J Korean Soc Clin Pharmacol Ther.
2012 Dec;20(2):145-154.
Bioequivalence and Dose Proportionality of Olmesartan Medoxomil Formulations
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Clinical Pharmacology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. mekka@snu.ac.kr
- 2Yuhan Corporation, 49-6, Daebang-dong, Dongjak-gu, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Biocore Corporation, #60-21, Gasan-dong, Geumcheon-gu, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
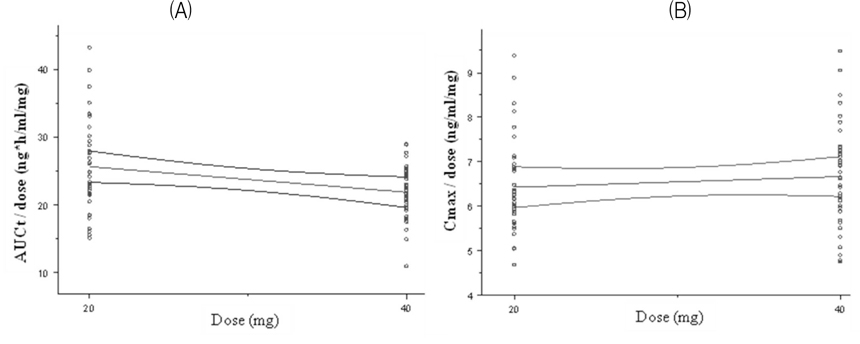
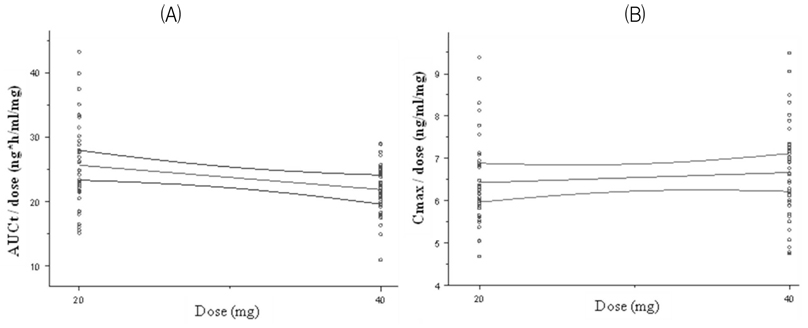
Olmesartan medoxomil is an angiotensin II receptor blocker commonly used in hypertension. First objective of this study was to evaluate the bioequivalence of two olmesartan formulations, Olmesartan 20 mg and 40 mg tablet (Yuhan, Pharmaceutical Corp. Seoul, Korea) as test drugs and Olmetec(R) 20 mg and 40 mg tablet (Daewoong, Pharmaceutical Corp. Seoul, Korea) as reference drugs. Second objective of this study was to evaluate the dose-proportionality of two formulations.
METHODS
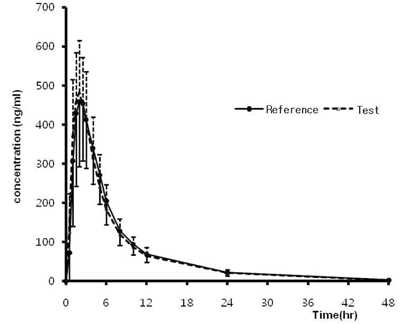
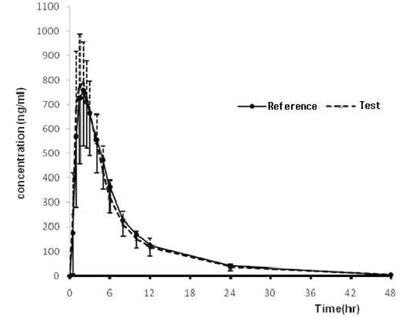
Two studies (20 mg, 40 mg) were conducted as a randomized, open-label, 2-period, crossover design. Each subject received one 20 mg or 40 mg tablet of the reference or test formulation of olmesartan medoxomil in each study. Blood samples were obtained during the 48-hour period after the dose in each treatment period. Wash-out period was 1 week in each study. Concentrations of olmesartan medoxomil in plasma were analyzed using a liquid chromatography system with tandem mass-spectrometric detection (LC/MS/MS). The primary pharmacokinetic parameters were Cmax (maximum concentration) and AUCt (area under the concentration-time curve from time 0 to the last sampling time).
RESULTS
A total number of 40 healthy male volunteers participated in the study and 37 volunteers completed both treatment periods in 20 mg trial. All 40 participants completed both treatment periods in 40 mg trial. The 90 % CIs for the geometric mean ratios of the pharmacokinetic parameters (test:reference drug) were 0.93 ~ 1.04 for AUCt and 0.97 ~ 1.08 for Cmax in 20 mg trial. The 90 CIs were 0.94 ~ 1.02 for AUCt and 1.00 ~ 1.11 for Cmax in 40 mg trial. All parameters of two studies satisfy the range of bioequivalence criterion.
CONCLUSION
The obtained results indicated that pharmacokinetic exposure to Olmesartan 20 mg and 40 mg tablet was bioequivalent to that of Olmetec(R) 20 mg and 40 mg tablet, respectively.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ferrario CM, Richmond RS, Smith R, Levy P, Strawn WB, Kivlighn S. Renin-angiotensin system as a therapeutic target in managing atherosclerosis. Am J Ther. 2004. 11(1):44–53.
Article2. Weir MR, Dzau VJ. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system: a specific target for hypertension management. Am J Hypertens. 1999. 12(12):205S–213S.
Article3. Mukae S, Itoh S, Aoki S, Iwata T, Nishio K, Sato R, Katagiri T. Association of polymorphisms of the renin-angiotensin system and bradykinin B2 receptor with ACE-inhibitor-related cough. J Hum Hypertens. 2002. 16(12):857–863.
Article4. Barrios V, Boccanelli A, Ewald S, Girerd X, Heagerty A, Krzesinski J, Lins R, Rodicio J, Stefenelli T, Woittiez A, Bhm M. Efficacy and tolerability of olmesartan medoxomil in patients with mild to moderate essential hypertension: the OLMEBEST Study. Clin Drug Investig. 2007. 27(8):545–558.
Article5. Jiang J, Liu D, Hu P. Pharmacokinetic and safety profile of olmesartan medoxomil in healthy Chinese subjects after single and multiple administrations. Pharmazie. 2009. 64(5):323–326.6. Paster RZ, Snavely DB, Sweet AR, Draper RA, Goldberg AI, Soffer BA, Sweet CS. Use of losartan in the treatment of hypertensive patients with a history of cough induced by angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Clin Ther. 1998. 20(5):978–989.
Article7. Gardner SF, Franks AM. Olmesartan medoxomil: the seventh angiotensin receptor antagonist. Ann Pharmacother. 2003. 37(1):99–105.
Article8. Brousil JA, Burke JM. Olmesartan medoxomil: an angiotensin II-receptor blocker. Clin Ther. 2003. 25(4):1041–1055.
Article9. Li K, Liang J, Hu B, Qiu Y, Luo C, Jiang Y, Lin X, Yang N. The relative bioavailability and fasting pharmacokinetics of three formulations of olmesartan medoxomil 20-mg capsules and tablets in healthy Chinese male volunteers: An open-label, randomized-sequence, single-dose, three-way crossover study. Clin Ther. 2010. 32(9):1674–1680.
Article10. Diletti E, Hauschke D, Steinijans VW. Sample size determination for bioequivalence assessment by means of confidence intervals. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol. 1991. 29(1):1–8.11. Korea Food & Drug Administration. Bioequivalence Test Standard, 2008-22. 2008. Seoul: Korea Food & Drug Administration.12. Administration. USFaD. Benicar (olmesartan medoxomil) tablets. last visited on 20 Jan 2012. http://www.fda.gov/Safety/MedWatch/SafetyInformation/ucm258490.htm. [Online].13. Schwocho LR, Masonson HN. Pharmacokinetics of CS-866, a new angiotensin II receptor blocker, in healthy subjects. J Clin Pharmacol. 2001. 41(5):515–527.
Article14. Smith BP, Vandenhende FR, DeSante KA, Farid NA, Welch PA, Callaghan JT, Forgue ST. Confidence interval criteria for assessment of dose proportionality. Pharm Res. 2000. 17(10):1278–1283.15. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for Industry: Bioavailability and Bioequivanece Studies for Orally Administered Drug Products - General Considerations. 2003. 03. Washington, DC.:16. von Bergmann K, Laeis P, Pchler K, Sudhop T, Schwocho LR, Gonzalez L. Olmesartan medoxomil: influence of age, renal and hepatic function on the pharmacokinetics of olmesartan medoxomil. J Hypertens Suppl. 2001. 19(1):S33–S40.
Article17. Laeis P, Pchler K, Kirch W. The pharmacokinetic and metabolic profile of olmesartan medoxomil limits the risk of clinically relevant drug interaction. J Hypertens Suppl. 2001. 19(1):S21–S32.
Article18. Rohatagi S, Lee J, Shenouda M, Haworth S, Bathala MS, Allison M, Rubets I, Heyrman R, Noveck R, Salazar DE. Pharmacokinetics of amlodipine and olmesartan after administration of amlodipine besylate and olmesartan medoxomil in separate dosage forms and as a fixed-dose combination. J Clin Pharmacol. 2008. 48(11):1309–1322.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pharmacokinetics and bioequivalence of two different 20 mg olmesartan tablets: A randomized, single-dose, two-period crossover study in healthy Korean male volunteers
- Telmisartan-induced sprue-like enteropathy: a case report and a review of patients using non-olmesartan angiotensin receptor blockers
- Fed and fasted bioequivalence assessment of two formulations of extended-release fixed-dose combination dapagliflozin/metformin (10/1,000 mg) tablets in healthy subjects
- Erratum: Pharmacokinetics and bioequivalence of two different 20 mg olmesartan tablets: A randomized, single-dose, two-period crossover study in healthy Korean male volunteers
- Pharmacokinetic properties and bioequivalence of gefitinib 250 mg in healthy Korean male subjects