Intest Res.
2017 Jul;15(3):419-421. 10.5217/ir.2017.15.3.419.
Telmisartan-induced sprue-like enteropathy: a case report and a review of patients using non-olmesartan angiotensin receptor blockers
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, India. docvishalsharma@gmail.com
- 2Department of Nephrology, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, India.
- KMID: 2382387
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5217/ir.2017.15.3.419
Abstract
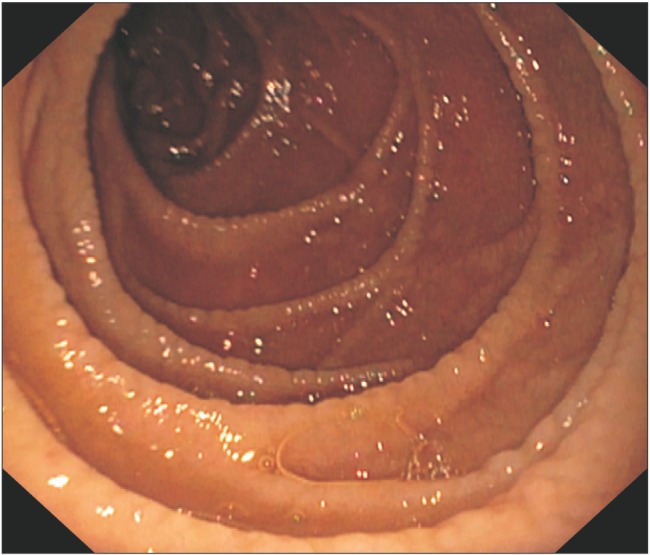
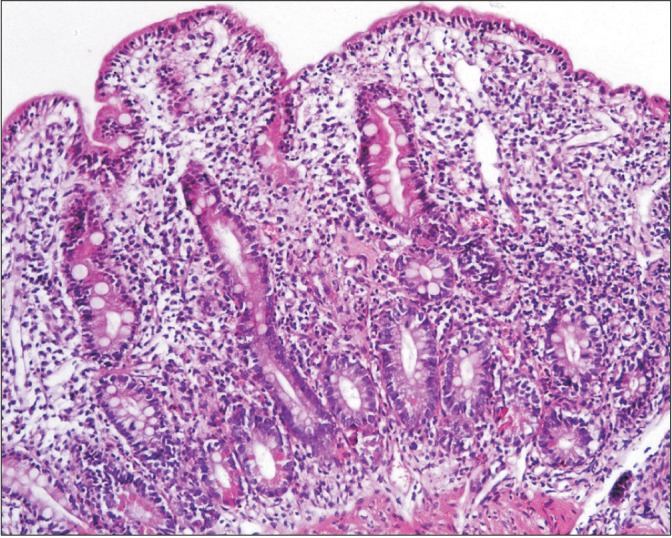
- Recent studies have identified sprue-like illness associated with the use of the antihypertensive agent olmesartan medoxomil. However, whether this condition is specific to the use of olmesartan or is associated with the use of drugs belonging to the class of "sartans" remains to be clarified. A 45-year-old woman with chronic kidney disease along with hypothyroidism and hypertension presented with chronic diarrhea and significant weight loss. Endoscopy of the upper gastrointestinal tract showed scalloping and grooving of the duodenum, and histopathological examination showed subtotal villous atrophy. She was on telmisartan for hypertension, which was discontinued. Subsequently, diarrhea ameliorated dramatically, and she regained weight. To our knowledge, this is the first study to report telmisartan-associated sprue-like enteropathy. Further, we have reviewed the cases of patients with sprue-like enteropathy caused by valsartan, irbesartan, and eprosartan.
MeSH Terms
-
Angiotensin Receptor Antagonists*
Angiotensins*
Atrophy
Celiac Disease
Diarrhea
Duodenum
Endoscopy
Female
Humans
Hypertension
Hypothyroidism
Middle Aged
Olmesartan Medoxomil
Pectinidae
Renal Insufficiency, Chronic
Upper Gastrointestinal Tract
Valsartan
Weight Loss
Angiotensin Receptor Antagonists
Angiotensins
Olmesartan Medoxomil
Valsartan
Figure
Reference
-
1. Choi EY, McKenna BJ. Olmesartan-associated enteropathy: a review of clinical and histologic findings. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2015; 139:1242–1247. PMID: 26414468.
Article2. Burbure N, Lebwohl B, Arguelles-Grande C, Green PH, Bhagat G, Lagana S. Olmesartan-associated sprue-like enteropathy: a systematic review with emphasis on histopathology. Hum Pathol. 2016; 50:127–134. PMID: 26997446.
Article3. Ianiro G, Bibbò S, Montalto M, Ricci R, Gasbarrini A, Cammarota G. Systematic review: sprue-like enteropathy associated with olmesartan. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014; 40:16–23. PMID: 24805127.
Article4. Cyrany J, Vasatko T, Machac J, Nova M, Szanyi J, Kopacova M. Letter: telmisartan-associated enteropathy: is there any class effect? Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014; 40:569–570. PMID: 25103353.
Article5. Cammarota G, Ianiro G, Bibbò S, Gasbarrini A. Letter: telmisartan associated enteropathy: is there any class effect? Authors' reply. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014; 40:570. PMID: 25103354.
Article6. Marthey L, Cadiot G, Seksik P, et al. Olmesartan-associated enteropathy: results of a national survey. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014; 40:1103–1109. PMID: 25199794.
Article7. Herman ML, Rubio-Tapia A, Wu TT, Murray JA. A case of severe sprue-like enteropathy associated with valsartan. ACG Case Rep J. 2015; 2:92–94. PMID: 26157924.
Article8. Maier H, Hehemann K, Vieth M. Celiac disease-like enteropathy due to antihypertensive therapy with the angiotensin-II receptor type 1 inhibitor eprosartan. Cesk Patol. 2015; 51:87–88. PMID: 25970720.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Olmesartan-associated Enteropathy with Acute Kidney Injury
- Olmesartan is not associated with the risk of enteropathy: a Korean nationwide observational cohort study
- Determination of candesartan or olmesartan in hypertensive patient plasma using UPLC-MS/MS
- Evaluation of effect over time after oral administration of telmisartan for chronic kidney disease in cats
- The Effect of Telmisartan on Endothelial Function and Arterial Stiffness in Patients With Essential Hypertension