J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2014 Jan;55(1):149-154.
A Case of the Third Nerve Palsy in a Patient with Orbital Aspergillosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea. glaucoma@pusan.ac.kr
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To report a case of orbital aspergillosis with third nerve palsy.
CASE SUMMARY
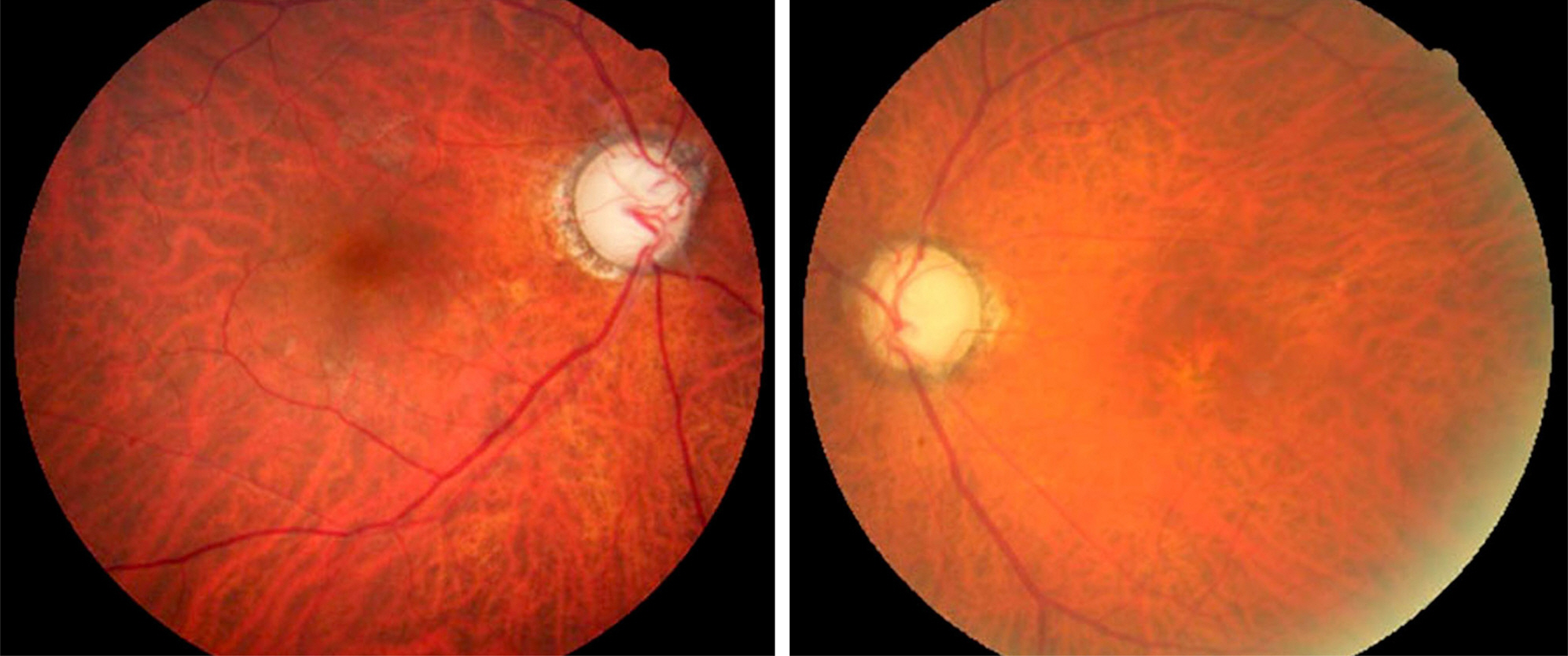
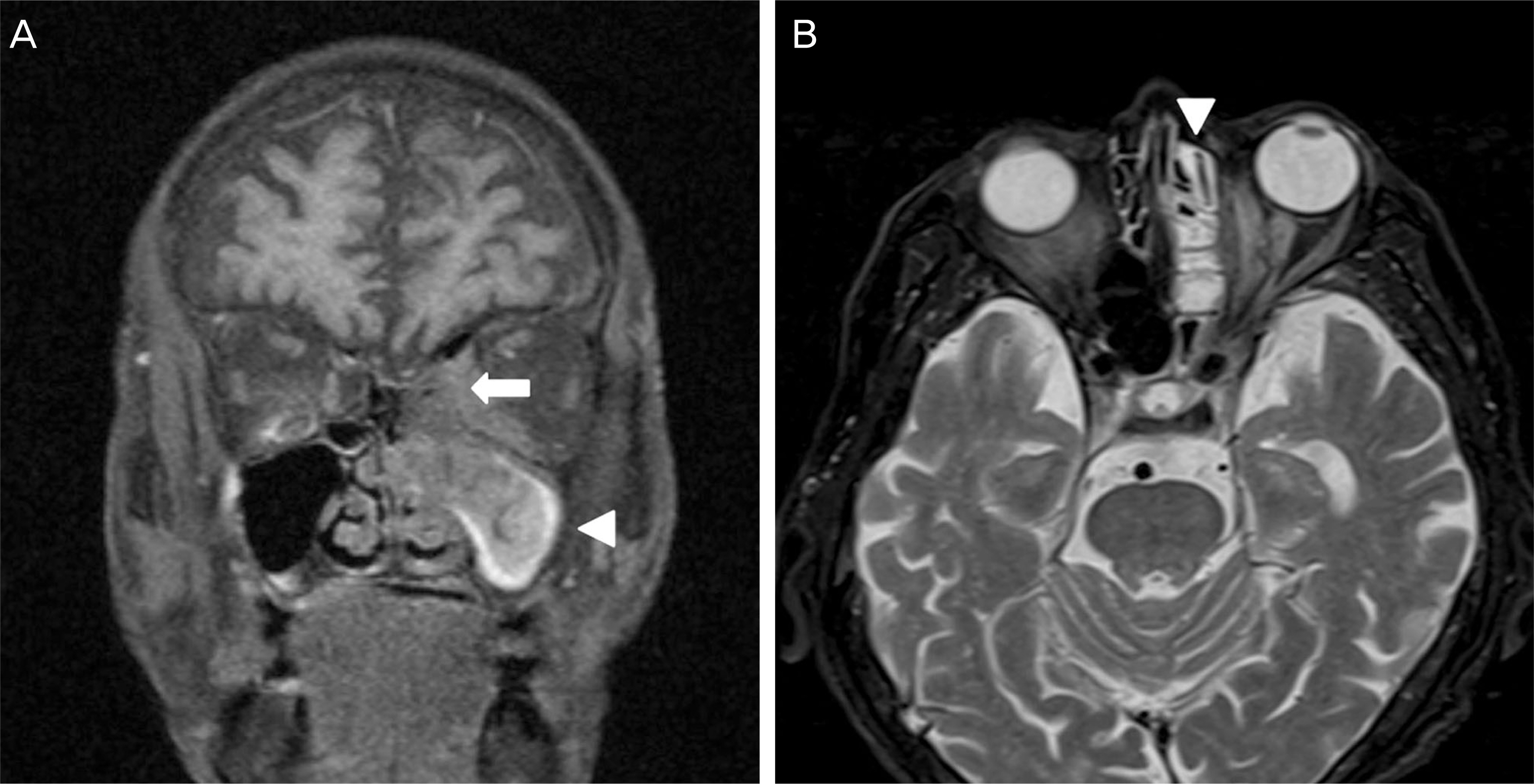
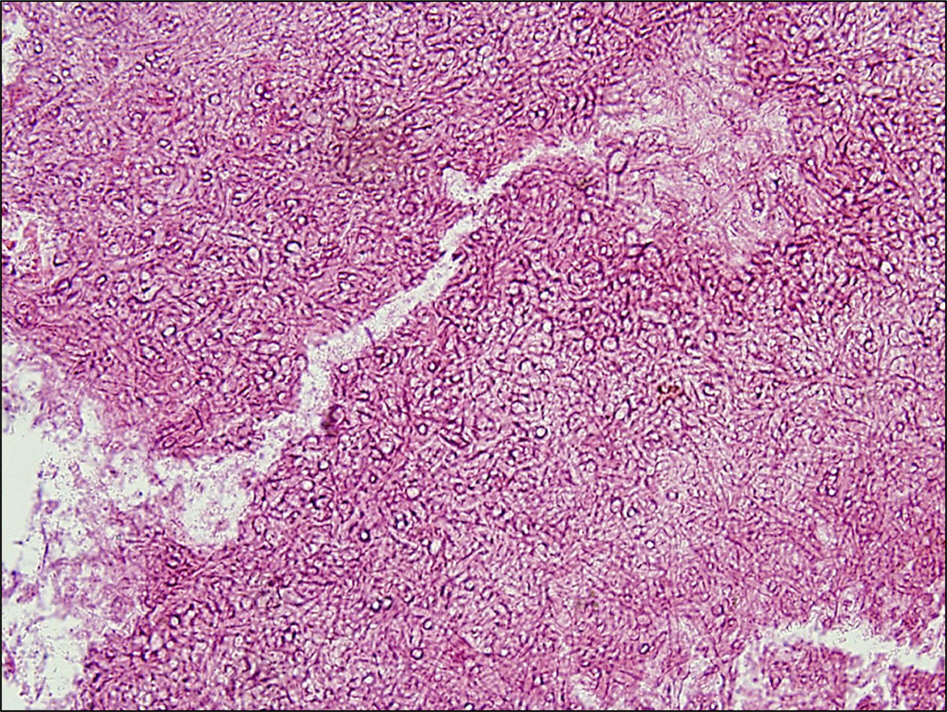
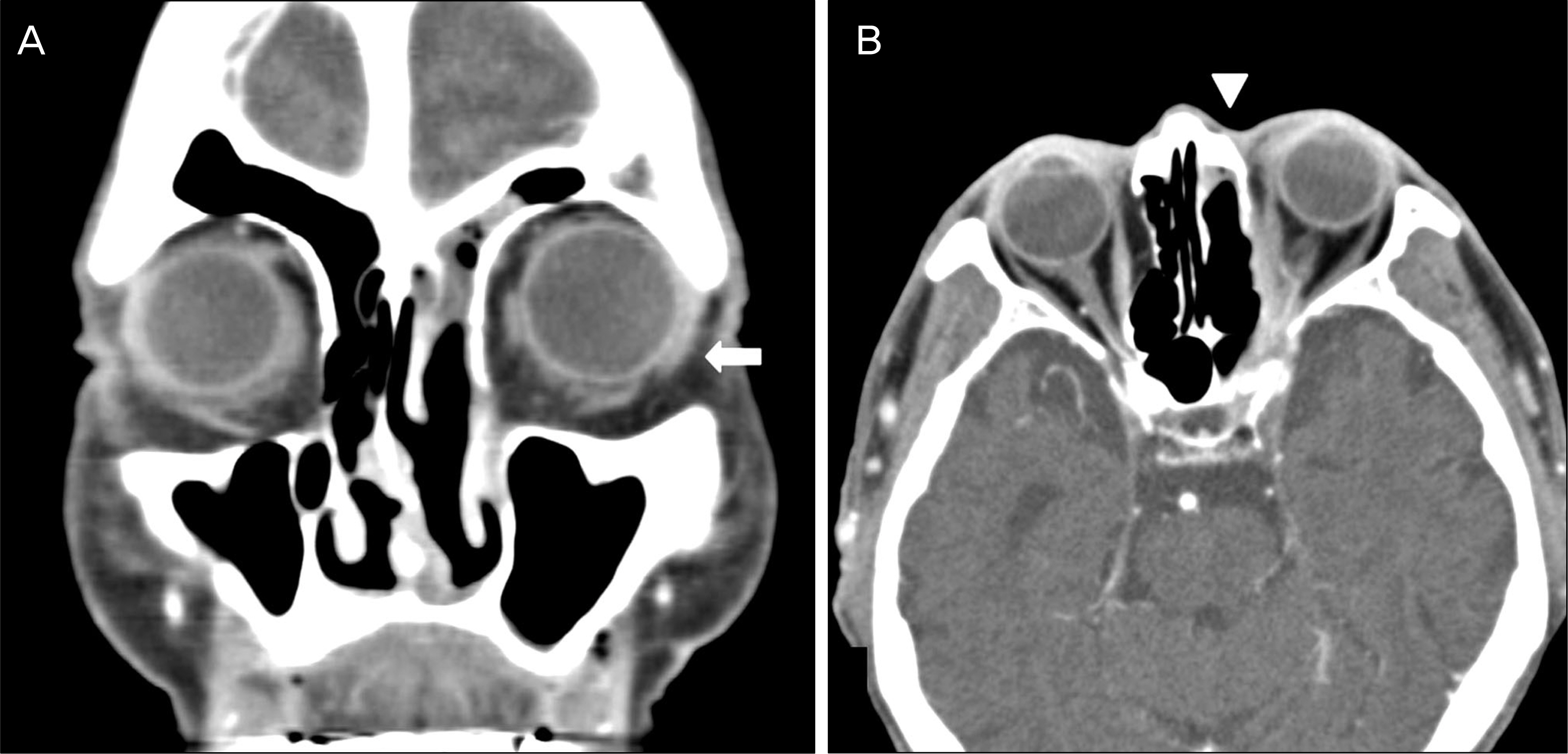
A 75-year-old male presented with abrupt onset of visual impairment, extraocular movement limitation, and ptosis. The patient previously experienced rhinolalia and headache and was diagnosed with sinusitis 2 months prior, and was treated with oral antibiotics for 1 week. Orbital magnetic resonance imaging revealed a mass with bone erosion including the nasal cavity, ethmoid bone, and left orbit suggestive of fugal sinusitis. Aspergillus was detected histopathologically in the mass which was removed by endoscopic surgery. Amphotericin B was administered intravenously for 7 days along with voriconazole. There was no recurrence during the follow-up period. Extraocular movement limitations and ptosis were recovered postoperatively.
CONCLUSIONS
The present study results indicate that visual impairment and third nerve palsy can develop in a patient with orbital aspergillosis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Albert DM, Jakobiec FA. Infectious process of the orbit. Christopher TW, Ann SB, John WS, editors. Principles and practice of ophthalmology. 1st ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders;1994.2. Aisner J, Schimpff SC, Bennett JE. . Aspergillus infections in cancer patients. Association with fireproofing materials in a new hospital. JAMA. 1976; 235:411–2.
Article3. Weber RS, Lopez-Berestein G.Treatment of invasive Aspergillus sinusitis with liposomal-amphotericin B. Laryngoscope. 1987; 97(8 Pt 1):937–41.
Article4. Dortzbach R, Segrest DR.Orbital Aspergillosis. Ophthalmic Surg. 1983; 14:240–4.5. Yumoto E, Kitani S, Okamura H, Yanagihara N.Sino-orbital asper-gillosis associated with total ophthalmoplegia. Laryngoscope. 1985; 95:190–2.
Article6. Harris GJ, Will BR.Orbital aspergillosis: conservative debridement and local amphotericin irrigation. Ophthalmic Plastic Reconstr Surg. 1989; 5:207–11.
Article7. Lee DC, Lee JH, Choi WS.A case of the sino-orbital-cerebral aspergillosis. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1999; 40:1678–83.8. Lim JW, Suh JW, Lee SJ.A case of fungall ball after external dacryocystorhinostomy. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:1481–5.9. Lee YH, Chung HY, Kim IC.A case of the orbital aspergillosis. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1996; 37:1555–60.10. Na HJ, Park HW, Sim HS.A case of aspergillosis of maxillary sinus. Korean J Otolaryngol. 1981; 25:124–7.11. Min YG, Joo YS, Jang SO.Mycotic infection of the maxillary sinus-report of 2 cases. Korean J Otolaryngol. 1981; 24:114–7.12. Kim BG, Kwon SH, Kim CH.A clinical analysis of 60 cases of mycetoma. Korean J Otolaryngol. 2003; 14:74.
Article13. Tsai RK, He MS, Cheu CL, Sheu MM.Transient third cranial nerve palsy caused by sphenoid sinus aspergillosis. J Neuro Ophthalmol. 2008; 28:239–40.
Article14. Romett JL, Newman RK.Aspergillosis of the nose and paranasal sinuses. The Laryngoscope. 1982; 92:764–6.
Article15. Green WR, Font RL, Zimmerman LE.Asperillosis of the orbit. Report of ten cases and review of the literature. Arch Ophthalmol. 1969; 82:302–13.16. Fernando SS, Lauer CS.Aspergillus fumigatus infection of the op-tic nerve with mycotic arteritis of cerebral vessels. Histopathology. 1982; 6:227–34.
Article17. Boogaerts MA, Verhoef GE, Zachee P. . Antifungal prophy-laxis with itraconazole in prolonged neutropenia: correlation with plasma levels. Mycoses. 1989; 32(Suppl 1):103–8.
Article18. Zinreich SJ, Kennedy DW, Malat J. . Fungal sinusitis: diag-nosis with CT and MR imaging. Radiology. 1998; 169:439–44.
Article19. Zieske LA, Kopke RD, Hamill R.Dematiaceouos fungal sinusitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1991; 105:567–77.20. Som PM, Dillon WP, Curtin HD. . Hypointense paranasal sinus foci: differential diagnosis with MR imaging and relation to CT findings. Radiology. 1990; 176:777–81.
Article21. Fisher BD, Armstrong D, Yu B, Gold JW.Invasive aspergillosis. Progress in early diagnosis and treatment. Am J Med. 1981; 71:571–7.22. Battock DJ, Grausz H, Bobrowsky M, Littman ML.Alternate-day amphotericin B therapy in the treatment of rhinocerebral phycomy-cosis (mucormycosis). Ann Intern Med. 1968; 68:122–37.
Article23. Dupont B.Itraconazole therapy in Aspergillosis: Study in 49 patients. J Am Acad Dermato. 1990; 123:607–14.
Article24. Boes B, Bashir R, Boes C. . Central nervous system aspergillosis. Analysis of 26 patients. J Neuroimaging. 1994; 4:123–9.
Article25. Hedges TR, Leung LS.Parasellar and orbital apex syndrome caused by aspergillosis. Neurology. 1976; 26:117–20.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of the Third, Fourth, and Sixth Nerve Palsy in a Patient with Cerebral Aspergillosis
- A Case of the Orbital Aspergillosis
- Ophthalmoplegia in Sphenoid Sinus Aspergillosis
- Two Cases of Rhino-Orbitocerebral Mucormycosises that Manifested as Noninflammatory Oculomotor Nerve Palsy
- A Case of Isolated Complete Oculomotor Nerve Palsy Following Endoscopic Sinus Surgery