 9(Suppl 6):vi71–vi76. PMID: 17959696.
Article34. Ryu K, Khrestian CM, Matsumoto N, Sahadevan J, Goldstein RN, Dorostkar PC, Waldo AL. Characterization of the critical cycle length of a left atrial driver which causes right atrial fibrillatory conduction. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2004; 6:3960–3963.
Article35. Sanders P, Berenfeld O, Hocini M, Jaïs P, Vaidyanathan R, Hsu LF, Garrigue S, Takahashi Y, Rotter M, Sacher F, Scavée C, Ploutz-Snyder R, Jalife J, Haïssaguerre M. Spectral analysis identifies sites of high-frequency activity maintaining atrial fibrillation in humans. Circulation. 2005; 112:789–797. PMID: 16061740.
Article36. Ashihara T, Haraguchi R, Nakazawa K, Namba T, Ikeda T, Nakazawa Y, Ozawa T, Ito M, Horie M, Trayanova NA. The role of fibroblasts in complex fractionated electrograms during persistent/permanent atrial fibrillation: implications for electrogram-based catheter ablation. Circ Res. 2012; 110:275–284. PMID: 22179057.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Relationship among Complex Fractionated Electrograms, Wavebreak, Phase Singularity, and Local Dominant Frequency in Fibrillation Wave-Dynamics: a Modeling Comparison Study
- Computational modeling of atrial fibrillation
- Comparison of Cheek Electrode with Sphenoidal Electrodes for Identification of Ictal Onset Activity
- Intracardiac Electrogram at Successful Site of Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation in Patients with Atrioventricular Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia
- Ethanol Infusion in the Vein of Marshall in a Patient with Persistent Atrial Fibrillation