J Korean Rheum Assoc.
2009 Dec;16(4):338-343.
A Case of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis in Association with an Overlap Syndrome of Systemic Sclerosis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea. byyoon@paik.ac.kr
Abstract
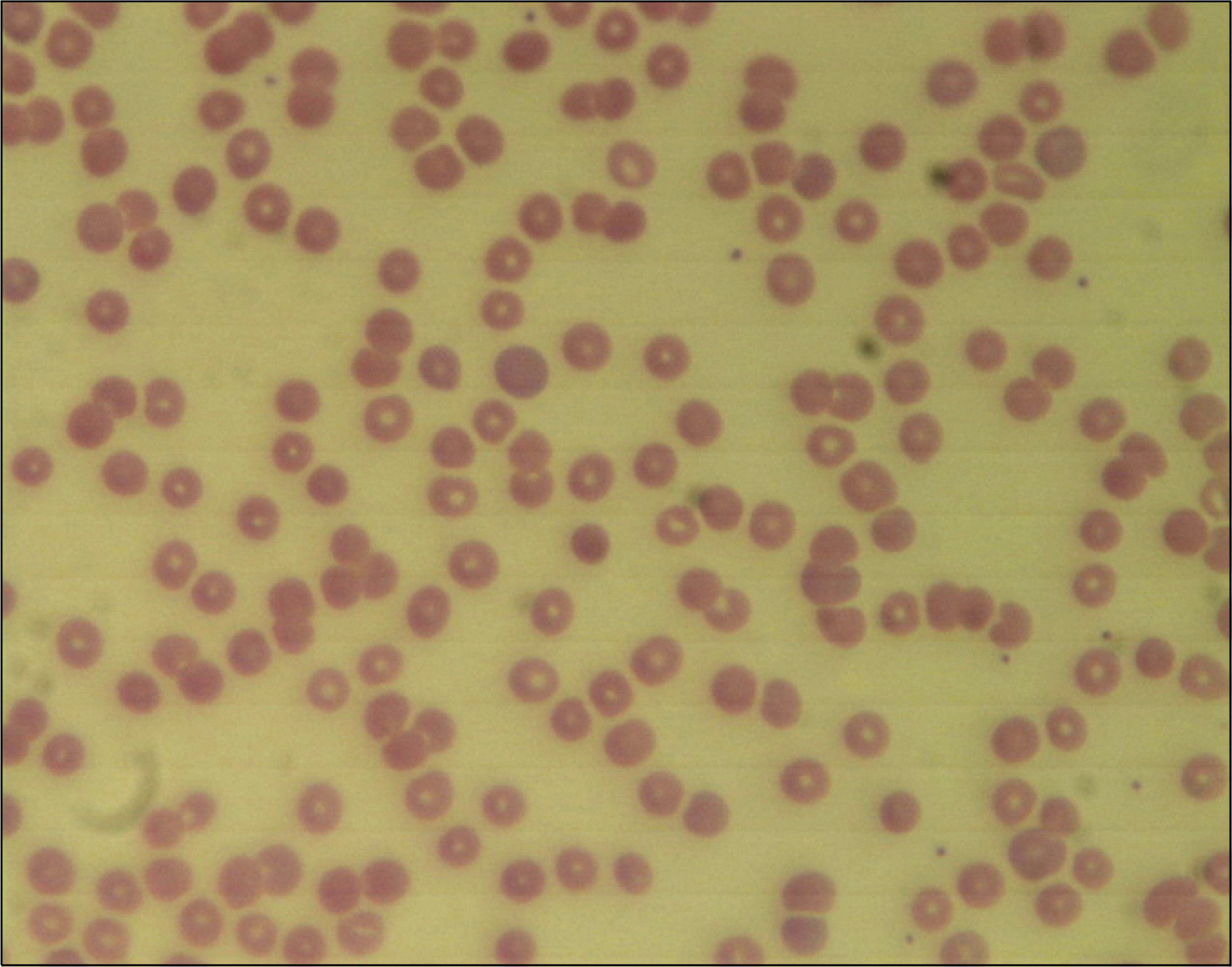
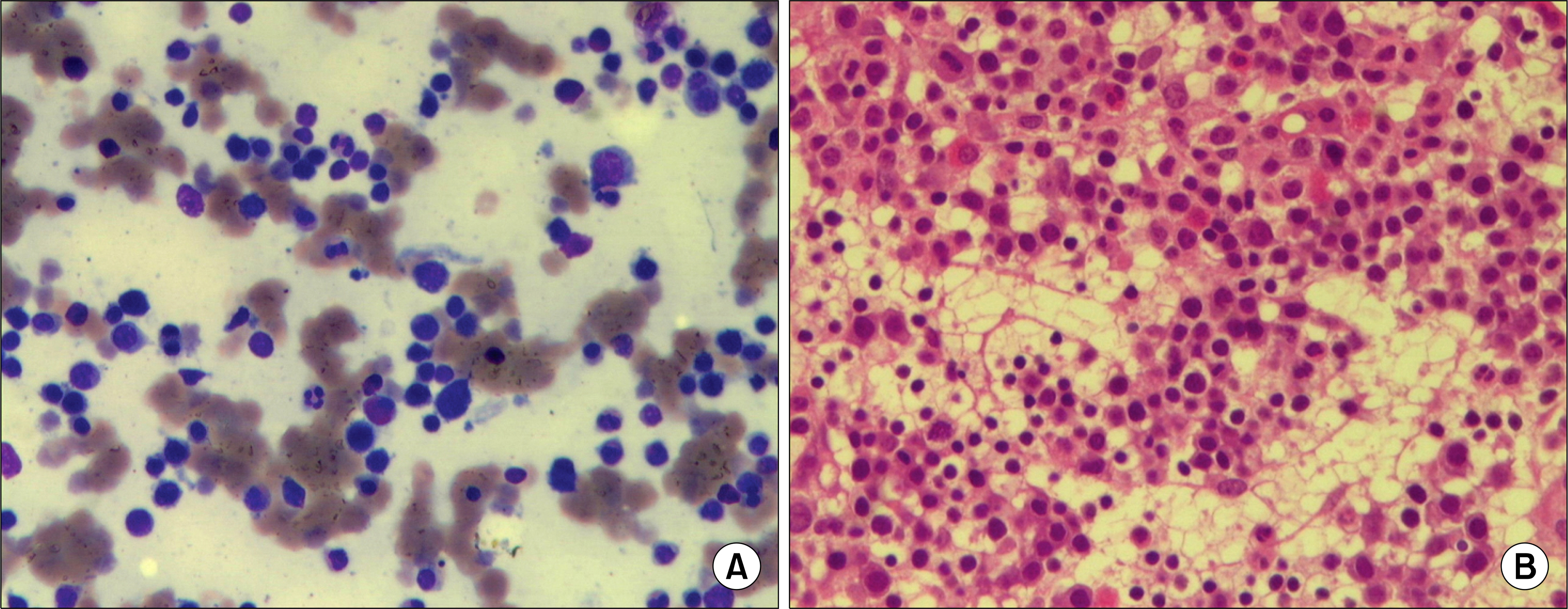
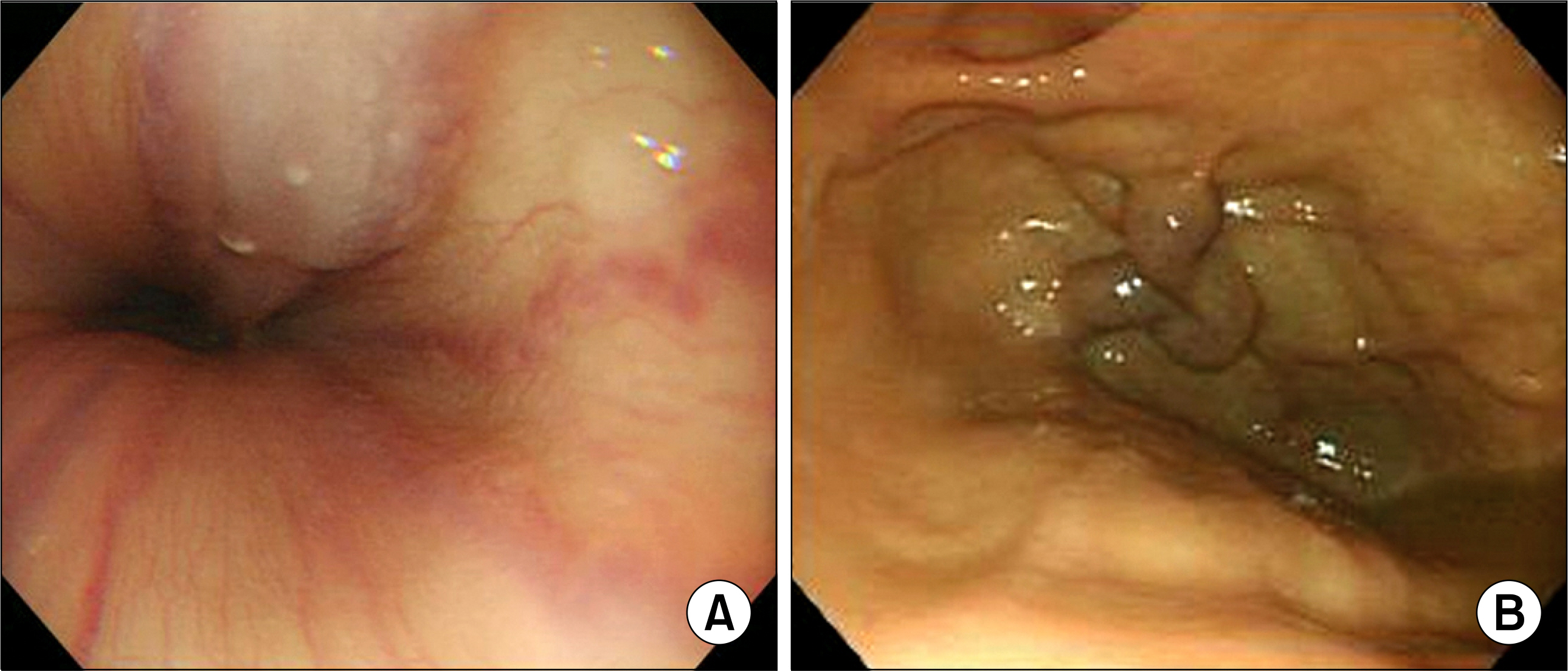
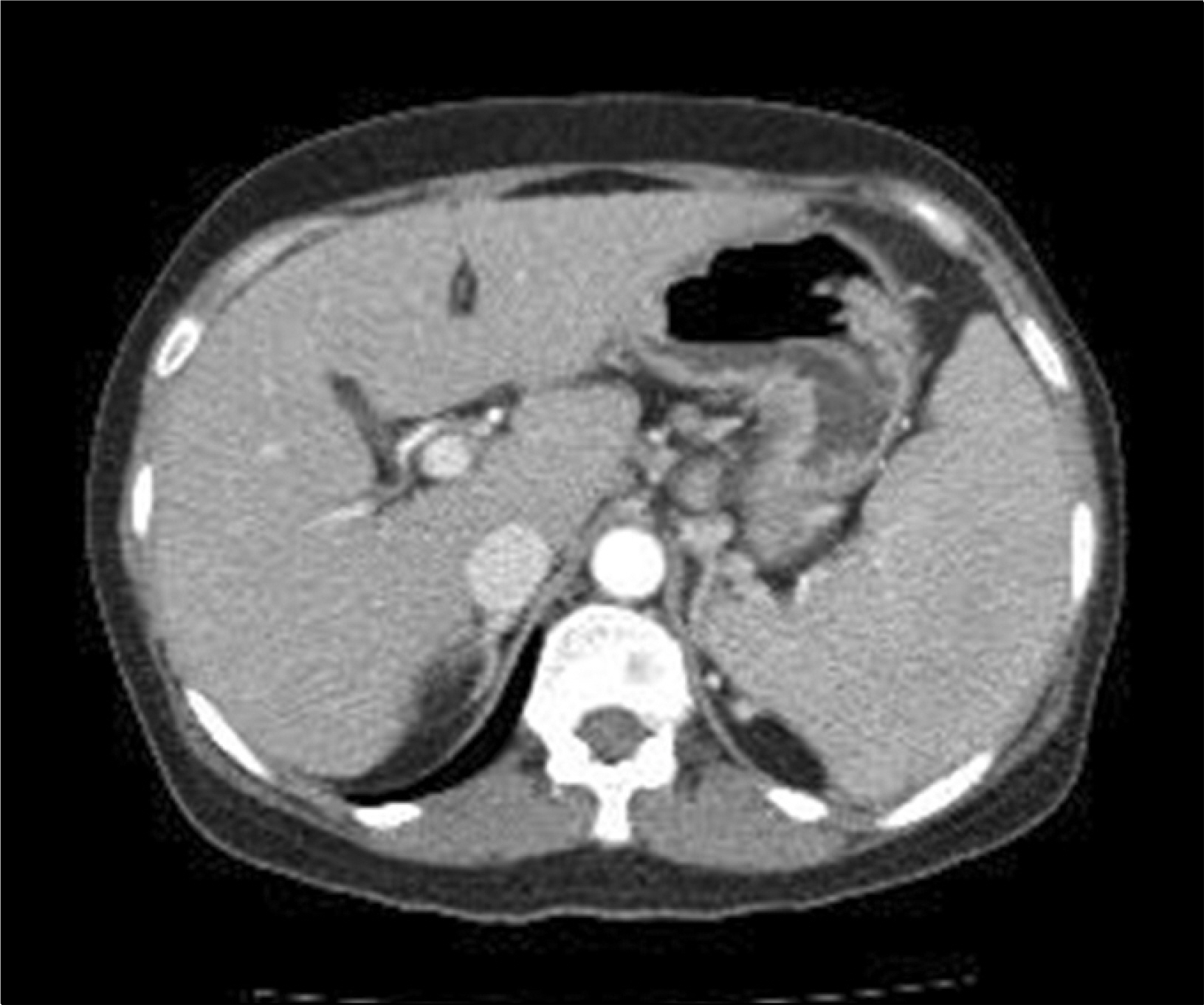
- Primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) is a slowly progressive autoimmune disease of the liver that is related to anti-mitochondria antibody and the disease is characterized by portal inflammation and immune-mediated destruction of the intrahepatic bile ducts. Several autoimmune diseases, such as hypothyroidism, Sjogren syndrome and systemic sclerosis (SSc), occur with increased frequency in patients with PBC. However, there are a few reports of a possible connection between systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) or autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA) and PBC. A 52-year-old female was admitted with fatigue and dyspnea that she had suffered with for the past month. She had suffered from jaundice for 2 weeks before admission. Many of the clinical manifestations and laboratory findings suggested the diagnosis of PBC with SSc of the limited type and AIHA. She was treated with methylprednisolone pulse therapy and ursodeoxycholic acid. We consequently diagnosed her as having SLE, as she satisfied the 4 relative diagnostic criteria-arthritis, AIHA, positive antinuclear antibody and positive antiphospholipid antibodies.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Anemia, Hemolytic, Autoimmune
Antibodies, Antinuclear
Antibodies, Antiphospholipid
Autoimmune Diseases
Bile Ducts, Intrahepatic
Dyspnea
Fatigue
Female
Humans
Hypothyroidism
Inflammation
Jaundice
Liver
Liver Cirrhosis, Biliary
Lupus Erythematosus, Systemic
Methylprednisolone
Middle Aged
Scleroderma, Systemic
Sjogren's Syndrome
Ursodeoxycholic Acid
Antibodies, Antinuclear
Antibodies, Antiphospholipid
Methylprednisolone
Ursodeoxycholic Acid
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Levine JS, Branch DW, Rauch J. The antiphospholipid syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2002; 346:752–63.
Article2. Kaplan MM, Gershwin ME. Primary biliary cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 2005; 353:1261–73.
Article3. Seki S, Tanaka K, Fujisawa M, Shiomi S, Kuroki T, Harihara S, et al. A patient with asymptomatic primary biliary cirrhosis in association with Sjogren's syndrome developing feature of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nippon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 1986; 83:2445–9.4. Cabanillas Nüñez Y, Rodríguez Vidigal FF, Soria Corón R, Díaz Rodríguez E, Bueno Jiménez C. Triple autoimmune association in man: Sjogren's syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus and primary biliary cirrhosis. An Med Interna. 1996; 13:407.5. Lee CG, Chang HK, Kim SY, Kang HH, Kim DJ, Chang CK, et al. A Case of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis in Association with Sjögren's Syndrome Developing Features of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. JKRA. 2001; 8:59–63.6. Wielosz E, Majdan M, Zychowska I, Jeleniewicz R. Coexistence of five autoimmune disease: diagnostic and therapeutic difficulties. Rheumatol Int. 2008; 28:919–23.7. Clements P, Lachenbruch P, Seibold J, Wigley FM. Inter- and intraobserver variability of total skin thickness score (modified Rodnan) in systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol. 1995; 22:1281–5.8. Schifter T, Lewinski UH. Primary biliary cirrhosis and systemic lupus erythematosus. A rare association. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1997; 15:313–4.9. Nakasone H, Sakugawa H, Fukuchi J, Miyagi T, Sugama R, Hokama A, et al. A patient with primary biliary cirrhosis associated with autoimmune hemolytic anemia. J Gastroenterol. 2000; 35:245–9.
Article10. Katsumata K. A case of systemic sclerosis complicated by autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Mod Rheumatol. 2006; 16:191–5.
Article11. Gurudu SR, Mittal SK, Shaber M, Gamboa E, Michael S, Sigal LH. Autoimmune hepatitis associated with autoimmune hemolytic anemia and anticardiolipin antibody syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. 2000; 45:1878–80.12. Rodríguez-Reyna TS, Alarcón-Segovia D. Overlap syndrome in the context of shared autoimmunity. Autoimmunity. 2005; 38:219–23.13. Alarcón-Segovia D. Shared autoimmunity: A concept for which the time has come. Autoimmunity. 2005; 38:201–3.
Article14. Rodríguez-Reyna TS, Alarcón-Segovia D. The different faces of shared autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev. 2006; 5:86–8.
Article15. Lyons R, Narain S, Nichols C, Satoh M, Reeves WH. Effective use of autoantibody tests in the diagnosis of systemic autoimmune disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005; 1050:217–28.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of overlap syndrome of systemic sclerosis/ systemic lupus erythematosus/Sjogren's syndrome
- Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome in a Patient with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Systemic Sclerosis Overlap Syndrome
- A Case of Diffuse Scleroderma Associated with Primary Biliary Cirrhosis and Isolated Pulmonary Hypertension
- Three Cases of Overlap Syndrome Consisting of Systemic Sclerosis and Rheumatoid Arthritis
- A Case of Overlap Syndrome with Systemic Sclerosis and Rheumatoid Arthritis