Korean Circ J.
2015 Sep;45(5):424-427. 10.4070/kcj.2015.45.5.424.
Ethanol Infusion in the Vein of Marshall in a Patient with Persistent Atrial Fibrillation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Cardiology, Korea University College of Medicine, Anam Hospital, Seoul, Korea. yhkmd@unitel.co.kr
- KMID: 2223807
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2015.45.5.424
Abstract
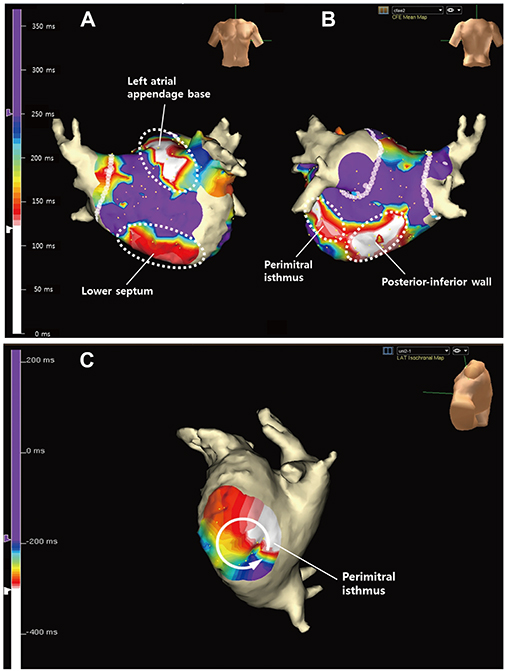
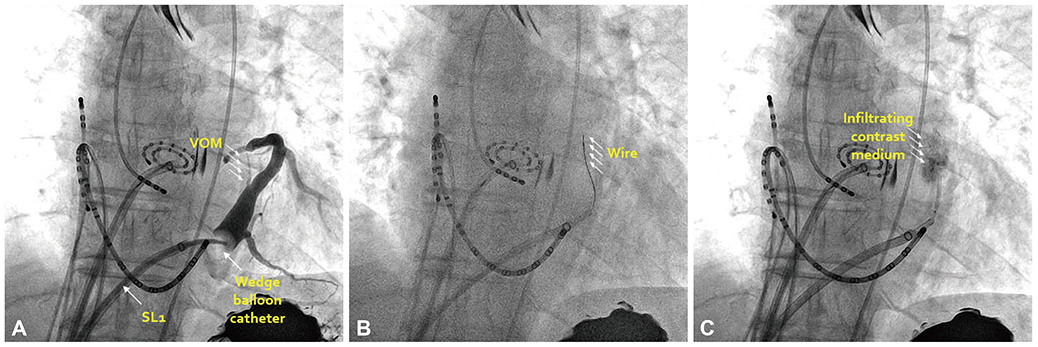
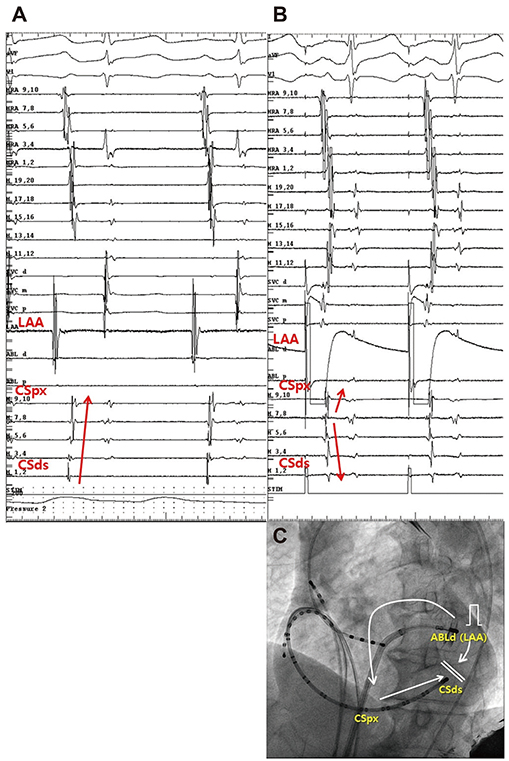
- We report the case of a 64-year-old male with persistent atrial fibrillation (AF) terminated by ethanol infusion into vein of Marshall as add-on therapy. Three-dimensional automated complex fractionated atrial electrogram (CFAE) during AF revealed clustering of CFAE at perimitral isthmus (PMI) and its unipolar mapping showed rotor-like activation, which was suggested to be critical in the perpetuation of AF. AF was organized to atrial tachycardia (AT) by 100% ethanol infusion in the vein of Marshall. Adjunctive radiofrequency ablation at PMI successfully terminated AT and led to bidirectional block of PMI.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hwang C, Chen PS. Ligament of Marshall: why it is important for atrial fibrillation ablation. Heart Rhythm. 2009; 6:12 Suppl. S35–S40.2. Hsu LF, Jaïs P, Keane D, et al. Atrial fibrillation originating from persistent left superior vena cava. Circulation. 2004; 109:828–832.3. Lin WS, Tai CT, Hsieh MH, et al. Catheter ablation of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation initiated by non-pulmonary vein ectopy. Circulation. 2003; 107:3176–3183.4. Kamanu S, Tan AY, Peter CT, Hwang C, Chen PS. Vein of Marshall activity during sustained atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2006; 17:839–846.5. Valderrábano M, Liu X, Sasaridis C, Sidhu J, Little S, Khoury DS. Ethanol infusion in the vein of Marshall: adjunctive effects during ablation of atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 2009; 6:1552–1558.6. Báez-Escudero JL, Morales PF, Dave AS, et al. Ethanol infusion in the vein of Marshall facilitates mitral isthmus ablation. Ethanol infusion in the vein of Marshall facilitates mitral isthmus ablation. Heart Rhythm. 2012; 9:1207–1215.7. Nademanee K. Mapping of complex fractionated atrial electrograms as target sites for AF ablation. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2011; 2011:5539–5542.8. Jadidi AS, Cochet H, Shah AJ, et al. Inverse relationship between fractionated electrograms and atrial fibrosis in persistent atrial fibrillation: combined magnetic resonance imaging and high-density mapping. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013; 62:802–812.9. Gaita F, Riccardi R, Caponi D, et al. Linear cryoablation of the left atrium versus pulmonary vein cryoisolation in patients with permanent atrial fibrillation and valvular heart disease: correlation of electroanatomic mapping and long-term clinical results. Circulation. 2005; 111:136–142.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Role of non‑pulmonary vein triggers in persistent atrial fibrillation
- Controlled Atrial Fibrillation after Pulmonary Vein Stenting
- Giant Vein of Marshall in a Patient With Persistent Atrial Fibrillation
- A Totally Thoracoscopic Ablation for Persistent Atrial Fibrillation
- Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation of Persistent Atrial Fibrillation with Myotonic Dystrophy and Achalasia-like Esophageal Dilatation