J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2014 Jun;49(3):202-208.
Clinical Results and Efficacy of Selective Nerve Root Blocks with Vertebroplasty in Treatment of Patients with Osteoporotic Compression Fracture Accompanied by Spinal Stenosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Dankook University Medical College, Cheonan, Korea. medi01@hanmail.net
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the efficacy of selective nerve root blocks with vertebroplasty in treatment of patients with osteoporotic compression fracture accompanied spinal stenosis showing neurogenic claudication.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
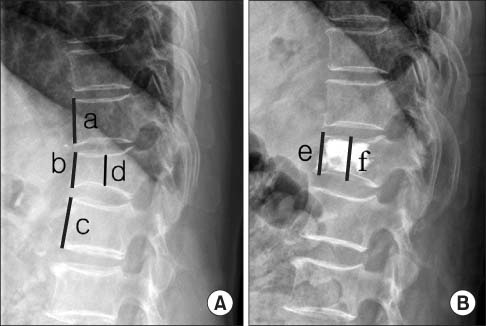
Of 80 patients admitted to our orthopedic department for osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture accompanied by neurogenic claudication due to spinal stenosis between May 2010 and September 2011, 40 patients who underwent only vertebroplasty and 40 patients who also underwent an additional selective nerve block were studied with a minimum follow-up period of one year. The two groups were compared for their age, sex, grade of spinal stenosis, bone mineral density (BMD), lordotic angle, pelvic tilt, sacral slope, pelvic incidence, restoration rate of vertebral height, preexisting fracture, intradiscal cement leakage, and for new adjacent vertebral fractures during a follow-up period of at least one year. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS version 17.0 and statistical significance was determined using the Student t-test and chi-square test with p<0.05.
RESULTS
No statistically significant difference (p> or =0.05) in age sex, grade of spinal stenosis, BMD, lordotic angle, pelvic tilt, pelvic incidence, restoration of vertebral height, preexisting fracture, and intradiscal cement leakage was observed between the vertebroplasty only group and the additional selective root block group. However, the incidence of new adjacent vertebral fractures between the groups was 13 of 40 patients in the vertebroplasty only group and four of 40 patients in the selective nerve block addition group; a statistically significant reduction was observed in the nerve block group (p<0.05).
CONCLUSION
In treatment of patients with osteoporotic compression fracture with neurogenic claudication due to spinal stenosis, addition of selective nerve block to vertebroplasty can lessen pain and the resulting postural change, thereby mitigating dynamic sagittal instability, which in turn results in reduced incidence of new adjacent vertebral fractures. As such, selective nerve block should be considered as a safe, simple, and effective tool for use in prevention of new adjacent vertebral fractures in patients with osteoporotic fracture who are suffering from neurogenic claudication.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Trout AT, Kallmes DF, Kaufmann TJ. New fractures after vertebroplasty: adjacent fractures occur significantly sooner. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006; 27:217–223.2. Kim MH, Lee AS, Min SH, Yoon SH. Risk factors of new compression fractures in adjacent vertebrae after percutaneous vertebroplasty. Asian Spine J. 2011; 5:180–187.
Article3. Kang SK, Lee CW, Park NK, et al. Predictive risk factors for refracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty. Ann Rehabil Med. 2011; 35:844–851.
Article4. Lee CS, Chung SS, Chung KH, Kim SR. Significance of pelvic incidence in the development of abnormal sagittal alignment. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2006; 41:274–280.
Article5. Lee GY, Lee JW, Choi HS, Oh KJ, Kang HS. A new grading system of lumbar central canal stenosis on MRI: an easy and reliable method. Skeletal Radiol. 2011; 40:1033–1039.
Article6. Lyles KW, Gold DT, Shipp KM, Pieper CF, Martinez S, Mulhausen PL. Association of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with impaired functional status. Am J Med. 1993; 94:595–601.
Article7. Grados F, Depriester C, Cayrolle G, Hardy N, Deramond H, Fardellone P. Long-term observations of vertebral osteoporotic fractures treated by percutaneous vertebroplasty. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2000; 39:1410–1414.
Article8. Kallmes DF, Comstock BA, Heagerty PJ, et al. A randomized trial of vertebroplasty for osteoporotic spinal fractures. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361:569–579.
Article9. Klazen CA, Lohle PN, de Vries J, et al. Vertebroplasty versus conservative treatment in acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (Vertos II): an open-label randomised trial. . Lancet. 2010; 376:1085–1092.
Article10. DePalma MJ, Ketchum JM, Frankel BM, Frey ME. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures in the nonagenarians: a prospective study evaluating pain reduction and new symptomatic fracture rate. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011; 36:277–282.11. Lin EP, Ekholm S, Hiwatashi A, Westesson PL. Vertebroplasty: cement leakage into the disc increases the risk of new fracture of adjacent vertebral body. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004; 25:175–180.12. Tseng YY, Yang TC, Tu PH, Lo YL, Yang ST. Repeated and multiple new vertebral compression fractures after percutaneous transpedicular vertebroplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009; 34:1917–1922.
Article13. Lindsay R, Silverman SL, Cooper C, et al. Risk of new vertebral fracture in the year following a fracture. JAMA. 2001; 285:320–323.
Article14. Liu WG, He SC, Deng G, et al. Risk factors for new vertebral fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty in patients with osteoporosis: a prospective study. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2012; 23:1143–1149.
Article15. Suzuki H, Endo K, Kobayashi H, Tanaka H, Yamamoto K. Total sagittal spinal alignment in patients with lumbar canal stenosis accompanied by intermittent claudication. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010; 35:E344–E346.
Article16. Lee CS, Lee CK, Kim YT, Hong YM, Yoo JH. Dynamic sagittal imbalance of the spine in degenerative flat back: significance of pelvic tilt in surgical treatment. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001; 26:2029–2035.17. Tran de QH, Duong S, Finlayson RJ. Lumbar spinal stenosis: a brief review of the nonsurgical management. Can J Anaesth. 2010; 57:694–703.18. Delport EG, Cucuzzella AR, Marley JK, Pruitt CM, Fisher JR. Treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis with epidural steroid injections: a retrospective outcome study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2004; 85:479–484.
Article19. Botwin KP, Gruber RD, Bouchlas CG, et al. Fluoroscopically guided lumbar transformational epidural steroid injections in degenerative lumbar stenosis: an outcome study. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2002; 81:898–905.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Combined Treatment of Degenerative Spinal Stenosis and Osteoporotic Compression Fracture
- Vertebroplasty in the Multiple Osteoporotic Compression Fracture
- The Effect of Nerve-Root Injection on Pain Relief in the Management of Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures
- Neurologic Complication after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty with Polymethylmethacrylate: A Case Report
- The Selective Spinal Nerve Root Block as Predictors of Outcome of Operative Treatment in the Lumbar Spine