J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2007 Jun;14(2):101-104. 10.4184/jkss.2007.14.2.101.
Neurologic Complication after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty with Polymethylmethacrylate: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea. osmin71@naver.com
- 2Seoul Chuk Spine Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1941662
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2007.14.2.101
Abstract
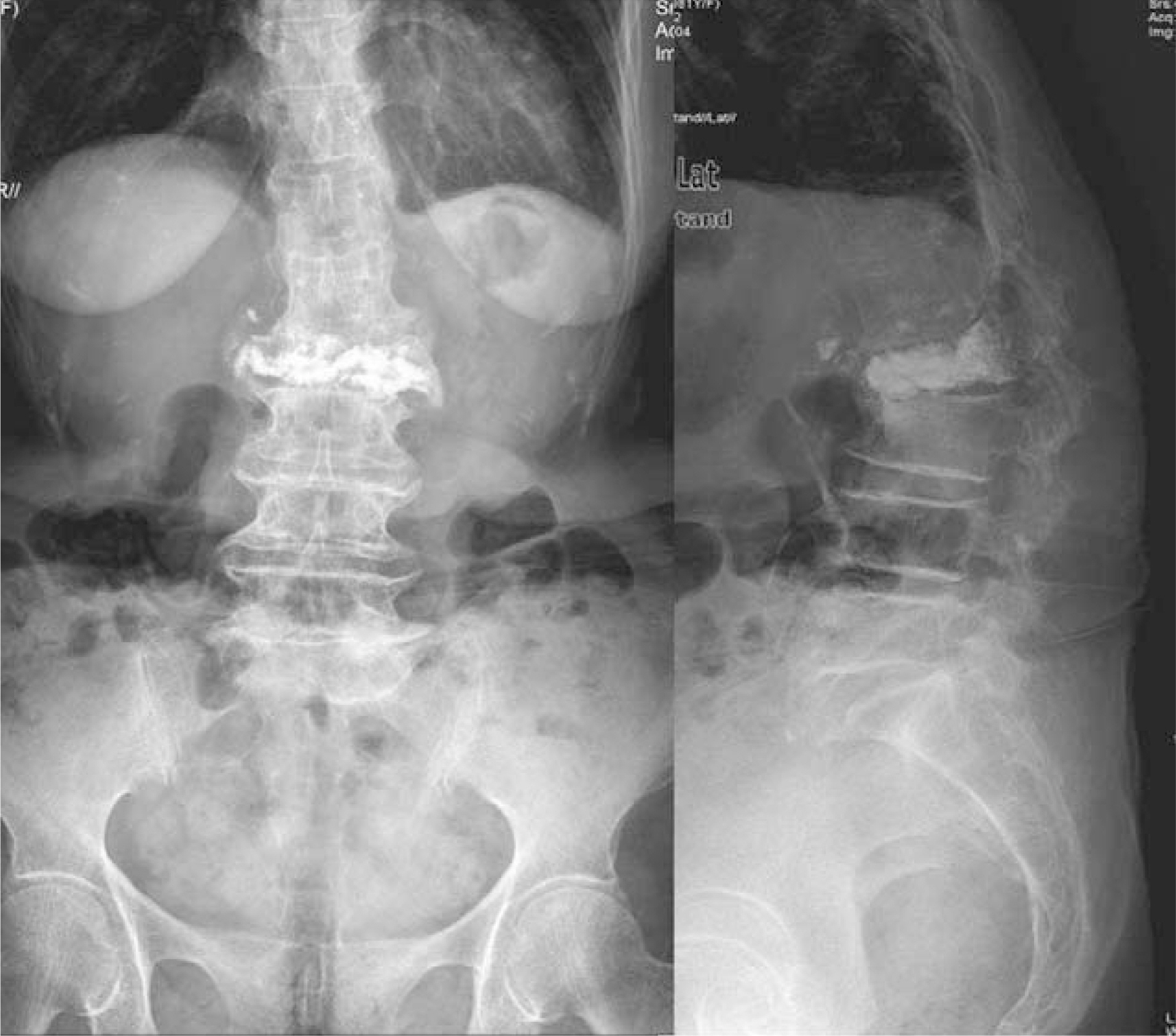
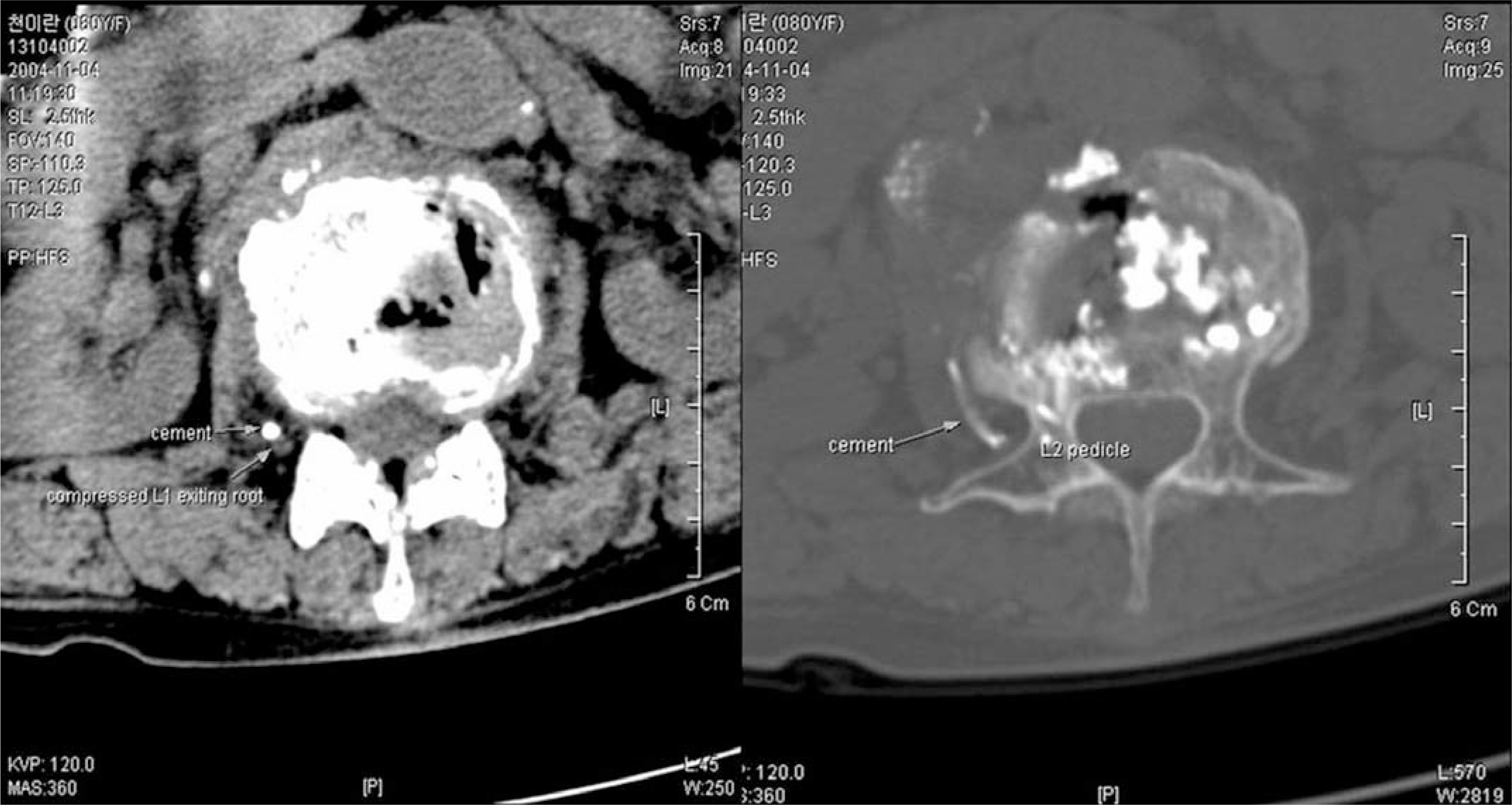
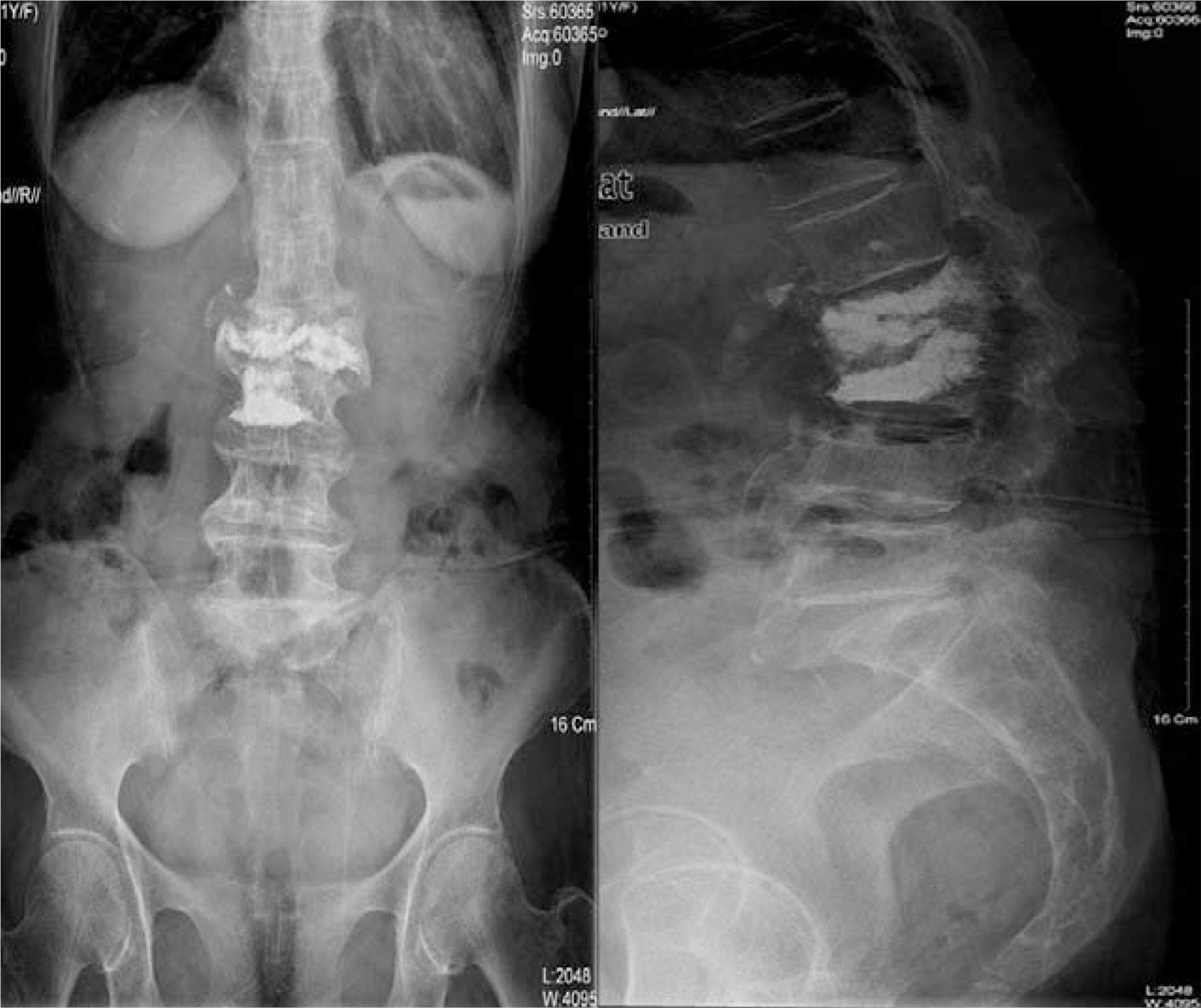
- In recent years, percutaneous vertebroplasty has frequently been used to treat osteoporotic compression fractures. This procedure is generally known to be safe because of the rare occurrence of complications. However, it is accompanied by the risk of cement leakage, and the cement can be easily removed using a surgical technique. Most neurological complications occurred due to extravasation of cement into the spinal canal. Comparatively, there were no reports of neurological complications due to the extravasation of cement into the paravertebral area. Here, we report a case of right-exiting L1 spinal root compression after percutaneous vertebroplasty with polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA). We proceeded to cement removal and nerve root decompression by a paraspinal open microsurgical technique in the event of neurological complication.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Barr JD, Barr MS, Lemley TJ, Mccann RM. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for pain relief and spinal stablization. Spine. 2000; 25:923–928.2). Deramond H, Depreister C, Galibert P, Le Gars D. Percutaneous vertebroplasty with polymethylmethacry-late; technique, indication, and results. Radiologic Clinics of North America. 1998; 36:533–546.3). Weill A, Chiras J, Simon JM, Rose M, Sola-Martinez T, Enkaoua E. Spinal metastasis: indications for and results of percutaneous injection of acrylic surgical cement. Radiology. 1996; 199:241–247.4). Galibert P, Deramond H, Rosat P, Le Gars D. Preliminary note on the treatment of vertebral angioma by percutaneous acrylic vertebroplasty. Neurochirurgie. 1987; 33:166–168.5). Cotton A, Boutry N, Cortet B, et al. .:. Percutaneous vertebroplasty: state of the art. Radiographics. 1998; 18:311–323.
Article6). Mathis JM, Eckel TS, Belkoff SM, Deramond H. Percutaneous vetebroplasty: therapeutic option for pain associated with vetevral compression fracture. J Back Muscu-loskel Rehab. 1999; 13:11–17.7). Jensen ME, Avery JE, Mathis JM, Kallmess DF, Cloft HJ, Dio JE. Percutaneous polymethylmethacrylate vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral body compression fracture: technical aspects. Am J Neuroradiol. 1997; 18:1897–1904.8). Harrington KD. Major neurological complications following percutaneous vertebroplasty with polymethylmethacrylate. J Bone Joint Surg. 2001; 83:1070–1073.
Article9). Ratliff J, Nguyen T, Heiss J. Root and spinal cord compression from methylmethacrylate vetebroplasty. Spine. 2001; 26:300–302.10). Cotton A, Dewatre F, Cortet B, et al. .:. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteolytic metastases and myeloma: effects of the percentage of lesion filling and the leakage of methyl methacrylate at clinical followup. Radiology. 1996; 200:525–530.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hypotension during Percutaneous Vertebroplasty with PMMA (Polymethylmethacrylate)
- Fatal Hemothorax Following Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: A Case Report
- Pulmonary Embolism after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty with Polymethylmethacrylate: A case report
- Lumbar Root Injury by the Leakage of Bone Cement after the Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: A case report
- Pulmonary Embolism after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty with Polymethylmethacrylate: Case Report