Korean J Gastroenterol.
2022 Mar;79(3):130-134. 10.4166/kjg.2022.007.
Olmesartan-associated Enteropathy with Acute Kidney Injury
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea
- 2Research Institute for Convergence of Biomedical Science and Technology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea
- KMID: 2527481
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2022.007
Abstract
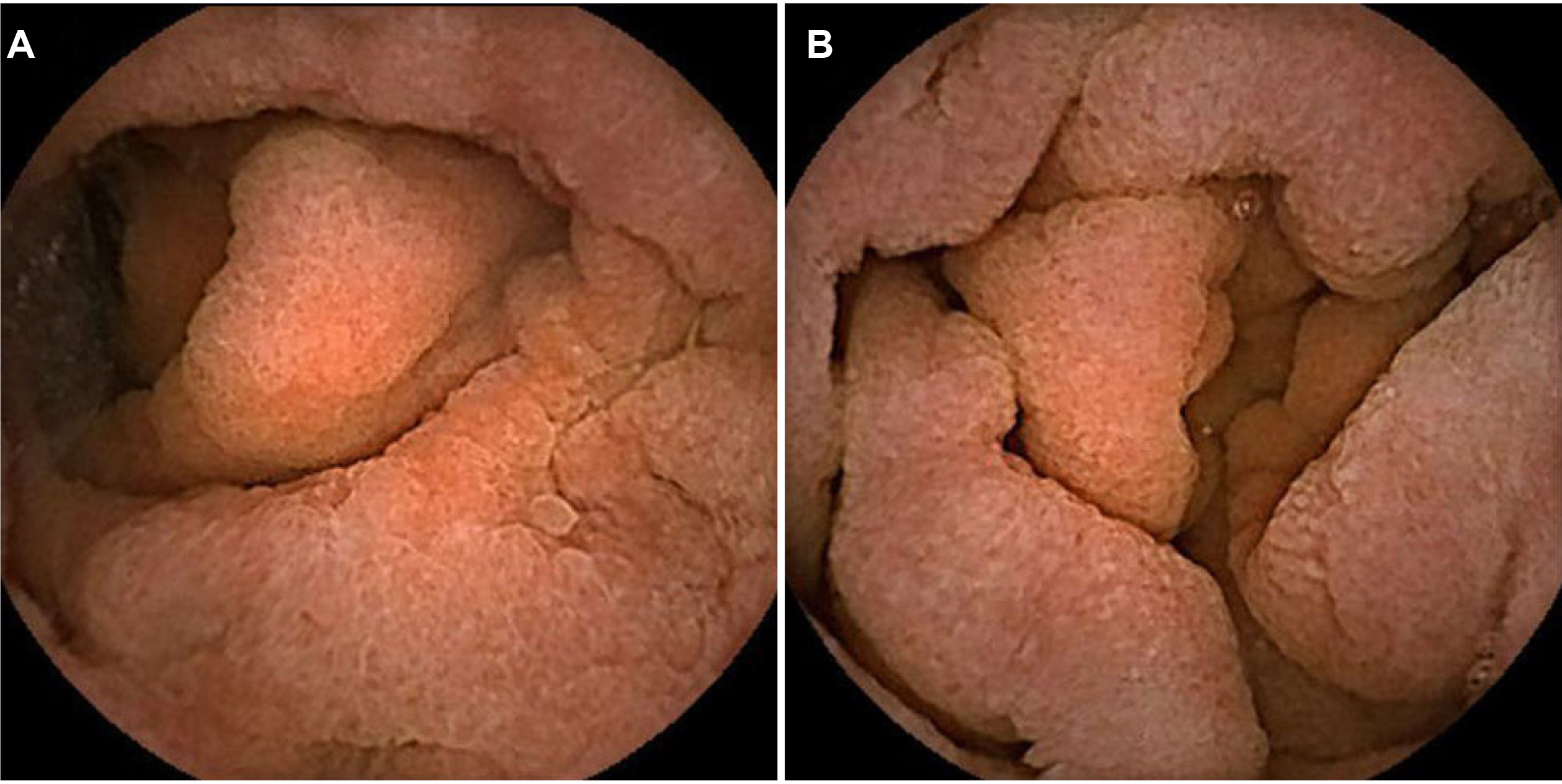
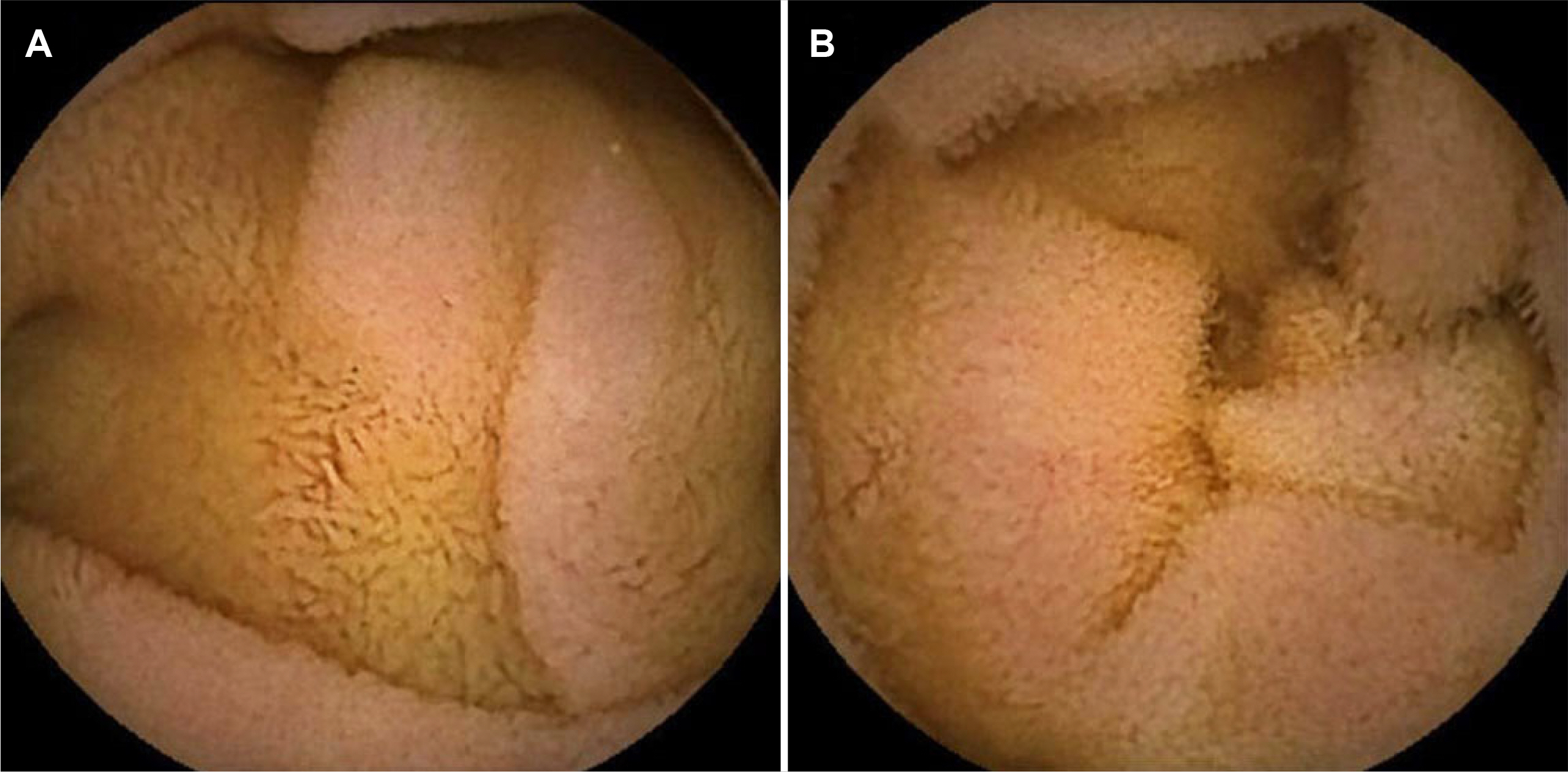
- Olmesartan, a recently introduced angiotensin II receptor blocker for hypertension, has been reported to cause drug-induced small bowel enteropathy. The diagnosis of olmesartan-associated enteropathy (OAE) needs clinical suspicion and the exclusion of coeliac disease, as it mimics coeliac sprue. Once diagnosed, it can be completely cured with the discontinuation of olmesartan. However, due to the extremely low incidence of OAE in Korea, clinical suspicion and diagnosis may be a challenge. The authors report the first case of OAE presenting with chronic diarrhea and acute kidney injury in Korea.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ianiro G, Bibbò S, Montalto M, Ricci R, Gasbarrini A, Cammarota G. 2014; Systematic review: sprue-like enteropathy associated with olmesartan. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 40:16–23. DOI: 10.1111/apt.12780. PMID: 24805127.
Article2. Rubio-Tapia A, Herman ML, Ludvigsson JF, et al. 2012; Severe spruelike enteropathy associated with olmesartan. Mayo Clin Proc. 87:732–738. DOI: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2012.06.003. PMID: 22728033. PMCID: PMC3538487.
Article3. Menne J, Haller H. 2012; Olmesartan and intestinal adverse effects in the ROADMAP study. Mayo Clin Proc. 87:1230–1232. DOI: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2012.10.005. PMID: 23218089. PMCID: PMC3547579.
Article4. Carneiro L, Moreira A, Pereira A, Andrade C, Soares J, Silva A. 2016; Olmesartan-induced sprue like enteropathy. GE Port J Gastroenterol. 23:101–105. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpge.2015.12.003. PMID: 28868441. PMCID: PMC5580175.
Article5. Kamal A, Fain C, Park A, et al. 2019; Angiotensin II receptor blockers and gastrointestinal adverse events of resembling sprue-like enteropathy: a systematic review. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 7:162–167. DOI: 10.1093/gastro/goz019. PMID: 31217979. PMCID: PMC6573796.
Article6. You SC, Park H, Yoon D, Park S, Joung B, Park RW. 2019; Olmesartan is not associated with the risk of enteropathy: a Korean nationwide observational cohort study. Korean J Intern Med. 34:90–98. DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2017.002. PMID: 29172402. PMCID: PMC6325440.
Article7. Adike A, Corral J, Rybnicek D, Sussman D, Shah S, Quigley E. 2016; Olmesartan-induced enteropathy. Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J. 12:230–232. DOI: 10.14797/mdcj-12-4-230. PMID: 28289500. PMCID: PMC5344475.
Article8. Roca-Argente L, Diaz-Jaime FC, López-Romero LC, et al. 2017; Acute kidney injury secondary to diarrhea caused by "sprue-like" enteropathy associated with olmesartan. Nefrologia. 37:548–550. DOI: 10.1016/j.nefro.2016.10.005. PMID: 28027786.
Article9. Esteve M, Temiño R, Carrasco A, et al. 2016; Potential coeliac disease markers and autoimmunity in olmesartan induced enteropathy: a population-based study. Dig Liver Dis. 48:154–161. DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2015.09.014. PMID: 26699826.
Article10. Marthey L, Cadiot G, Seksik P, et al. 2014; Olmesartan-associated enteropathy: results of a national survey. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 40:1103–1109. DOI: 10.1111/apt.12937. PMID: 25199794.
Article11. Scialom S, Malamut G, Meresse B, et al. 2015; Gastrointestinal disorder associated with olmesartan mimics autoimmune enteropathy. PLoS One. 10:e0125024. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125024. PMID: 26101883. PMCID: PMC4477936.
Article12. Hujoel IA, Rubio-Tapia A. 2016; Sprue-like enteropathy associated with olmesartan: a new kid on the enteropathy block. GE Port J Gastroenterol. 23:61–65. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpge.2016.02.005. PMID: 28868435. PMCID: PMC5580180.
Article13. Gonakoti S, Khullar S, Rajkumar A. 2019; Olmesartan associated enteropathy: a rare underdiagnosed cause of diarrhea and weight loss. Am J Case Rep. 20:111–116. DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.913207. PMID: 30683835. PMCID: PMC6364444.
Article14. Dias E, Morais R, Gullo I, Lopes P, Teixeira M, Macedo G. 2020; Olmesartan-associated enteropathy: heterogeneity of involvement along gastrointestinal tract. Porto Biomed J. 5:e079. DOI: 10.1097/j.pbj.0000000000000079. PMID: 33195870. PMCID: PMC7657573.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Telmisartan-induced sprue-like enteropathy: a case report and a review of patients using non-olmesartan angiotensin receptor blockers
- Olmesartan-associated Enteropathy with Acute Kidney Injury
- Olmesartan is not associated with the risk of enteropathy: a Korean nationwide observational cohort study
- Severe but reversible acute kidney injury resulting from Amanita punctata poisoning
- Definition and Diagnostic Criteria of Acute Kidney Injury