J Korean Soc Radiol.
2010 Jun;62(6):575-578.
MR Findings of Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Thigh: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan University Hospital, Ulsan, Korea. kangbs0708@freechal.com
- 2Department of Pathology, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan University Hospital, Ulsan, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan University Hospital, Ulsan, Korea.
Abstract
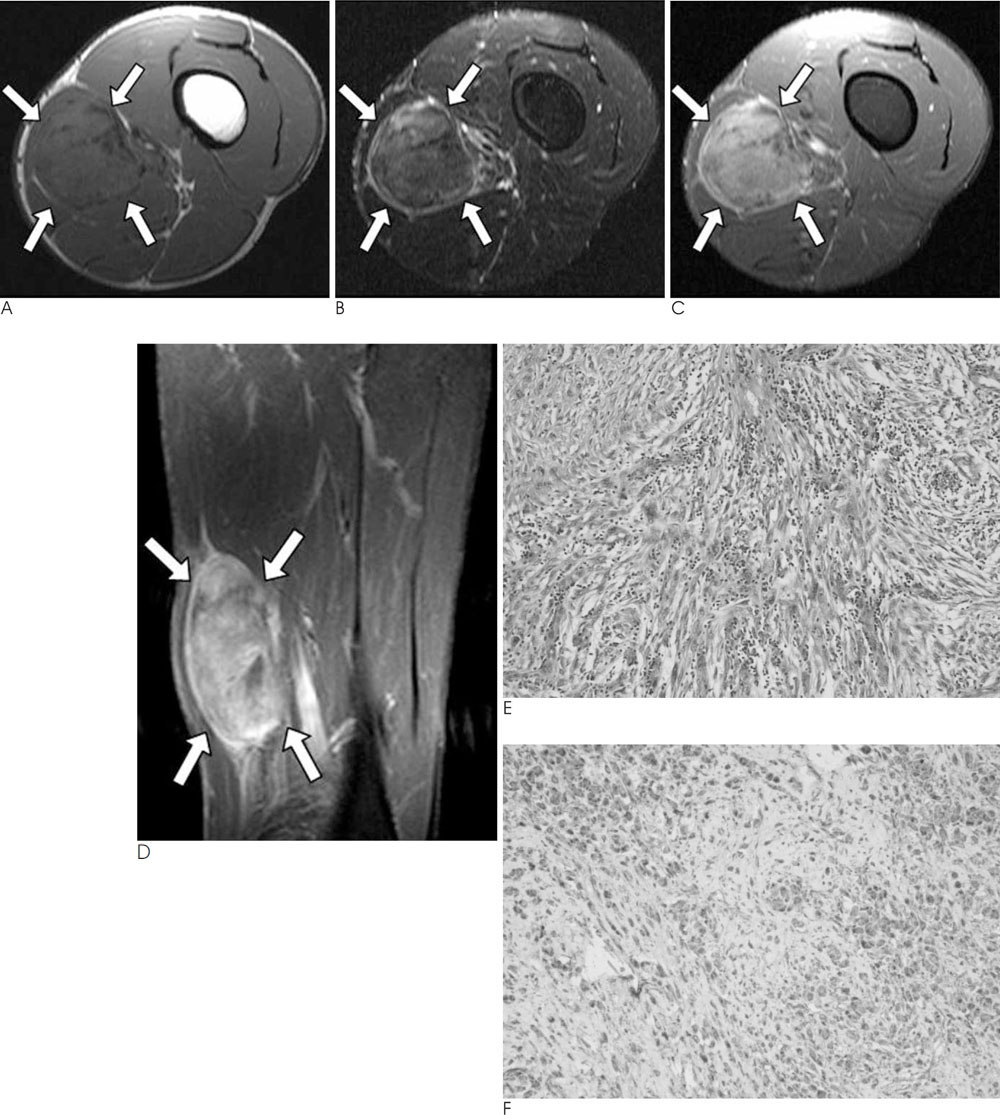
- Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor is a rare benign condition of an unknown etiology and it may be clinically misdiagnosed as a malignant tumor. We examined a 28-year-old male with a slowly-growing mass in his left thigh. The MR images showed a relatively well-defined, intermuscular mass lesion with heterogeneous enhancement. The histopathologic examination of the resected specimen revealed inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor. We report here on the MR findings of inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the thigh in this patient.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gleason BC, Hornick JL. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumours: where are we now? J Clin Pathol. 2008; 61:428–437.2. Narla LD, Newman B, Spottswood SS, Narla S, Kolli R. Inflammatory pseudotumor. Radiographics. 2003; 719–729.3. Pettinato G, Manivel JC, De Rosa N, Dehner LP. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (plasma cell granuloma). Clinicopathologic study of 20 cases with immunohistochemical and ultrastructural observations. Am J Clin Pathol. 1990; 94:538–546.4. Coffin CM, Patel A, Perkins S, Elenitoba-Johnson K, Perlman E, Griffin CA. ALK1 and p80 expression and chromosomal rearrangements involving 2p23 in inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor. Mod Pathol. 2001; 14:569–576.5. Bandwein MS, Som PM. Tumors and tumor-like conditions. In : Som PM, Curtin HD, editors. Head and neck imaging. 4th ed. St. Louis, MO: Mosby;2003. p. 250–251. p. 320–321. .6. Han MH, Chi JG, Kim MS, Chang KH, Kim KH, Yeon KM, et al. Fibrosing inflammatory pseudotumors involving the skull base: MR and CT manifestations with histopathologic comparison. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1996; 17:515–521.7. Irie H, Honda H, Kaneko K, Kuroiwa T, Fukuya T, Yoshimitsu K, et al. Inflammatory pseudotumors of the spleen: CT and MRI findings. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1996; 20:244–248.8. Georgia JD, Lawrence DP, DeNobile JW. Inflammatory pseudotumor in the retrorectal space: CT and MR appearance. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1996; 20:410–412.9. Kransdorf MJ, Murphey MD. Vascular and lymphatic tumors / Benign fibrous and fibrohistiocytic tumors / Malignant fibrous and fibrohistiocytic tumors / Neurogenic tumors. In: Imaging of soft tissue tumors. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins;2006. p. 179–180. p. 217–231. p. 271–293. p. 337–348.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of Nasal Septum after Septoplasty: A Case Report
- A Case of Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Maxillary Sinus
- Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Breast: A Case Report
- Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of Kidney
- Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor in Posterior Mediastinum