J Korean Med Assoc.
2012 Nov;55(11):1113-1120.
Treatment of chronic hepatitis C
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. noshin@hanyang.ac.kr
Abstract
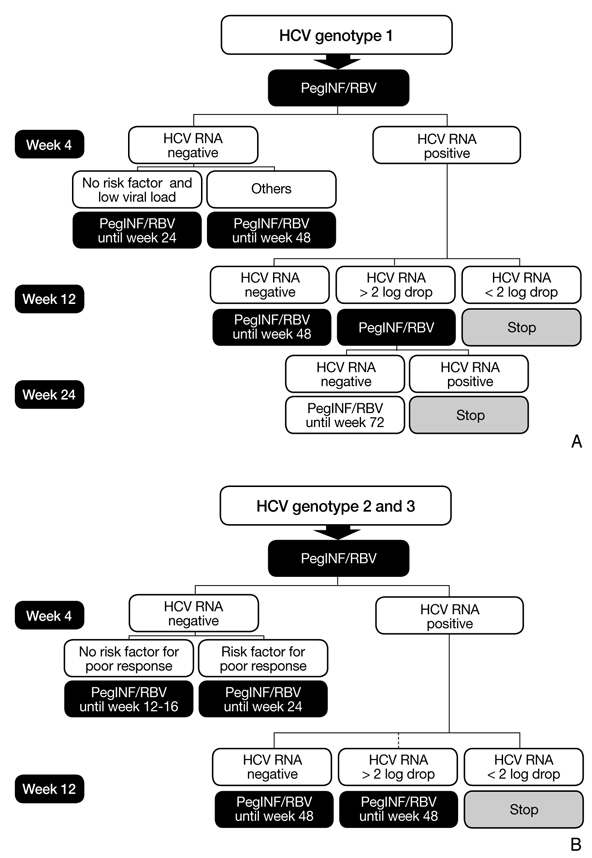
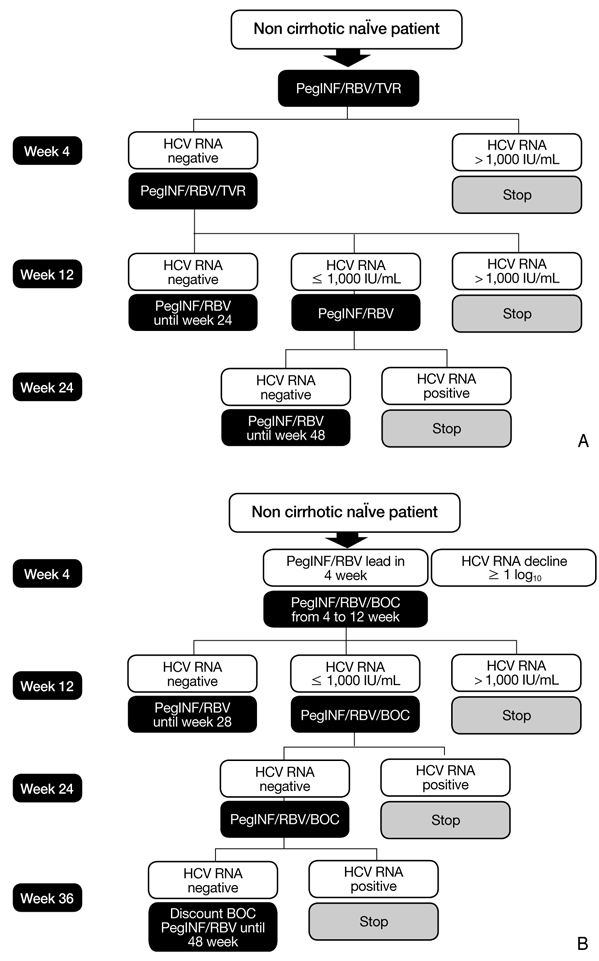
- In the past 10 years, the standard treatment for chronic hepatitis C has been pegylated interferon and ribavirin for 24 to 48 weeks, based on genotype. Until now, fixed schedule therapy for chronic hepatitis C infection is the standard treatment in most countries. Response-guided therapy (RGT) is an emerging concept in which treatment decisions are based on how the virus responds to treatment. RGT has not been accepted into practice guidelines in all countries. The RGT approach takes into account both viral and host factors. RGT allows clinicians to provide a shorter duration of treatment, sparing patients of ongoing side effects and medical costs. We review several new treatment guidelines on new direct protease inhibitors. In late 2011, telaprevir and boceprevir were approved for treating chronic hepatitis C. Nowadays, the strategy for hepatitis C genotype 1 has been revolutionized by these two drugs. Other new direct acting antiviral agents have increased the sustained viral response significantly in chronic hepatitis genotype 1 patients in several recent clinical trials. In the future, Hepatitis C treatment will be personalized according to early viral response and baseline viral load. An interferon-free regimen will also be available for chronic hepatitis C.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ghany MG, Strader DB, Thomas DL, Seeff LB. American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Diagnosis, management, and treatment of hepatitis C: an update. Hepatology. 2009. 49:1335–1374.
Article2. Lee DS, Park SY, Lee HS, Choi SY, Jung DW, Shon HS, Shon JW, Park JH, Kim SW, Jung IK, Jung MK, Chun SW, Cho CM, Kwon YO, Kim SK, Choi YH, Tak WY. Outcome of combination therapy of pegylated inerferone with ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C: single center study. Korean J Hepatol. 2009. 15(3s):S134.3. Kim HI, Kim SK, Kim YS, Jeong SW, Jang JY, Lee SH, Mun JH, Kim HS, Lee MS, Kim BS. Efficacy of peginterferon alpha-2b and ribavirin combination therapy for chronic hepatitis C patients. Korean J Hepatol. 2010. 16(3s):S223.4. Kim JI, Kim SH, Lee BS, Lee HY, Lee TH, Kang YW, Lee HY, Kim AN, Yang HW, Kim YS, Nam SW, Park BC, Chai HB, Kim SB, Song IH, Park JY, Kim HS. The effect of peginterferon plus ribavirin for initial treatment of chronic hepatitis C living in Daejon and Chungcheong. Korean J Hepatol. 2008. 14(3s):S131.5. Park SH, Park CK, Lee JW, Kim YS, Jung SH, Kim YS, Kim JH, Hwang SK, Lim KS, Lim HJ, Lee CK, Jung JY, Cho SW, Lee JS, Park YM, Chang JW, Yang JM, Shon JH. Efficacy and tolerability of peginterferon alfa plus ribavirin in the routine daily treatment of chronic hepatitis C patients in Korea: a multi-center, retrospective observational study. Korean J Hepatol. 2010. 16(3s):S58.6. Ruiz-Extremera A, Munnoz-Gamez JA, Salmeron-Ruiz MA, de Rueda PM, Quiles-Perez R, Gila-Medina A, Casado J, Belen Martin A, Sanjuan-Nunez L, Carazo A, Pavon EJ, Ocete-Hita E, Leon J, Salmeron J. Genetic variation in interleukin 28B with respect to vertical transmission of hepatitis C virus and spontaneous clearance in HCV-infected children. Hepatology. 2011. 53:1830–1838.
Article7. Manns MP, Wedemeyer H, Cornberg M. Treating viral hepatitis C: efficacy, side effects, and complications. Gut. 2006. 55:1350–1359.
Article8. European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: management of hepatitis C virus infection. J Hepatol. 2011. 55:245–264.9. Davis GL, Wong JB, McHutchison JG, Manns MP, Harvey J, Albrecht J. Early virologic response to treatment with peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2003. 38:645–652.
Article10. Yee HS, Chang MF, Pocha C, Lim J, Ross D, Morgan TR, Monto A. Department of Veterans Affairs Hepatitis C Resource Center Program. National Hepatitis C Program Office. Update on the management and treatment of hepatitis C virus infection: recommendations from the Department of Veterans Affairs Hepatitis C Resource Center Program and the National Hepatitis C Program Office. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012. 107:669–689.
Article11. Mangia A, Minerva N, Bacca D, Cozzolongo R, Ricci GL, Carretta V, Vinelli F, Scotto G, Montalto G, Romano M, Cristofaro G, Mottola L, Spirito F, Andriulli A. Individualized treatment duration for hepatitis C genotype 1 patients: a randomized controlled trial. Hepatology. 2008. 47:43–50.
Article12. Shiffman ML, Suter F, Bacon BR, Nelson D, Harley H, Solá R, Shafran SD, Barange K, Lin A, Soman A, Zeuzem S. ACCELERATE Investigators. Peginterferon alfa-2a and ribavirin for 16 or 24 weeks in HCV genotype 2 or 3. N Engl J Med. 2007. 357:124–134.
Article13. Song YJ, Lee YJ, Choi BJ, Choi SB, Kim JH, Jung EU, Lee SH, Kim JH, Choi JS, Ji SR, Sul SY. Tailored therapy for treatmentnaive chronic hepatitis C with pegylated interferon- and ribavirin: real practice experience. Korean J Hepatol. 2010. 16(3s):S57.14. Pearlman BL, Ehleben C, Saifee S. Treatment extension to 72 weeks of peginterferon and ribavirin in hepatitis c genotype 1-infected slow responders. Hepatology. 2007. 46:1688–1694.
Article15. Sanchez-Tapias JM, Diago M, Escartin P, Enriquez J, Romero-Gomez M, Barcena R, Crespo J, Andrade R, Martinez-Bauer E, Perez R, Testillano M, Planas R, Sola R, Garcia-Bengoechea M, Garcia-Samaniego J, Munoz-Sanchez M, Moreno-Otero R. TeraViC-4 Study Group. Peginterferon-alfa2a plus ribavirin for 48 versus 72 weeks in patients with detectable hepatitis C virus RNA at week 4 of treatment. Gastroenterology. 2006. 131:451–460.
Article16. Teoh NC, Farrell GC, Chan HL. Individualisation of antiviral therapy for chronic hepatitis C. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010. 25:1206–1216.
Article17. Jacobson IM, McHutchison JG, Dusheiko G, Di Bisceglie AM, Reddy KR, Bzowej NH, Marcellin P, Muir AJ, Ferenci P, Flisiak R, George J, Rizzetto M, Shouval D, Sola R, Terg RA, Yoshida EM, Adda N, Bengtsson L, Sankoh AJ, Kieffer TL, George S, Kauffman RS, Zeuzem S. ADVANCE Study Team. Telaprevir for previously untreated chronic hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med. 2011. 364:2405–2416.
Article18. Sherman KE, Flamm SL, Afdhal NH, Nelson DR, Sulkowski MS, Everson GT, Fried MW, Adler M, Reesink HW, Martin M, Sankoh AJ, Adda N, Kauffman RS, George S, Wright CI, Poordad F. ILLUMINATE Study Team. Response-guided telaprevir combination treatment for hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med. 2011. 365:1014–1024.
Article19. Zeuzem S, Andreone P, Pol S, Lawitz E, Diago M, Roberts S, Focaccia R, Younossi Z, Foster GR, Horban A, Ferenci P, Nevens F, Mullhaupt B, Pockros P, Terg R, Shouval D, van Hoek B, Weiland O, Van Heeswijk R, De Meyer S, Luo D, Boogaerts G, Polo R, Picchio G, Beumont M. REALIZE Study Team. Telaprevir for retreatment of HCV infection. N Engl J Med. 2011. 364:2417–2428.
Article20. Poordad F, McCone J Jr, Bacon BR, Bruno S, Manns MP, Sulkowski MS, Jacobson IM, Reddy KR, Goodman ZD, Boparai N, DiNubile MJ, Sniukiene V, Brass CA, Albrecht JK, Bronowicki JP. SPRINT-2 Investigators. Boceprevir for untreated chronic HCV genotype 1 infection. N Engl J Med. 2011. 364:1195–1206.
Article21. Bacon BR, Gordon SC, Lawitz E, Marcellin P, Vierling JM, Zeuzem S, Poordad F, Goodman ZD, Sings HL, Boparai N, Burroughs M, Brass CA, Albrecht JK, Esteban R. HCV RESPOND-2 Investigators. Boceprevir for previously treated chronic HCV genotype 1 infection. N Engl J Med. 2011. 364:1207–1217.
Article22. Dupin N, Mallet V, Carlotti A, Vallet-Pichard A, Pol S. Severe skin rash in case of readministration of telaprevir in a patient who previously experienced a non severe rash. Hepatology. 2012. 55:2042–2043.
Article23. Kiser JJ, Burton JR, Anderson PL, Everson GT. Review and management of drug interactions with boceprevir and telaprevir. Hepatology. 2012. 55:1620–1628.
Article24. Ramachandran P, Fraser A, Agarwal K, Austin A, Brown A, Foster GR, Fox R, Hayes PC, Leen C, Mills PR, Mutimer DJ, Ryder SD, Dillon JF. UK consensus guidelines for the use of the protease inhibitors boceprevir and telaprevir in genotype 1 chronic hepatitis C infected patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2012. 35:647–662.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- 2017 KASL clinical practice guidelines management of hepatitis C: Treatment of chronic hepatitis C
- KASL guideline of managent of chronic hepatitis C
- A Study on Periphral T Cell Subsets in Asymptomatic HBsAg Carriers and Children with Chronic Hepatitis B and Hepatitis B vaccine Inoculated Infants
- Pre-S Defective Hepatitis B Virus in Patients with Acute and chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection
- KASL clinical practice guidelines for management of chronic hepatitis B