J Korean Soc Clin Pharmacol Ther.
2013 Jun;21(1):52-62.
A Randomized, Placebo Controlled, Double Blind, Parallel Group, Multiple Dosing, Dose Escalation Clinical Study to Evaluate Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics and Tolerability of Zofenopril in Healthy Korean Subjects
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Seoul National University College of Medicine and Hospital, Seoul, South Korea. ksyu@snu.ac.kr
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Zofenopril is a new Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) inhibitor for the treatment of the patients with hypertension and congestive heart failure. This study aimed to evaluate the pharmacokinetics (PKs)/pharmacodynamics (PDs) and tolerability of zofenopril in healthy Korean subjects.
METHODS
A randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled, multiple dosing parallel group study with two dosage groups (zofenopril 30 mg or 60 mg) was conducted in healthy Korean male subjects. Each dosage group consisted of 10 subjects and they were randomly assigned to receive zofenopril or placebo with a ratio of 4:1. PK characteristics of zofenopril and its active metabolite, zofenoprilat, were evaluated after single or multiple dosing. Serum ACE activities and blood pressures were measured for PD evaluation. Adverse events, clinical laboratory tests, electrocardiograms, vital signs and physical examinations were performed for tolerability evaluation.
RESULTS
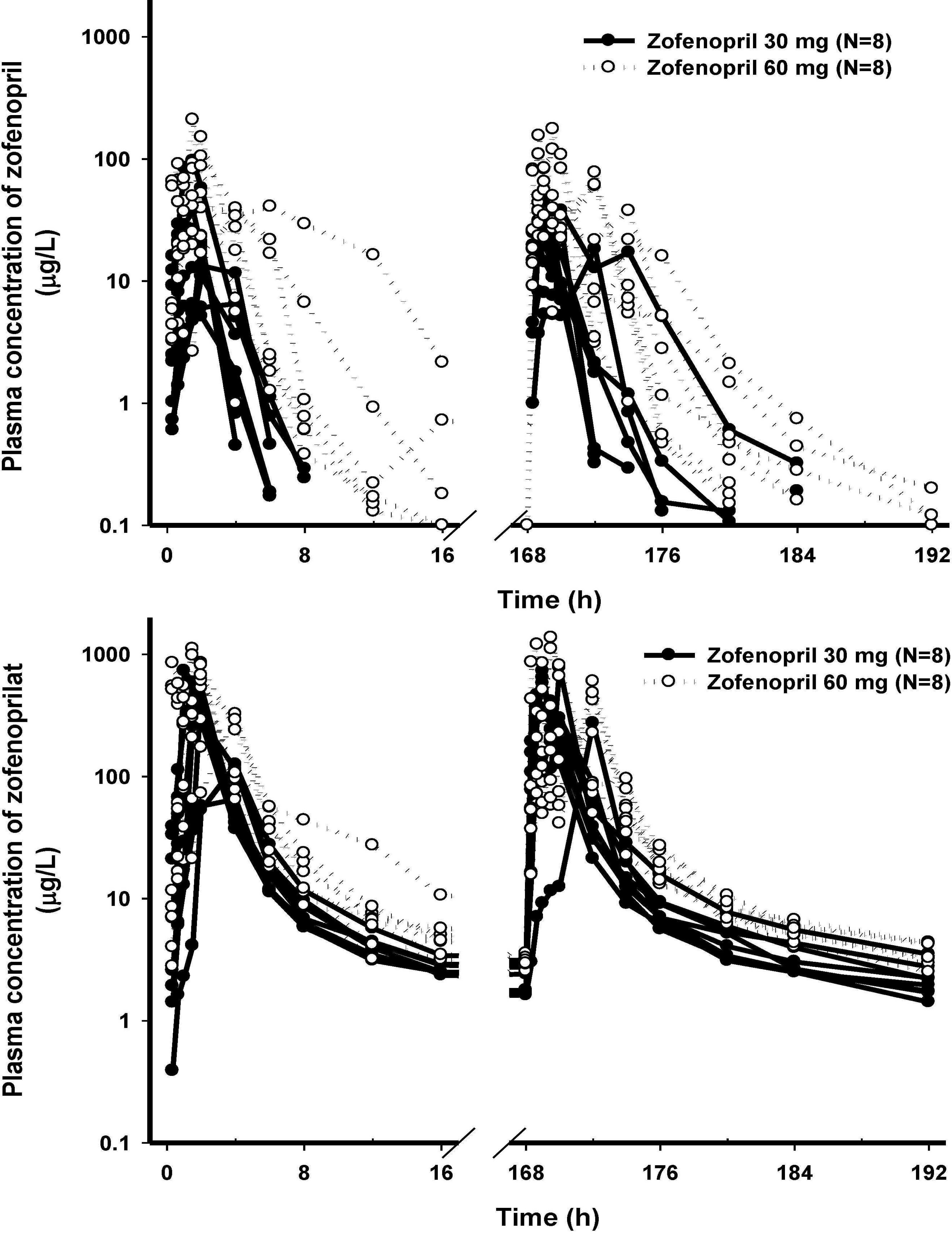
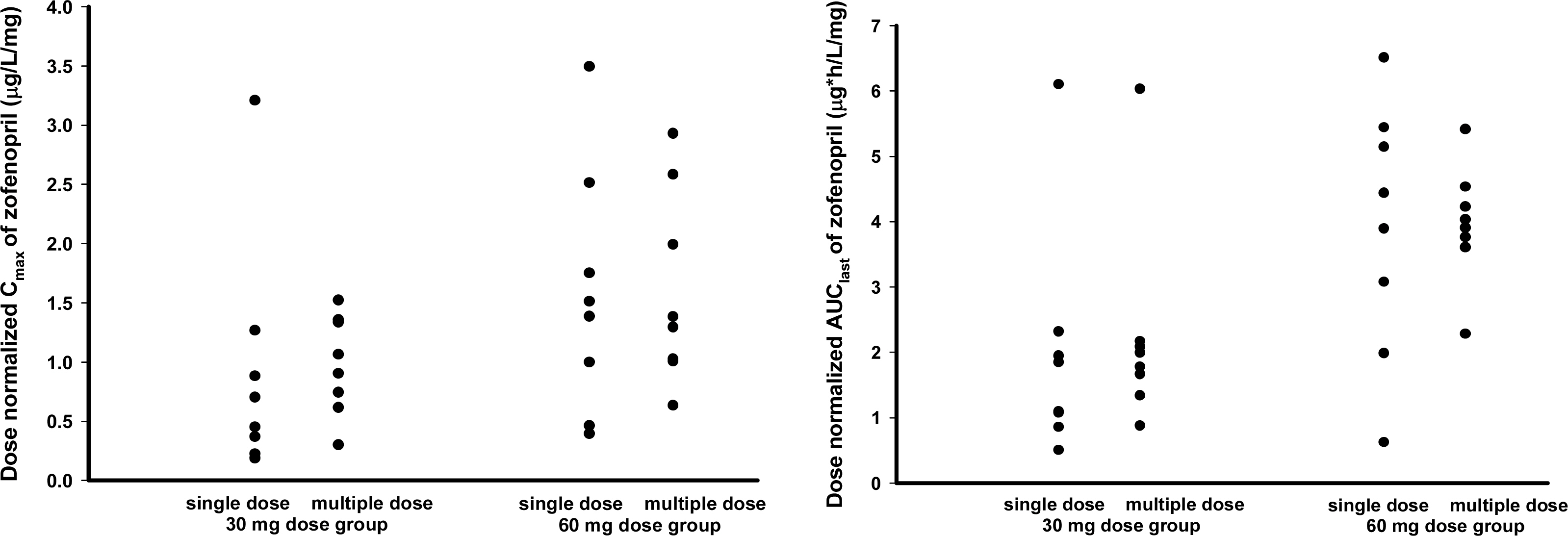
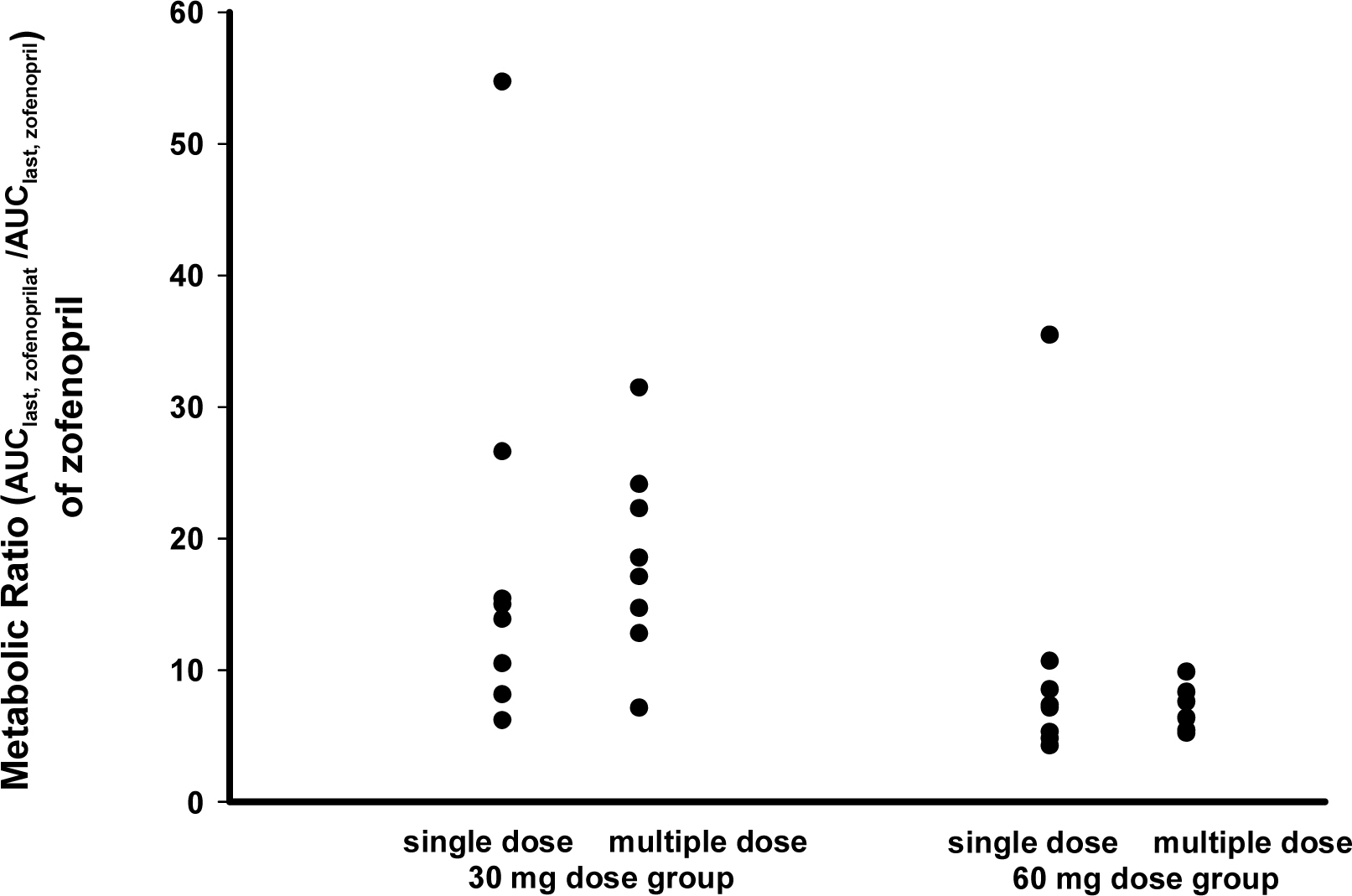
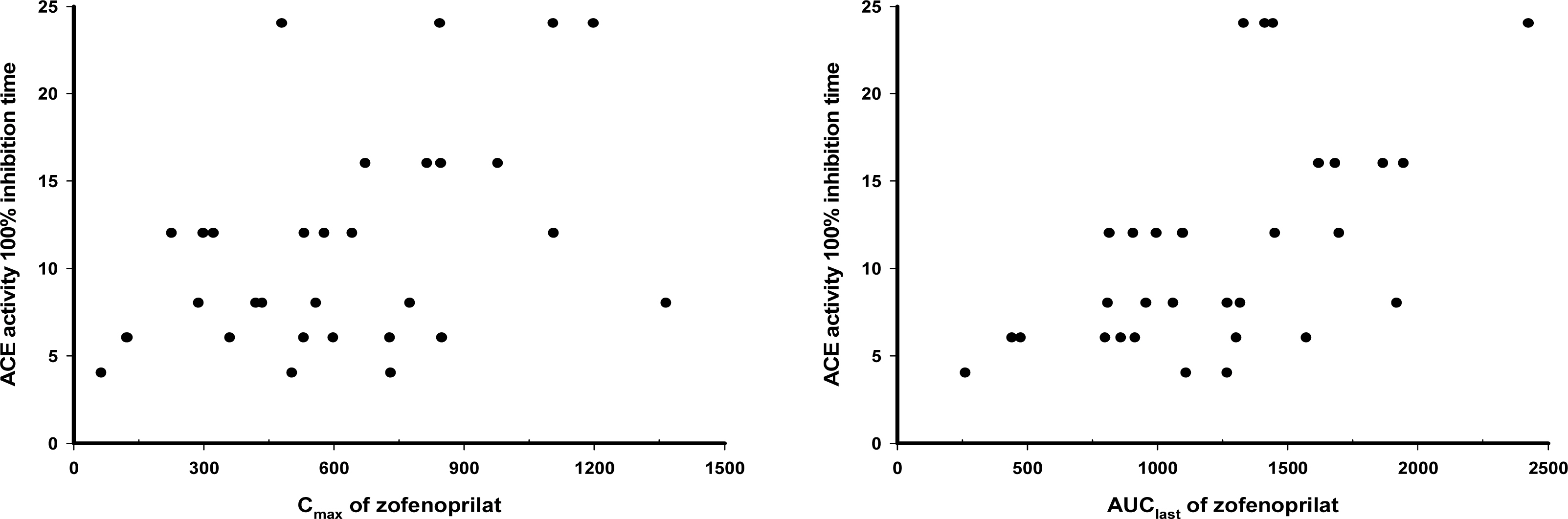
The PK characteristics of zofenopril and zofenoprilat after single dose and multiple doses were similar to one another. The metabolic ratio of zofenoprilat to zofenopril after single dose and multiple doses were 12.4 and 14.9, respectively, in the 30 mg dosage group, and were 6.8 and 6.6, respectively, in the 60 mg dosage group. Complete serum ACE activity inhibition was observed within 1 hour in both doses but it was maintained longer in the 60 mg dosage group compared to the 30 mg dosage group. There were no clinically significant abnormalities in tolerability evaluations.
CONCLUSION
The PK/PD characteristics of zofenopril and zofenoprilat after single or multiple administrations were explored. Zofenopril was well tolerated after multiple administrations in healthy Korean subjects.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. MacFadyen RJ, Lees KR, Reid JL. Tissue and plasma angiotensin converting enzyme and the response to ACE inhibitor drugs. Brit J Clin Pharmacol. 1991; 31(1):1–13.
Article2. Campbell DJ. Endogenous angiotensin II levels and the mechanism of action of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor type 1 antagonists. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol Suppl. 1996; 3:S125–S131.3. Song JC, White CM. Clinical pharmacokinetics and selective pharmacodynamics of new angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors: an update. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2002; 41(3):207–224.4. Reid JL. From kinetics to dynamics: are there differences between ACE inhibitors? Eur Heart J. 1997; 18:E14–E18.
Article5. Marzo A, Dal Bo L, Mazzucchelli P, Ceppi Monti N, Crivelli F, Ismaili S, Giusti A, Richard Uhr M. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic comparative study of zofenopril and enalapril in healthy volunteers. Arzneimittelforschung. 2002; 52(4):233–242.
Article6. Subissi A, Evangelista S, Giachetti A. Preclinical Profile of Zofenopril: An Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitor with Peculiar Cardioprotective Properties. Cardiovas Drug Reviews. 1999; 17(2):115–133.
Article7. Morrison RA, Burkett DE, Arnold ME, D’Arienzo CJ, Weinstein SH. Sites of first-pass bioactivation (hydrolysis) of orally administered zofenopril calcium in dogs. Pharm Res. 1991; 8(3):370–375.8. Cushman DW, Wang FL, Fung WC, Grover GJ, Harvey CM, Scalese RJ, Mitch SL, Deforrest JM. Comparisons in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo of the actions of seven structurally diverse inhibitors of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE). Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1989; 28(2):115S–130S.
Article9. Marzo A, Dal Bo L, Mazzucchelli P, Ceppi Monti N, Aleotti Tettamanti R, Crivelli F, Richard Uhr M, Ismaili S, Giusti A. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of zofenopril in healthy volunteers. Arzneimittel-Forschung. 1999; 49(12):992–996.10. Malacco E, Malacco E, Castiglioni G, Corradi L, Cristofari M, Fogari R, Pisani A, Venco A. Dose-Response Relationship of Zofenopril in Essential Hypertension: A 24-Hour Blood Pressure-Monitoring Study. Clin Drug Inves. 2002; 22(1):9–15.11. Dal Bo L, Mazzucchelli P. Marzo A. Assay of zofenopril and its active metabolite zofenoprilat by liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatography B: Biom Sci Applic. 2000; 749(2):287–294.12. Israili ZH, Hall WD. Cough and angioneurotic edema associated with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor therapy. A review of the literature and pathophysiology. Ann Intern Med. 1992; 117(3):234–242.13. Bangalore S, Kumar S, Messerli FH. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor associated cough: deceptive information from the Physicians’ Desk Reference. Am J Med. 2010; 123(11):1016–1030.
Article14. Whitworth JA. 2003 World Health Organization (WHO)/Intemational Society of Hypertension (ISH) statement on management of hypertension. J Hypertens. 2003; 21(11):1983–1992.15. Williams B. The changing face of hypertension treatment: treatment strategies from the 2007 ESH/ESC hypertension Guidelines. J Hypertens Suppl. 2009; 27(3):S19–S26.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics and Safety of JES9501 after Single and Multiple Oral Administration in Healthy Subjects
- Tolerability and Pharmacokinetics Following a Single Dose of Vardenafil in Healthy Korean Volunteers
- Pharmacokinetics of T-614 after Single Oral Administration in Healthy Korean Volunteers
- Evaluation of Pharmacokinetics and Tolerability of Eplerenone after Multiple Oral Doses of 100 mg in Healthy Korean Volunteers
- Pharmacodynamic principles and target concentration intervention