J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2012 Sep;52(3):261-263.
Deep Brain Stimulation of the Globus Pallidus in a 7-Year-Old Girl with DYT1 Generalized Dystonia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Maryknoll Medical Center, Busan, Korea. stereomk@naver.com
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Bongseng Memorial Hospital, Busan, Korea.
Abstract
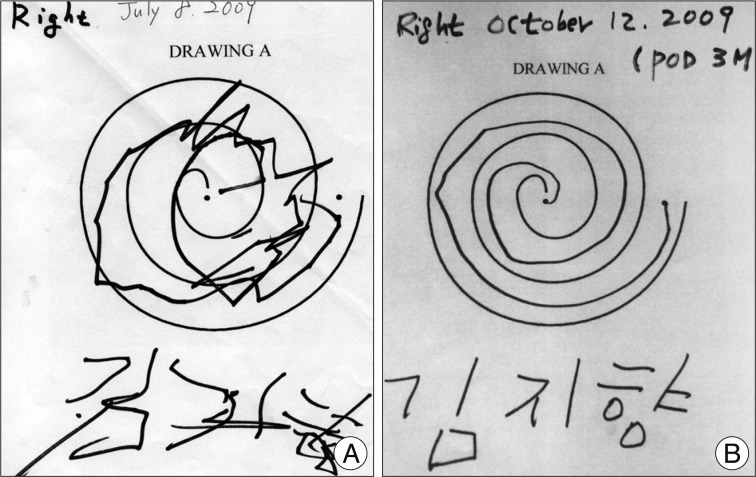
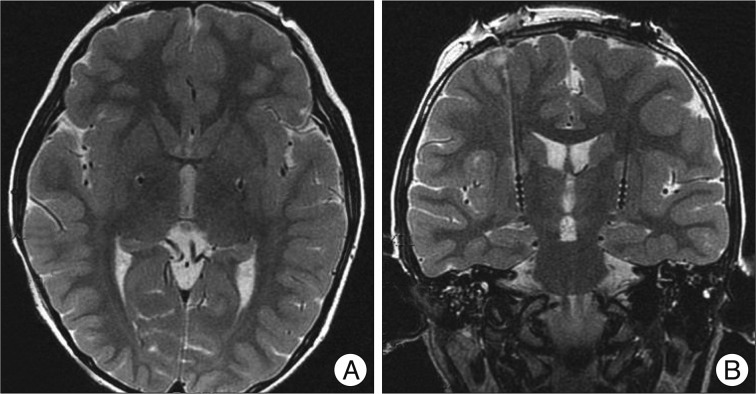
- The experience of pediatric deep brain stimulation (DBS) of the globus pallidus internus (GPi) in the treatment of early-onset DYT1 generalized dystonia is still limited. Here, we report the surgical experience of bilateral GPi-DBS under general anesthesia by using microelectrode recording in a 7-year-old girl with early-onset DYT1 generalized dystonia. Excellent improvement of her dystonia without neurological complications was achieved. This case report demonstrates that GPi-DBS is an effective and safe method for the treatment of medically refractory early-onset DYT1 generalized dystonia in children.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Alterman RL, Tagliati M. Deep brain stimulation for torsion dystonia in children. Childs Nerv Syst. 2007; 23:1033–1040. PMID: 17551738.
Article2. Augood SJ, Penney JB Jr, Friberg IK, Breakefield XO, Young AB, Ozelius LJ, et al. Expression of the early-onset torsion dystonia gene (DYT1) in human brain. Ann Neurol. 1998; 43:669–673. PMID: 9585364.
Article3. Constantoyannis C, Berk C, Honey CR, Mendez I, Brownstone RM. Reducing hardware-related complications of deep brain stimulation. Can J Neurol Sci. 2005; 32:194–200. PMID: 16018154.
Article4. Coubes P, Cif L, El Fertit H, Hemm S, Vayssiere N, Serrat S, et al. Electrical stimulation of the globus pallidus internus in patients with primary generalized dystonia : long-term results. J Neurosurg. 2004; 101:189–194. PMID: 15309907.
Article5. Dekaban AS. Changes in brain weights during the span of human life : relation of brain weights to body heights and body weights. Ann Neurol. 1978; 4:345–356. PMID: 727739.
Article6. Gross RE, Mewes K, Ghani G. Bakay RA, editor. Anesthesia for movement disorder surgery. Movement Disorder Surgery. The Essentials. 2008. New York: Stuttgart;p. 70–82.7. Isaias IU, Alterman RL, Tagliati M. Outcome predictors of pallidal stimulation in patients with primary dystonia : the role of disease duration. Brain. 2008; 131:1895–1902. PMID: 18567622.
Article8. Jeong SG, Lee MK, Kang JY, Jun SM, Lee WH, Ghang CG. Pallidal deep brain stimulation in primary cervical dystonia with phasic type : clinical outcome and postoperative course. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2009; 46:346–350. PMID: 19893724.
Article9. Marks WA, Honeycutt J, Acosta F, Reed M. Deep brain stimulation for pediatric movement disorders. Semin Pediatr Neurol. 2009; 16:90–98. PMID: 19501337.
Article10. Pinsker MO, Volkmann J, Falk D, Herzog J, Steigerwald F, Deuschl G, et al. Deep brain stimulation of the internal globus pallidus in dystonia : target localisation under general anaesthesia. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2009; 151:751–758. PMID: 19468677.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of Globus Pallidus Interna Deep Brain Stimulation on a Dystonia Patient with the GNAL Mutation Compared to Patients with DYT1 and DYT6
- Globus Pallidus Interna Deep Brain Stimulation for Chorea-Acanthocytosis
- Successful Pallidal Stimulation in a Patient with KMT2B-Related Dystonia
- Pregnancy and Delivery in a Generalized Dystonia Patient Treated with Internal Globus Pallidal Deep Brain Stimulation: a Case Report
- Combined Therapy of Orthopedic Surgery after Deep Brain Stimulation in Cerebral Palsy Mixed Type: A Case Report