J Rheum Dis.
2016 Jun;23(3):187-192. 10.4078/jrd.2016.23.3.187.
A Case of Sarcoidosis That Improved upon Discontinuation of Etanercept
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Hospital, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. shinseok@chonnam.ac.kr
- KMID: 2326735
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2016.23.3.187
Abstract
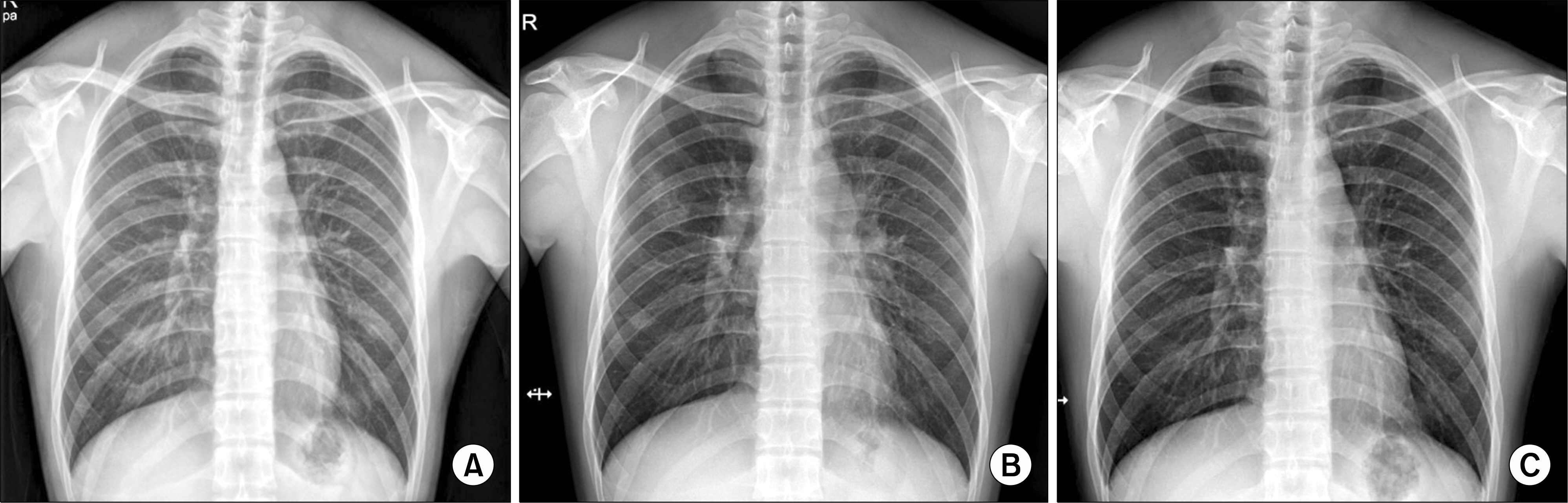
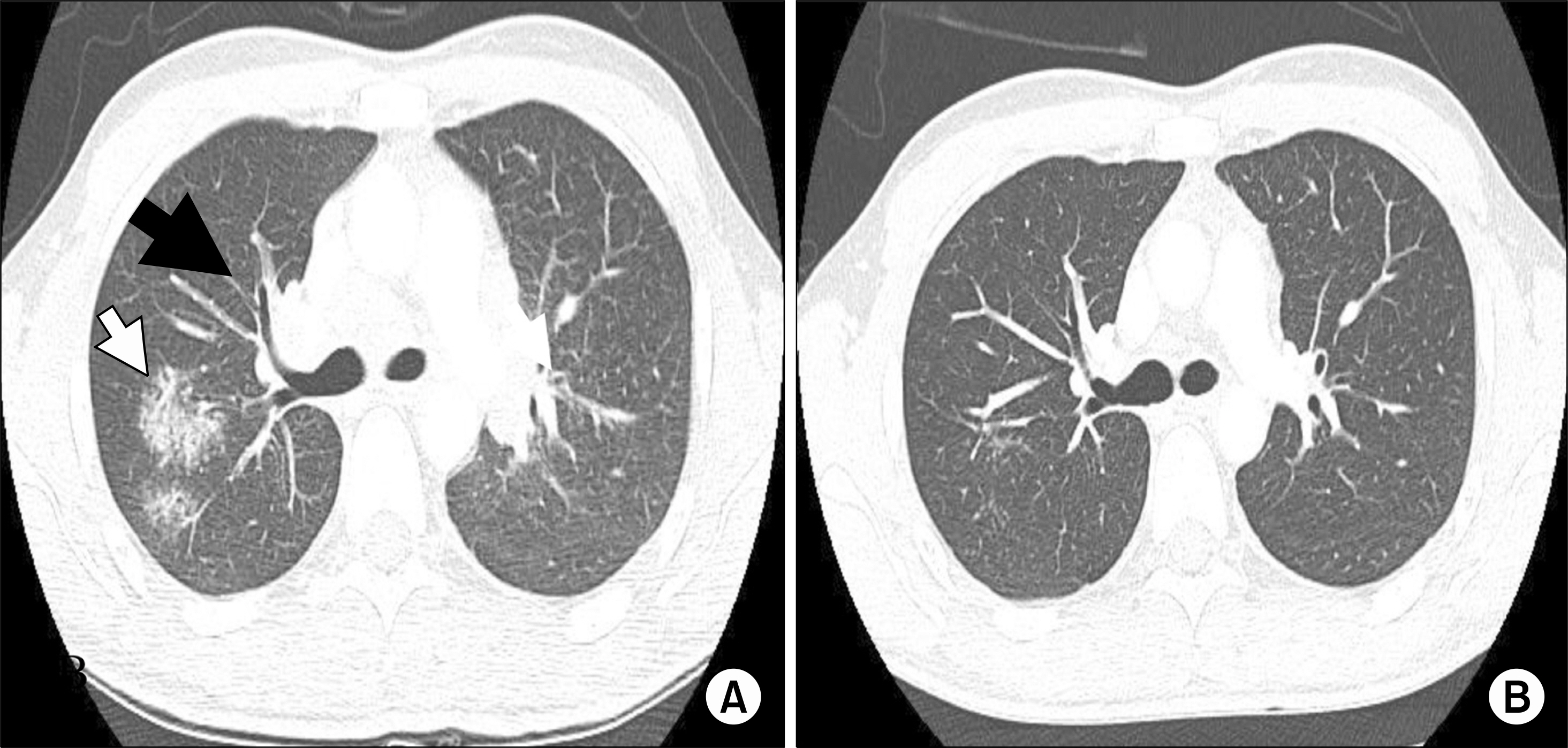
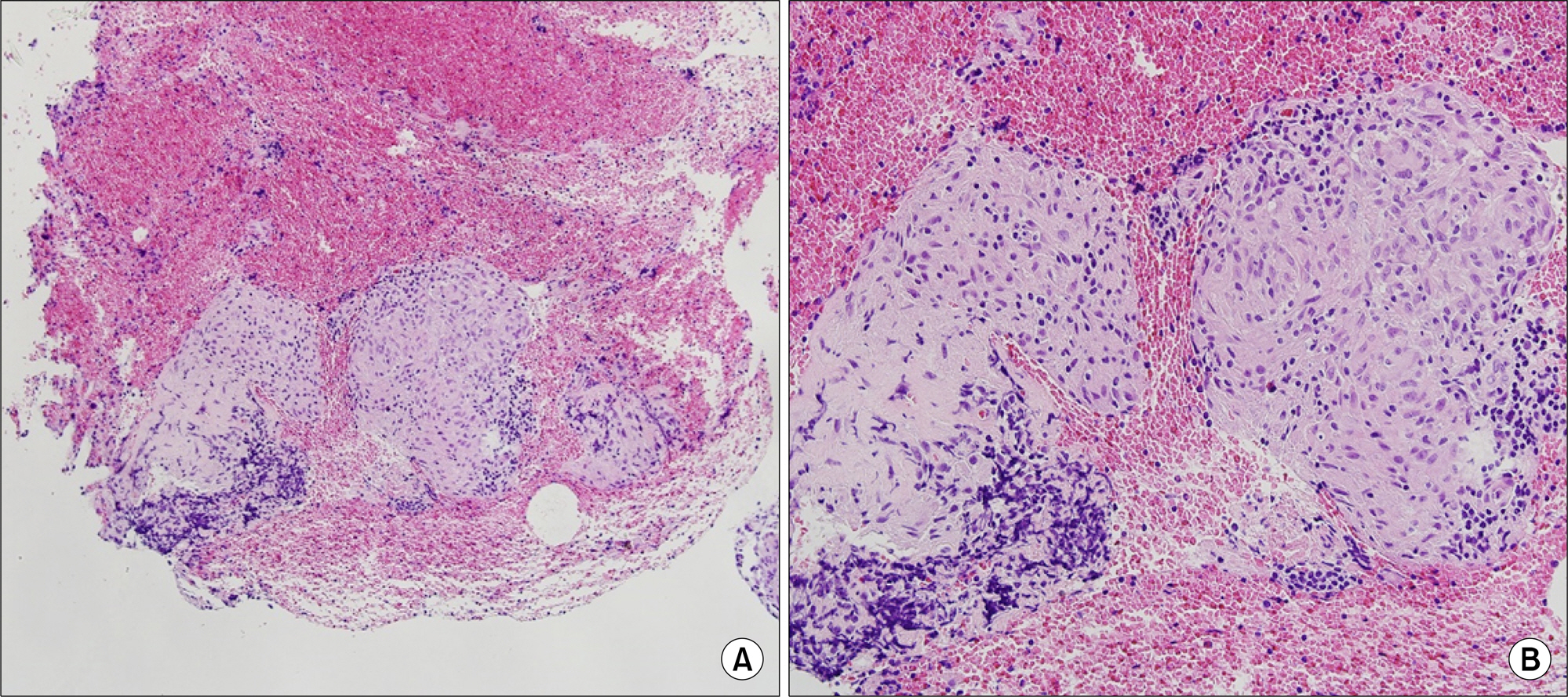
- A 31-year-old man who had been prescribed etanercept over a 3-year period for treatment of ankylosing spondylitis presented with newly developed dry cough, chills, myalgia, and weight loss. Chest computed tomography showed multiple reticulonodular pulmonary infiltrates and bilateral mediastinal, hilar, and peribronchial lymphadenopathy. Biopsy of a paratracheal lymph node revealed chronic granulomatous inflammation without necrosis, and the serum angiotensin-converting enzyme level was elevated. Sarcoidosis was diagnosed. His laboratory and radiological findings, and clinical symptoms improved only after discontinuation of etanercept without treatment. Although etanercept-induced sarcoidosis is rare, this case report suggests that sarcoidosis should be considered in the differential diagnosis of patients treated with the tumor necrosis factor inhibitor.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hunninghake GW, Costabel U, Ando M, Baughman R, Cordier JF, du Bois R, et al. ATS/ERS/WASOG statement on sarcoidosis. American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society/World Association of sarcoidosis and other granulomatous disorders. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 1999; 16:149–73.2. Antoniu SA. Targeting the TNF-alpha pathway in sarcoidosis. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2010; 14:21–9.3. Crommelin HA, Vorselaars AD, van Moorsel CH, Koren-romp IH, Deneer VH, Grutters JC. Anti-TNF therapeutics for the treatment of sarcoidosis. Immunotherapy. 2014; 6:1127–43.
Article4. Vigne C, Tebib JG, Pacheco Y, Coury F. Sarcoidosis: an underestimated and potentially severe side effect of an-ti-TNF-alpha therapy. Joint Bone Spine. 2013; 80:104–7.
Article5. Miyagi R, Ideguchi H, Soga T, Yamakawa Y, Otsuki H, Niino H, et al. Development of pulmonary and cardiac sarcoidosis during etanercept therapy. Int J Rheum Dis. 2014; 17:810–2.
Article6. van der Linden S, Valkenburg HA, Cats A. Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum. 1984; 27:361–8.7. Lee SH, Kim SI, Song JS, Kim TH, Sohn JW, Kim SH, et al. Sarcoidosis induced by adalimumab in rheumatoid arthritis. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2011; 71:464–9.
Article8. Park SY, Kim EK, Hwang DW, Lee KW, Paik SS, Jung KH, et al. A case of development of sarcoidosis during tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonist therapy. J Rheum Dis. 2011; 18:41–5.
Article9. Massara A, Cavazzini L, La Corte R, Trotta F. Sarcoidosis appearing during anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha therapy: a new “class effect” paradoxical phenomenon. Two case reports and literature review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2010; 39:313–9.10. Daïen CI, Monnier A, Claudepierre P, Constantin A, Eschard JP, Houvenagel E, et al. Sarcoid-like granulomatosis in patients treated with tumor necrosis factor blockers: 10 cases. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2009; 48:883–6.11. Wallis RS, Ehlers S. Tumor necrosis factor and granuloma biology: explaining the differential infection risk of etanercept and infliximab. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2005; 34(5 Suppl 1):34–8.
Article12. Furst DE, Wallis R, Broder M, Beenhouwer DO. Tumor necrosis factor antagonists: different kinetics and/or mechanisms of action may explain differences in the risk for developing granulomatous infection. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2006; 36:159–67.
Article13. Baughman RP, Drent M, Kavuru M, Judson MA, Costabel U, du Bois R, et al. Infliximab therapy in patients with chronic sarcoidosis and pulmonary involvement. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006; 174:795–802.
Article14. Utz JP, Limper AH, Kalra S, Specks U, Scott JP, Vuk-Pavlovic Z, et al. Etanercept for the treatment of stage II and III progressive pulmonary sarcoidosis. Chest. 2003; 124:177–85.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Ankylosing Spondylitis Accompanying Sarcoidosis
- Real-World Experience with Etanercept Therapy and the Switching Pattern among Korean Patients with Psoriasis after Withdrawal of Etanercept
- Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Blocker-Induced Erythrodermic Sarcoidosis in with Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- A Case of Development of Sarcoidosis During Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha Antagonist Therapy
- Refractory Plaque Psoriasis Treated with a Combination of Etanercept and Low Dose Methotrexate